Revenue and profit are items in the income statement that are measures of return. Revenue is the gross amount of earnings from the sale of products and services, whereas profit is the net amount or what’s left after deducting expenses and other charges.
Terms You Should Remember
- Gross or total revenues: This is the total amount of earnings from selling goods and services to customers. Gross revenues can be determined by multiplying the selling price and the quantity of goods and services sold.
- Gross profit or margin: This is the amount of earnings after deducting cost of goods sold (COGS) or cost of services from gross revenue.
- Operating profit: This is the amount of earnings left after deducting operating expenses from gross profit but before income taxes.
- Net profit: This is the net and final amount of earnings left after deducting all expenses and charges, including income tax provisions.
Read our article about the basics of accounting and bookkeeping for a complete overview of important concepts and definitions.
Revenue and Profit in the Income Statement
Below is the annual consolidated income statement of Microsoft Corporation for fiscal years ending 2022, 2021, and 2020. We’ll use it as our illustration to distinguish revenue from profit.
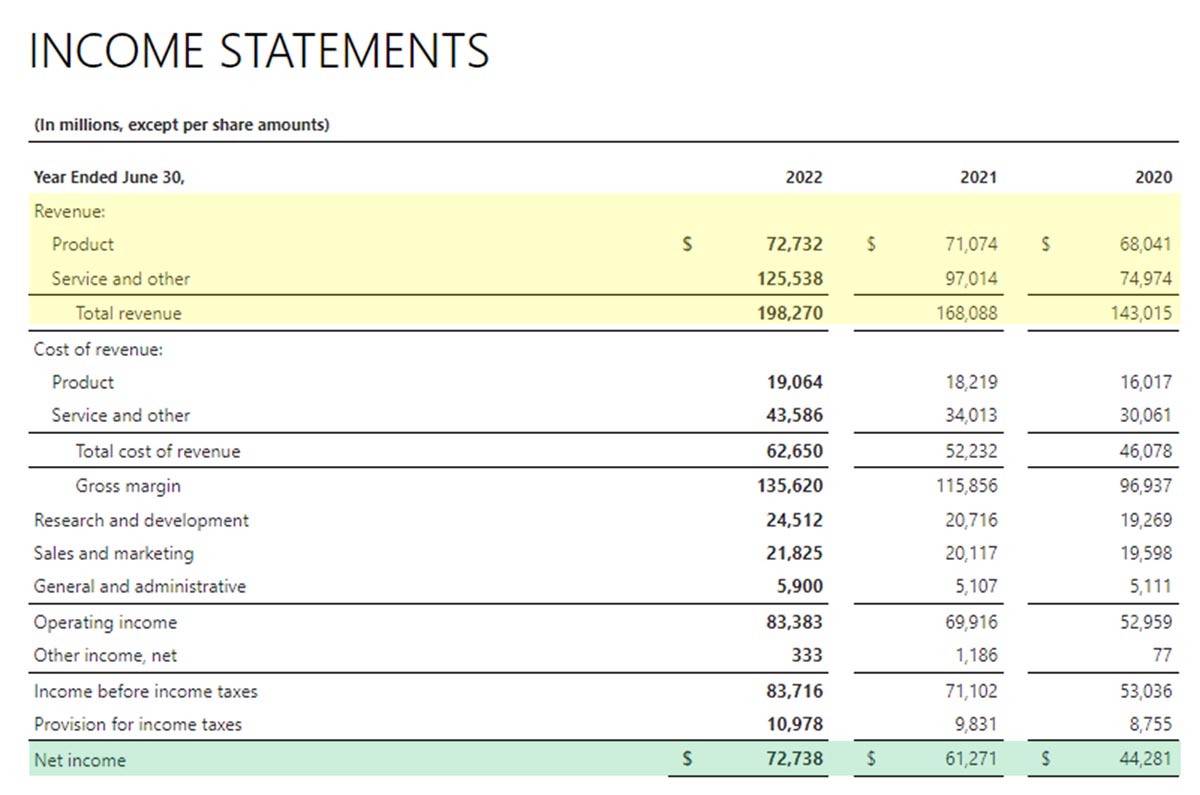
Income Statement of Microsoft Corporation
Revenues represent the parts highlighted in yellow, while profit is the part highlighted in green. To give you a quick snapshot of these two concepts, the table below compares revenue vs profit under specific criteria.
