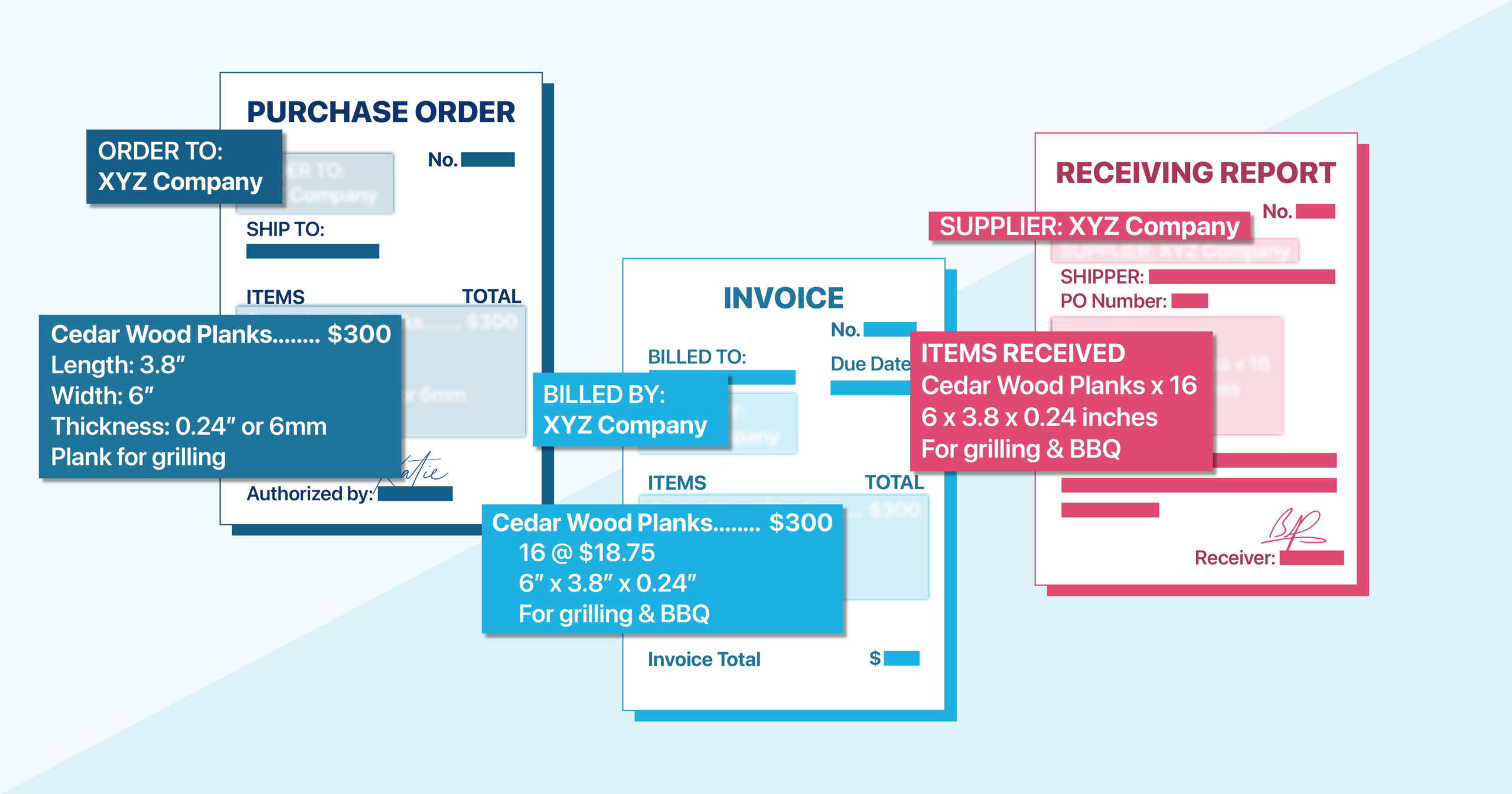
A receiving report (RR) is a formal document used to record the arrival and condition of goods ordered from a supplier.
What Is a Receiving Report? Example, Purpose & Types
This article is part of a larger series on Bookkeeping.
An RR is essentially a confirmation and record of what was received against what was ordered and acts as a verification document before the accounts payable (A/P) department processes payment to the supplier. It ensures the goods were received as ordered before releasing funds.
Key Takeaways:
- RRs help track inventory levels by documenting what is received.
- RRs can be used to authorize payment to the supplier.
- RRs allow you to check the condition of delivered items, identifying any damages or missing items.
- Specific information in an RR can vary depending on the company’s needs and the type of RR used.
- RRs have two main types: pre-printed forms and electronic RRs.
