Screening tenants for a rental property is a critical process that can significantly impact a property’s success and profitability. By implementing effective screening methods, landlords can attract reliable and responsible tenants who meet their rental obligations and help property owners maximize their investment potential. We’ll explore seven key steps on how to screen tenants to ensure landlords make informed decisions to fill their vacancies while adhering to Fair Housing Laws.
Tenant Screening Checklist & Decision Flowchart
Property owners should plan ahead by utilizing a tenant screening checklist to guarantee they’ve covered the necessary steps in the tenant screening process. Download our free checklist and tenant decision flowchart, which outlines how to screen tenants. The checklist includes rental application items, ways to verify income and employment, and tenant interview questions.
1. Understand & Comply With Fair Housing Laws
It is important to have a comprehensive understanding of Fair Housing Laws before embarking on the screening process. Familiarize yourself with federal, state, and local regulations to ensure compliance and avoid discriminatory practices. Landlords must screen rental applicants fairly and equally, without bias, based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, familial status, or disability.
To avoid breaking fair housing laws, landlords should follow these general guidelines:
- Treat all applicants equally: Treat every applicant fairly and equally regardless of their background or characteristics. Avoid any form of discrimination or bias during the process of screening tenants.
- Use consistent screening criteria: Develop a clear set of qualifications and requirements based on factors like income, rental history, creditworthiness, and references. Apply these criteria uniformly for all applicants and avoid making exceptions for specific individuals or groups.
- Advertise responsibly: When advertising your rental property on rental listing sites, avoid any language, images, or statements that could be interpreted as discriminatory. Focus on describing the property features, amenities, and location rather than using language targeting certain groups of people.
- Ask legal and objective screening questions: During interviews or interactions with applicants, ask only legal and objective screening questions directly related to their qualifications as tenants. Refrain from inquiries about protected characteristics, family status, or disabilities.
- Maintain accurate records: Keep detailed records of all interactions, communications, applications, and screening results. Documentation can demonstrate that your tenant selection process is fair and unbiased.
- Employ screening services: Utilize reputable tenant screening services or credit reporting agencies to conduct credit and background checks during the verification process. These services are equipped to handle sensitive information and ensure compliance with fair housing laws.
2. Use a Rental Application to Prescreen Tenants
Utilizing a well-designed rental application is a practical step in screening tenants to protect your real estate investment properties. A comprehensive application helps gather essential information like personal details, employment history, income verification, references, and consent for background and credit checks. The application acts as a prescreening tool, allowing you to screen tenants and determine their suitability for your rental property.
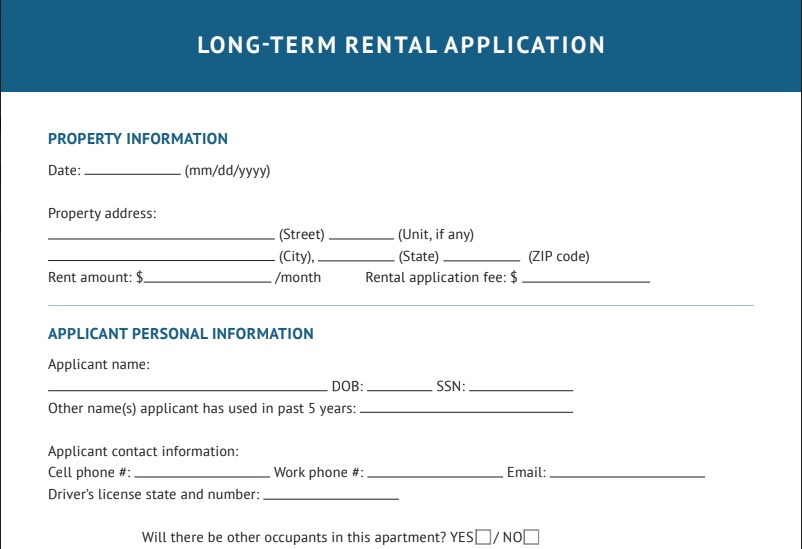
Example rental application
A rental application for screening tenants should encompass several key pieces of information to support landlords in assessing the fit of potential tenants. Here are some essential details that should be listed on your application:
- Personal and contact information: The application should require the applicant’s full name, current address, phone number, and email address. This permits landlords to contact applicants and verify their identity.