REVENUE | PROFIT | |
|---|---|---|
Position in the Income Statement | Topmost | Bottom |
Best Measure for Performance of | Company’s major products in terms of sales value and volume | Company as a whole |
Relevant for | Marketing managers and personnel responsible for sales growth | Business owners, all managerial roles, and stakeholders |
Best Metric for | Predicting sales trends, patterns, and consumer behavior | Assessing overall company profitability and future goal-setting |

Revenue Section of Microsoft’s Income Statement
You can easily spot revenues at the topmost part of the income statement. Revenues represent the total dollar amounts of sales and services.
To compute total revenue, we follow this formula:
Total Revenue = Net Sales + Service Revenues + Other Revenues
Whereas net sales is:
Net Sales = Gross Sales – Sales Returns – Sales Discounts
Sales returns occur when a customer returns a good to the seller in exchange for a refund. Sales discounts are reductions to the selling price of the product to stimulate sales.

Profit Section of Microsoft’s Income Statement
Meanwhile, profit (also called net profit or net income) is the amount left to the business owners after deducting all expenses and charges. In Microsoft’s Income Statement, we can see what the net income amount is after deducting provisions for income taxes.
To compute profit, we follow this formula:
Profit = Income before taxes – Income tax
After deducting income tax, all the net income now belongs to the owner. In the image above, the net income of $72,738 million now belongs to the owners of Microsoft Corporation.
Difference Between Gross Profit vs Operating Profit
While revenue and profit are the topmost and bottommost parts of the income statement, respectively, gross profit and operating profit are found in the middle. By using Microsoft’s income statement, we’ll discuss in greater detail the difference between gross profit and operating profit.
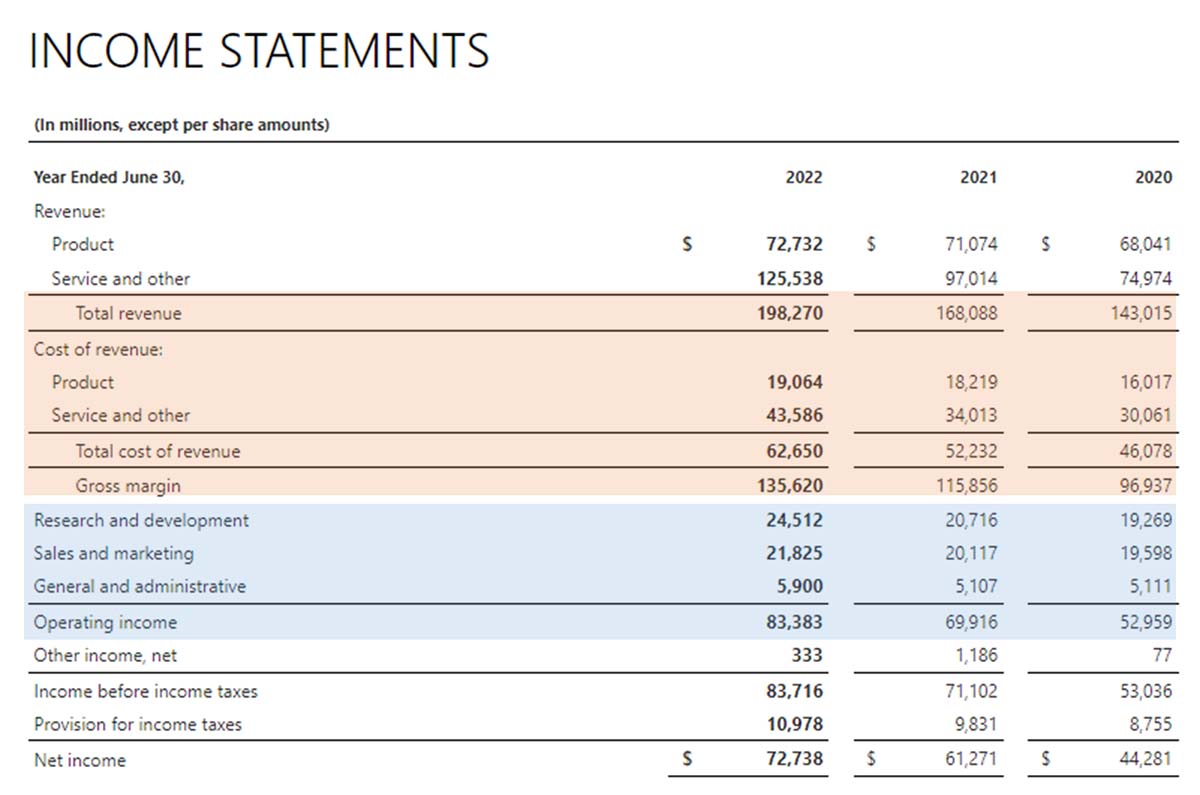
Income Statement of Microsoft Corporation
The gross profit section is highlighted in orange, while the operating profit section is in blue.

Gross Profit Section of Microsoft’s Income Statement
Also called gross margin, gross profit measures the business’ profit based solely on the sale of goods and services. In Microsoft’s Income Statement, it has a gross profit of $135.620 million from product sales. Under normal circumstances, gross profit will always be a positive number because businesses always sell at a markup. No business would sell products below cost.
Total revenues and gross profit have a direct relationship. As revenues increase, gross profit will increase as well. Arriving at the gross profit requires deducting direct costs or COGS. Microsoft used the term “cost of revenue” since it offers goods and services. But if you’re purely a merchandising business, the term cost of goods sold is more appropriate.