Receiving Report Example
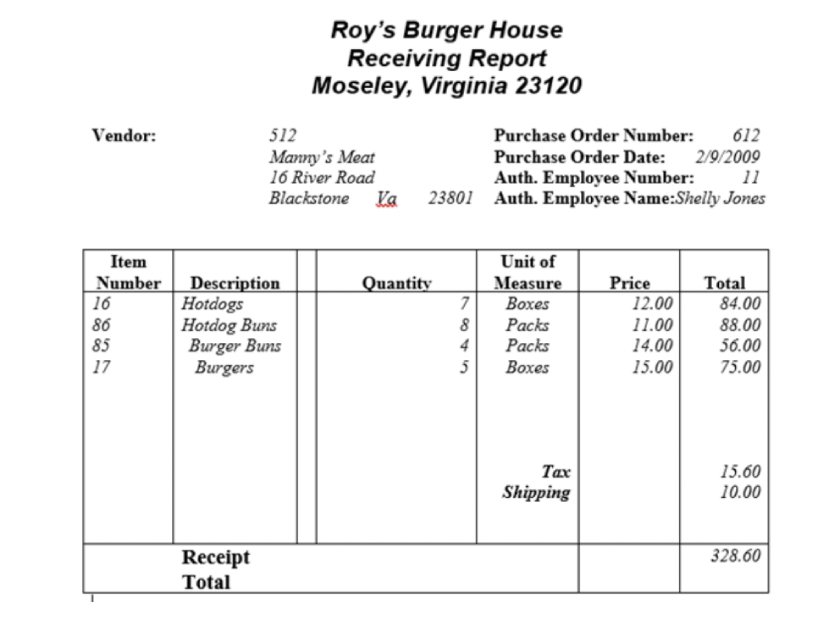
Sample receiving report
In our RR example above, Roy’s Burger House received a shipment of hotdogs, burgers, and buns. The supplier (Manny’s Meat), the purchase order (PO) number (612), and the date (2/9/2009)—as well as the authorizing employee number (11) and name (Shelly Jones) in case there are any questions—are shown.
Each item is broken down by item number, description, quantity, unit of measure, and price, along with the total for tax and shipping. This gives all of the information that is needed to authorize payment for the invoice that will later be sent by the supplier.
What Information Is Included in a Receiving Report?
An RR typically includes several key pieces of information to document the arrival and condition of goods that were received from a supplier. Here’s a breakdown of the essential elements:
- PO number: A PO number is a unique identifier that links the RR to a specific purchase order placed with the supplier. It ensures the goods received correspond to the order that was previously approved. You might also find other reference numbers used by the company for tracking purposes.
- Date of receipt: This records the date the goods were physically received by the business. It is important for accurate inventory tracking and helps determine lead time from suppliers.
- Supplier information: This section identifies the company or vendor that supplied the goods. It typically includes the supplier’s name and address for reference and recordkeeping purposes.
- Description of each item received: This is a breakdown of the specific items received and includes the following: quantity, condition, and variations from the order.
- Signature of receiving staff member: The authorized receiving staff member signs the report to acknowledge receipt of the goods and verify the information documented on the report. This ensures accountability for the receiving process.
In addition, the following information may also be captured:
- Lot or batch numbers: Recording lot or batch numbers can help track specific production batches, especially for perishable items or items with expiration dates.
- Serial numbers: For high-value items or items with unique identifiers, including serial numbers on the RR can provide additional security and tracking capabilities.
- Delivery information: Some reports might capture details like the carrier used for delivery or any specific delivery instructions.
What Is the Purpose of a Receiving Report?
- Payment authorization: In some cases, the RR acts as a verification step before the A/P department processes payment to the supplier.
- Verification: When used correctly, an RR verifies that the items received match the quantity and description of items listed on the PO.
- Documentation: An RR serves as a record for inventory control and accounting purposes by helping to track what items are now on hand.
- Discrepancy resolution: If there are any discrepancies between what was ordered and what was received (e.g., missing items or damaged goods), the RR provides documentation to initiate communication with the supplier for a resolution.
Our related resources:
Types of Receiving Reports
Two main types of RRs are used in the receiving process:
- Pre-printed forms: Many companies use pre-printed forms with specific sections to be filled in for consistency and ease of use. These forms often include sections for the following: PO number, date received, supplier information, item details, condition of goods, discrepancy notes, and signature of receiving staff.
- Electronic RRs: Some companies use electronic systems to generate and manage RRs. These systems can streamline the process, improve data accuracy, and integrate with inventory management software.
Benefits of Detailed Receiving Reports
Detailed RRs go beyond basic verification. They offer a wealth of information that contributes to accurate inventory management, cost savings, improved communication with suppliers, and better overall business operations.
Here’s a breakdown of the key benefits:
Best Practices for Optimizing the Use of Receiving Reports
To optimize the use of RRs, it is important to adopt the following:
- For thorough data collection, ensure the report’s details (like item descriptions, quantities, and unit prices) are correct. Carefully examine each item for any damage or discrepancies with the order. Note these on the report, attaching photos or videos for stronger documentation if desired.
- For streamlined processes, use pre-designed templates, as they can save time and ensure all necessary information is captured in the report. Implement a unique numbering system for each report to identify any missing documents and to maintain a clear history.
- For enhanced functionality, match the RR with the PO and invoice to ensure everything aligns before making payments. Use RRs to update inventory levels accurately, preventing stockouts and overstocking.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is a document used to record the arrival of items that were ordered, noting their condition and any discrepancies. It verifies that the received items match the PO and serves as a record for inventory control, accounting, and potential communication with the supplier.
Typically, the receiving staff, such as the warehouse or store manager, fills out the RR upon delivery of the goods.
It improves inventory accuracy by reflecting actual stock levels. It also enhances quality control through early identification of damaged or expired goods. It helps prevent fraud by identifying discrepancies with the order and streamlines payment processing with verified quantities and conditions.
The RR documents these discrepancies, whether they are missing items or damaged goods. First, investigate the cause and briefly try to understand the reason for the issue. Then, notify the supplier of the discrepancy as soon as possible. Depending on the situation, you can choose to resolve the issue by replacing the item, returning damaged items for credit, or negotiating a lower price for the partial shipment.
Bottom Line
Overall, RRs play a crucial role in streamlining receiving processes, ensuring accurate inventory control, and facilitating communication with suppliers. They also provide valuable data for accounting purposes and can contribute to better inventory management and cost control.