- Employment history: Requesting details about the applicant’s employment history, including current and previous employers, job titles, and employment durations, helps examine their stability and income source. This offers an understanding of their ability to meet their financial obligations.
- Income verification: A rental application should include a section where applicants can present proof of income, such as recent pay stubs, employment contracts, or tax documents. Verifying income ensures that tenants have the financial means to pay rent consistently.
- References: Applicants should be asked to provide references from previous landlords or professional contacts who can vouch for their character and reliability. Contacting references offers significant insights into the applicant’s rental history, payment habits, and general conduct as a tenant.
- Rental history: It is important to gather knowledge about the applicant’s previous rental history, including addresses of previous residences, dates of tenancy, and reasons for moving. This enables landlords to evaluate their rental track record and understand where their tenant has lived and in what types of properties.
- Consent for credit and background checks: Including a section where applicants grant consent for credit and background checks is crucial. This authorization lets landlords request personal information from the right legal entities on the tenant.
- Additional information: Depending on specific preferences or property requirements, the application may include additional sections, such as questions about pets and vehicle information, or ask any questions that might help determine their eligibility.
Safeguard Sensitive Information
As landlords and property managers, it is not only your responsibility to select suitable tenants but also to handle sensitive information from rental applications with the utmost care and ensure compliance with data protection laws. Here are some ways to safeguard sensitive information to ensure privacy and compliance:
- Understand applicable data protection laws: Before diving into the tenant screening process, familiarize yourself with your region’s relevant data protection laws. This may vary depending on location, so conduct thorough research and adhere to the guidelines.
- Implement secure document storage: Create a secure and organized system for storing tenant documents. Whether you prefer digital or physical files, restrict access to authorized personnel. Implement password protection for digital files and install security systems for physical records to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- Use encryption for digital communication: In the digital age, communication plays a crucial role in the tenant screening process. Whenever exchanging sensitive information through email or other digital platforms, use encryption tools to secure the content. This extra layer of protection helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures that information remains confidential.
- Minimize data collection: Collect only the information necessary for the tenant screening process. Avoid requesting irrelevant or excessive personal details that may pose a risk to privacy. By minimizing the data collected, you reduce the potential for data breaches and demonstrate a commitment to respecting tenant privacy.
- Regularly update security measures: Stay proactive in safeguarding sensitive information by regularly updating your security measures. This includes software updates, firewall maintenance, and periodic security audits. Staying ahead of potential vulnerabilities creates a more robust defense against unauthorized access to tenant information.
3. Run a Credit Report & Background Check
Once you’ve obtained a completed rental application, the next step on how to screen renters is to run a credit and background check on them. A credit report provides landlords with vital information to assess a prospective tenant’s financial responsibility and reliability. It also helps determine whether they can meet financial obligations like paying rent on time. A background check is another valuable tool to gain insights into a tenant’s history and make informed decisions when screening tenants.
Key elements found on a prospective tenant’s credit report and background check include:
Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|
Credit Score | This provides an overall snapshot of their creditworthiness. A higher score typically indicates a more responsible approach to managing financial obligations. Most landlords like to see a score of 700 or above. |
