Trailing twelve months (TTM) refers to a company’s past 12 consecutive months of performance data used in financial reporting. The TTM method is essential because it provides companies with detailed, recent financial data for internal audits, financial analysis, and corporate planning. It’s useful for evaluating revenue growth, margins, sales and expense trends, working capital management, key performance indicators (KPIs), and other financial metrics.
Summer Savings: Get 70% off QuickBooks for 3 months. Ends July 31th. |
|
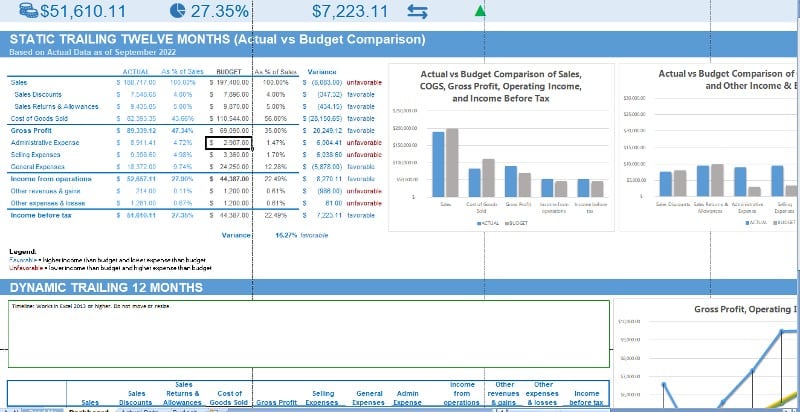
Free TTM Income Statement Spreadsheet
Our free TTM income statement spreadsheet computes the latest 12 months of financial data automatically with column and line charts for illustration. To use this spreadsheet without problems, you must at least have Microsoft Excel 2013, and before using it, update the data using income statement information from your actual and budgeted income statements
In the dashboard of this spreadsheet, you’ll see the static and dynamic TTM income statements. The Static TTM shows you only the past 12 months while the Dynamic TTM can show you data from any month or year.
Get the necessary reports to fill out our TTM spreadsheet with the help of QuickBooks Online. With its Plus plan, you can generate standard and custom financial reports, including reports by class or location. Visit QuickBooks Online and get 50% off for three months plus a free guided setup.
How To Calculate Trailing Twelve Months
TTM can be used to analyze financial data from income statements and cash flow statements. Analysts use different methods to calculate TTM depending on which financial report the data is sourced from. However, TTM doesn’t necessarily coincide with the ending of a calendar year or a company’s fiscal year. Let’s discuss how to compute TTM for monthly and quarterly reports.
TTM Calculation for Monthly Reports
Add the values for each month during the last 12 months to get an annualized value. If you’re using the income statement, add all income statement line items, such as revenues, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and net income, of the current month and 11 months prior to it.
The same process applies when using the cash flow statement. Add up cash provided (receipts > disbursements) or used (receipts < disbursements) by operating, investing, and financing activities to arrive at the net increase or decrease in cash. Afterward, add the beginning cash balance to determine the ending cash balance.
Here’s a visual guide for preparing a TTM using monthly reports:
TTM Calculation Using Quarterly Reports
There are two ways to perform a TTM calculation for quarterly reports. The first method is easier to understand than the second. However, they’ll provide the same information:
- You can add up all current quarters and get the remaining quarters from previous years. For example, if the current quarter is Q2, you should get Q2 and Q1 of the current year then pick up Q4 and Q3 of the previous year to have an annualized report.
- Use last year’s financial statements, add up all current quarters from the most recent reporting period, and subtract the same quarters from the previous year.
Let’s assume that the current quarters are Q2 and Q1. Add the values of Q2 and Q1 to last year’s financial statements then deduct Q2 and Q1 of previous year to get the annualized TTM report.
Pros & Cons of Using Trailing Twelve Months
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Shows the most recent 12-month financial performance of a business | Can be tedious to do since you need to work back using monthly or quarterly company reports |
| Helps investors and creditors evaluate and value a company by performing financial statement and ratio analysis using TTM figures, especially for computing the price-earning ratio | Yields irrelevant data for businesses under volatile sectors such as energy, technology, and commodities, to name a few |
| Helps business owners make strategic decisions that drive company performance | Requires an accounting information system in place to pick up monthly or quarterly data quickly |
Importance of TTM
1. Eliminates seasonality
Using TTM analysis eliminates seasonal fluctuations in the business that occur every year because it looks at trends for a more extended period. Financial analysis using TTM provides a more accurate picture of a business’ financial health because it uses the most recent data over a longer period than monthly or quarterly.
2. Tracks leading indicators
It shows trends that can help you quickly track leading indicators, including total income, gross profit, and net income—showing any growth or decline from your most recent 12 months of performance. With this, you can make strategic business plans and wiser decisions that drive sales, improve performance, and achieve other business goals.
3. Provides up-to-date financial information
Financial professionals like analysts and underwriters often perform valuation and credit analyses of companies throughout the year using TTM. When conducting this valuation and analysis, relying on year-end or calendar year financial data won’t provide an accurate picture of the company’s current financial health—TTM will be more helpful.
While manually pulling TTM reports can be tedious, accounting software like QuickBooks Online, our best small business accounting software, makes it more accessible to generate them.
You can input information from QuickBooks Online reports in our downloadable TTM income statement spreadsheet to see how your financials look in the past 12 months. However, we don’t recommend sending our spreadsheet to lenders for credit analyses and valuation since it isn’t a detailed income statement.
4. Helps in assessing financial condition of the company
Some companies can grow significantly within a year, while other businesses can trend down because of volatility. The use of TTM to evaluate a company’s financial health and progress will help both internal and external stakeholders assess the most current and accurate financial standing of a company.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, TTM is the most recent 12 months of financial data that may overlap between years. YTD (or year-to-date), on the other hand, is the most recent financial data from the start of the financial year up to the most current month.
No, because TTM is only for internal use. It’s not part of the standard set of financial statements. Use the TTM only to measure internal performance and financial health.
Bottom Line
Using TTM gives business insights into its recent performance and current financial health. It also shows trends that can help external stakeholders determine the growth and decline of a business. The data from the TTM method is more current and seasonally adjusted, which can be helpful for business owners, potential investors, creditors, financial analysts, and auditors wanting to see more relevant measures.