Gross profit is computed as:
Gross Profit = Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
COGS is the amount you paid to purchase or manufacture the goods for sale. We deduct COGS from sales to arrive at the gross profit so that we’ll know how much we earned from product sales alone. However, businesses also incur other costs that are unrelated to products but are essential to the business as a whole. We’ll discuss this in the next section.
Business operations incur costs to keep the business running. For example, you have to pay for utilities, accounting services, insurance, marketing, and salaries—and these costs don’t have a direct relationship with your main products. However, these expenses are necessary so that the business can sell its main products. We call these costs as operating expenses.
Operating profit is computed as:
Operating Profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses

Operating Profit Section of Microsoft’s Income Statement
We can see from Microsoft’s Income Statement that they incurred costs related to research and development, sales and marketing, and general and administrative. These three major operating expense groups are indirectly related to Microsoft’s products. However, they are crucial for Microsoft’s success.
For example, R&D expenses keep Microsoft competitive in the hardware and software market. Microsoft uses R&D expenses to innovate new products that it will eventually sell to consumers. Without R&D, Microsoft would lag behind its competitors.
Generate a profit and loss (P&L) statement with the right accounting software. Our evaluation of the best small business accounting software can help you decide which solution fits your business’ needs.
Analyzing Revenues, Gross Profit, Operating Profit & Net Profit
The table below shows different ways on how you can use revenue, gross profit, operating profit, and net profit data to perform a business analysis. Knowing where and how to look at income statement data can help you make better business decisions and understand how the business operates.
Read our guide on what bookkeeping is and what a bookkeeper does to learn about how a bookkeeper maintains your accounting records.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
While both are important, net profit gives a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance because it takes into account all the expenses incurred to generate the revenue.
No, this would mean that you have a negative COGS or operating expenses. Profit is always lower than revenue because expenses are always positive.
Bottom Line
Revenue is the total earnings generated by the sales of goods or services while profit is the amount of revenue that remains after accounting for all additional income streams, operating costs, and expenses. Understanding how both revenue and profit affect your business is key to its success.