Payment History | In the applicant's payment history, landlords can look for patterns of late rent payments, delinquencies, or accounts in collections. Consistent on-time payments demonstrate a tenant’s financial responsibility. |
Debt-to-income Ratio | This indicates their level of financial obligations compared to their income. A lower ratio suggests a better ability to manage additional rental expenses. |
Outstanding Debts | Look for any outstanding debts or judgments against the applicant, as these may affect their ability to pay rent consistently. |
Criminal Records | Check for any criminal records or convictions. While minor offenses may not be immediate grounds for rejection, serious offenses should be carefully evaluated. |
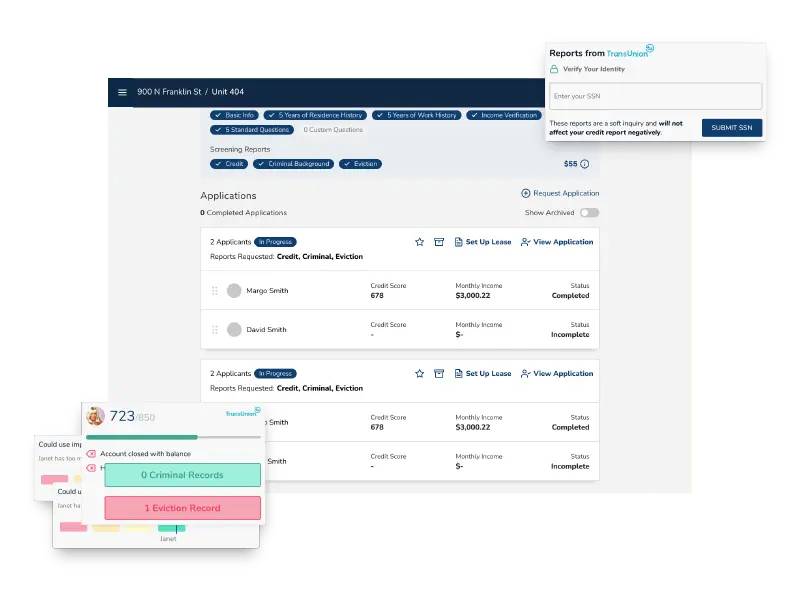
Tenant screening (Source: Avail)
To process credit and background checks, consider Avail, an online platform that offers online tenant screening services. With Avail’s easy-to-use interface and powerful features, landlords can efficiently screen tenants and conduct thorough background checks. By partnering with reliable screening providers, Avail delivers comprehensive reports that contain credit checks, criminal records, and eviction history. Landlords can access them directly through the platform, enabling them to make informed decisions when selecting tenants.
4. Verify Income & Employment
Ensuring the stability of rental payments is important for landlords. To achieve this, landlords usually ask for proof of income and employment from tenants. A standard guideline landlords follow is the “three times the monthly rent” rule. This means a tenant is expected to have a monthly income at least three times the monthly rent.
For instance, if the monthly rent is $1,500, the tenant should have a minimum monthly income of $4,500.
However, this multiple can be increased or decreased. For example, in New York City, tenants must earn 40 times the monthly rent to qualify for an apartment. Therefore, if you want to rent a $2,000 per month apartment, your annual income must be at least $80,000 a year.
Use our tenant income qualifier below to calculate if your tenant is eligible for your building. Input the following numbers:
- Gross Monthly Rent: The amount of money you will charge tenants monthly to live in your property.
- Tenant Gross Yearly Income: The amount of money, before taxes, that your tenant earns annually.
- Income Multiplier: The number you will use to qualify your tenant’s earnings.
The outputs will show:
- Tenant Income Qualifier: The amount of money your tenant needs to earn to qualify for the apartment
- Gross Monthly Tenant Income: The tenant’s annual income divided by 12 months to get the tenant’s monthly earnings.
Some landlords may have higher or lower income requirements based on specific circumstances and preferences. Landlords can verify income and employment by contacting employers, requesting pay stubs and employment contracts, or using professional verification services like RentPrep.
5. Check Previous Addresses, Landlord & Eviction History
In addition to verifying income, when learning how to screen tenants for rental property, landlords must verify an applicant’s previous addresses and landlord and eviction history. Thoroughly vetting application information increases confidence that the applicant meets your rental qualifications and will be a good tenant.
By asking for references and rental history data on the tenant application, landlords can uncover intelligence about a prospective tenant’s eviction history, previous addresses, and former landlord relationship status. Details you want to discuss with a tenant’s former landlord are payment history, adherence to lease terms, property maintenance, behavior as a tenant, and any issues or disputes during the tenancy.
When contacting a tenant’s former landlord, consider asking the following questions:
- Can you confirm the applicant’s tenancy at your property?
- How long did the applicant reside at your property?
- Did the applicant consistently pay rent on time? Were there any instances of late payments?
- How would you describe the applicant’s communication and cooperation during their tenancy?
- Did the applicant maintain the property in good condition?
- Were there any reported issues or complaints from neighbors or other tenants related to the applicant?
- Did the applicant provide proper notice when planning to move out?
- Were there any lease violations, disputes, or conflicts during their tenancy?
- Would you consider renting to this applicant again in the future?
6. Interview Applicants & Ask Screening Questions
Once you’ve reviewed all application details and determined to proceed with a prospective tenant, conducting face-to-face or virtual interviews with applicants may help you finalize your decision.
Questions to Ask During a Screening Interview
When screening potential renters, landlords should prepare questions tailored to their particular requirements, covering rental preferences, lifestyle, and ability to meet rental obligations. Pay attention to their communication skills, professionalism, and general demeanor during the interview to gauge their compatibility. Here are some sample questions to assess if the tenant will be a good fit:
Example Questions You Can Ask | Example Questions You CANNOT Ask |
|---|---|
Do you have any pets? | Do you have any medical conditions? |
Are you willing to comply with the property's rules and regulations? | What is your sexual orientation? |
How long have you been employed in your current role? | Do you have any plans to start a family? |
Have you ever broken a rental agreement? | Are you married or single? |
Are you able to meet the monthly rent obligations? | Do you have any disabilities? |
To avoid breaking Fair Housing Laws during the tenant interview process, landlords should ensure that the questions asked are legal and objective. These questions should be directly related to the applicant’s qualifications as a tenant. Focus on factors such as income, rental history, and references. Furthermore, landlords may develop a standardized interview format with a consistent set of questions for all applicants to ensure fairness and avoid potential accusations of discriminatory practices.
Red Flags to Look Out for When Conducting Interviews
During screening interviews, it’s essential to watch for potential red flags that may signal a mismatch with your criteria or raise concerns about trustworthiness. Your prospective tenants are individuals to whom you may entrust your valuable property, emphasizing the need for a thorough evaluation. By staying alert to red flags, you can enhance your ability to select trustworthy and suitable tenants for your property. Here’s a list of red flags to look out for during interviews:
- Unusual behavior: Signs of disrespect, rudeness, or evasiveness during the interview process.
- Ambiguous responses: Difficulty in providing clear and concise answers, which may indicate issues in the tenant-landlord relationship.
- Inconsistent rental history: Discrepancies in past rental references or frequent moves within a short period.
- Unwillingness to consent for background checks: Hesitation or refusal to authorize necessary background and credit checks.
- Impractical expectations: Overly demanding or unrealistic expectations regarding the property or lease terms.
7. Accept or Reject the Applicants After Screening
After carefully evaluating each applicant’s qualifications and ensuring alignment with your established criteria, landlords must decide whether to accept or reject their tenant’s application. The basis for this decision should encompass factors such as creditworthiness, rental history, income stability, and overall compatibility to make an informed decision. Communicate your decision promptly and in compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Formulating the Criteria
Landlords should formulate transparent screening criteria to facilitate a more structured evaluation process. This becomes particularly significant when dealing with multiple applications and the need to identify the most suitable tenant for the property. Consider including the following details in your rental criteria checklist to aid in selecting the right tenant:
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Sufficient Income | The applicant should have income that meets or exceeds the requirement of three times the monthly rent. |
Stable Employment | A stable work history shows a continuous duration of time in their current job. This indicates reliability and a higher likelihood of consistent income. |
Verifiable Income | Verify the applicant's income through their current employer documents or tax returns. This helps confirm their financial stability and ability to meet rental obligations. |
Satisfactory Credit | Assess the applicant's credit history to ensure a strong credit profile. This indicates responsible financial behavior and increases the likelihood of timely rent payments. |
Clean Criminal Background | Check for a criminal background free of felonies or misdemeanors to prioritize tenant safety and security. |
Positive Rental History | Evaluate the applicant's previous residence and landlord history for a favorable track record of fulfilling lease obligations and maintaining their past properties. |
After determining whether the prospective tenant meets your criteria, you can accept or reject their application.
How a landlord navigates accepting a tenant application is critical to starting the new landlord-tenant relationship positively. To finalize the leasing process, the landlord should follow certain steps that involve clear communication, preparing a lease agreement, and ensuring a smooth transition into the rental property. Here are the steps a landlord should take when accepting a tenant application:
Step 1: Notify the Tenant
Inform the tenant or their agent representation of your decision to accept their application. Landlords should promptly communicate the good news and express their enthusiasm about their tenancy.
Step 2: Provide a Lease Agreement
Prepare a lease agreement that outlines the terms and conditions of the tenancy. Decide whether you are drafting a one-year lease or a month-to-month tenant agreement. The lease should contain important details, such as the rental amount, lease duration, security deposit, pet policies (if applicable), and other defined terms.
Step 3: Schedule a Meeting to Discuss Lease Terms
Arrange a meeting with the tenant to review and sign the lease agreement in person or virtually. Be available to clarify any questions they may have.
Step 4: Conduct a Move-in Inspection
Schedule a move-in inspection to document the condition of the rental property before the tenant moves in. Walk through the property together and note any existing damages or necessary repairs. Have the tenant sign the inspection report for mutual agreement.
Step 5: Exchange Contact Information
Ensure you exchange contact details with the tenant so that you can reach them, or they can reach you when needed. You may also provide them with your preferred method of communication for future correspondence.
Step 6: Offer a Welcome Package
Creating a welcome package can be helpful during this transition process. The package can include important information like a copy of the signed lease agreement, contact details for maintenance requests, garbage disposal instructions, and any additional property-specific rules that you may need them to follow.

Apartment rental agreement example (Source: pdfFiller)
These next steps of accepting a tenant’s application will help landlords establish a strong foundation for a successful tenancy. Once your tenant has moved and settled in, check in on them periodically to ensure no issues need to be addressed.
When choosing a tenant, it’s better to forego a candidate than to rent to a potentially bad one. Although it might not be pleasant, the process of evicting a tenant is much worse. If there are clear indicators that a candidate is problematic, you are within your right to decline them. However, you must comply with adverse action Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) laws.
The FCRA plays a crucial role in how landlords can utilize consumer credit reports when making decisions on tenant applications. When denying a tenant application based on data obtained from a consumer credit report, the FCRA requires landlords to present an “adverse action letter” to the applicant. This letter must outline the reasons for the denial and incorporate the particular credit information that influenced the decision.
Some legal reasons to deny an applicant after screening include:
- Their income can’t support the rent
- Their credit is too low, or their payment history is poor across several accounts
- They have a criminal history that indicates potential risk
- Employment is unverifiable, they have too little work history, or the employer indicates workplace trouble
- Prior residence research turns up evictions, judgments for property damage, unpaid rent, or problems with neighbors or law enforcement
Be prepared with supporting documentation when declining a prospective tenant, and stay within the boundaries of the law. Online tenant screening provides the necessary data to ensure you do not make subjective decisions or improperly deny candidates.
Tools to Assist With Screening Tenants
Landlords can leverage advanced software to screen prospective tenants. These tools offer a variety of features like automated rental applications, online background checks, and credit assessments. By using tools throughout the process of screening tenants, landlords can save time, reduce manual paperwork, and make data-driven decisions. This ultimately helps select the most qualified and reliable tenants for your rental properties.
The following are tenant screening services landlords can use:
Software |  | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Best For | Robust tenant screening capabilities | User-friendly mobile app | Digital tenant application process | Free online rental application forms |
Key Features |
|
|
|
|
Starting Price | $58 per month | $35 per application | $29 per application | $55 per application (paid by renters) |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When screening potential renters, landlords should ask questions tailored to their specific requirements, covering rental preferences, lifestyle, and ability to meet rental obligations. To comply with the Fair Housing Laws, questions should focus on objective factors, such as income, rental history, and references. Some sample questions include “Do you have any pets?”; “Are you willing to comply with the property’s rules and regulations?”; and “Can you pay the lease application fee?”
Keeping track of renters can be simplified by using rental management software. This helps you collect, organize, and safeguard important information while efficiently managing transactions. Baselane is an example of a platform providing a streamlined approach to rent collection. Tenants can pay rent online, eliminating the need for paper checks or in-person transactions. Additionally, Baselane offers landlords financial management tools to track income and expenses, providing a convenient way to generate detailed financial reports.
It is important to understand the legal requirements surrounding security deposits in your jurisdiction. Generally, landlords must hold security deposits in a separate account, provide tenants with a written receipt, and follow certain procedures for their return or deduction. Familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations to ensure compliance and avoid disputes.
Bottom Line
Taking the time to learn how to screen tenants will reduce the headache of having to evict a bad tenant in the long run. Landlords should implement a thorough tenant screening process to minimize potential tenant scams, secure responsible tenants, and foster a positive landlord-tenant relationship. Leveraging technology and software tools can help you find the best way to screen tenants by streamlining the process and providing valuable insights into prospective tenants.
