Fake checks are fraudulent or counterfeit versions of legitimate checks, created with the intent to deceive individuals or businesses. These checks may look authentic but lack sufficient funds, are entirely fabricated, or are tampered with.
To avoid potential financial and operational loss, a business must learn how to spot a fake check by being familiar with security features to look for in a check, setting policies for accepting check payments, and educating employees on how to tell if a check is counterfeit. Some features to spot in a fake check are poor paper quality, blurry texts, incorrect account details, and missing security features.
Key takeaways:
- Fake checks can cause significant financial risks that could lead to monetary loss, damaged business reputation, and even legal consequences.
- Businesses should learn to spot security features such as watermarks, holograms, security threads, special inks, and the Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) line to detect a fake check.
- When businesses spot a fake check, they should cease further transactions, contact the issuing bank, document key details, inform their own bank, report to law enforcement, and warn others to mitigate potential risks.
Despite the significant drop in the number of check payments, 7.2% per year from 2018 to 2021, the number of check fraud cases reported by banks from 2021 to 2022 almost doubled. This increased prevalence of check fraud makes it even more important for businesses to learn how to spot a fake check.
Types of Fake Checks
The deceptive use of fake checks comes in various forms, each with its own set of characteristics and red flags. Knowing how to tell if a check is fake can help businesses safeguard their financial interests.
Counterfeit Checks | Altered Checks | Fraudulent Checks |
|---|---|---|
Physical replicas of genuine checks | Legitimate checks that have been tampered with | Checks used with deceptive intent |
Created to closely mimic the appearance and characteristics of real checks using advanced printing techniques | Genuine checks with specific altered details (such as payee name or amount) | Can be a counterfeit check or an altered check; uses stolen checkbooks or false information |
Counterfeit Checks
Counterfeit checks are basically fake copies of real checks, made to trick businesses or individuals. Legitimate checks are typically printed on high-quality paper with unique characteristics. Counterfeit checks may appear blurry, have irregular fonts, or lack the distinct texture found in genuine checks.
These fake checks usually don’t have the special security features you’d find on authentic checks, like watermarks, holograms, or color-shifting ink, so it’s important to take a close look to spot the difference.
Altered Checks
Altered checks are legitimate checks that have been tampered with to change details like the payee’s name or the amount. Fraudsters may attempt to modify the information on the check, so it’s crucial to carefully inspect for any signs of tampering, such as erasures or inconsistencies in handwriting.
Two of the usual cases of altered checks are:
- A fraudster gets hold of a genuine check, alters the payee’s name, and encashes it or deposits it to their account
- The payee alters the amount in the check and encashes or deposits it for a higher amount
Fraudsters will want to alter as little detail as possible so cases of altered checks often involve something as simple as adding another zero to the amount.
Fraudulent Checks
Fraudulent checks are fake checks created with false information, often through theft or fabrication. These checks may involve stolen checkbooks or entirely made-up account details, and it’s essential to scrutinize them for inconsistencies to prevent falling victim to financial scams.
Some examples of uses of fraudulent checks are:
- Writing bad checks: The account holder purposely issues a check without any funds to cover it in the account
- Forging signatures on stolen checks: A fraudster steals a checkbook and uses them by forging the signature of the account holder
- Identity theft: A fraudster opens a checking account using someone else’s identity and uses the issued checkbook for deceptive purposes
10 Features to Spot a Fake Check
Ensuring the authenticity of a check is important in safeguarding your business from financial fraud. Paying close attention to specific security features can significantly help in detecting fake checks. Here are key features to scrutinize:
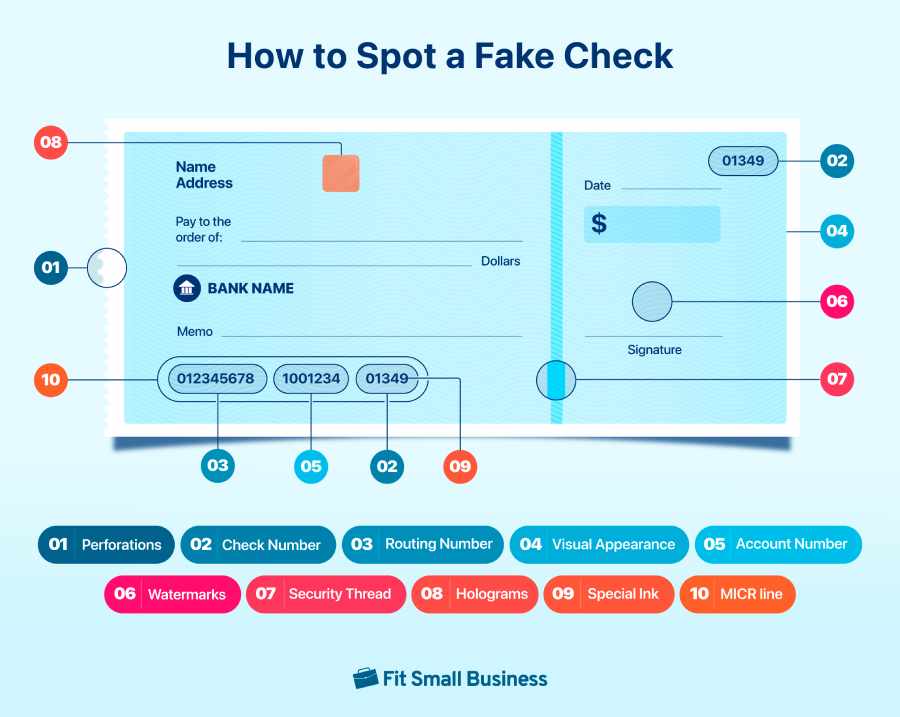
1. Perforations
Legitimate checks typically feature perforations along the edges that create a clean and uniform tear when detached. Examine the edges of the check to ensure there are perforations and they are consistent in spacing and appearance.
Fake checks may exhibit irregular perforations (or none at all), resulting in jagged or uneven tears when attempting to detach a section. Pay attention to the tear quality, as discrepancies in perforation could indicate a counterfeit check.
2. Check Number
Scrutinizing the check number is one of the fastest and easiest details available to verify the authenticity of a check. Firstly, irregularities in the sequential order of check numbers can be indicative of potential fraud. Be vigilant for missing check numbers, unchanged numbers from one check to the next, or checks with numbers out of order. Anomalous patterns in the check number sequence, such as a newer check having a lower number than an older one, should prompt immediate scrutiny.
Another red flag is the placement of the check number on the check. Legitimate checks consistently display the check number in the top right-hand corner. Any deviation from this standard, such as the number being located elsewhere on the check, may signal a potential issue.
Furthermore, while a low check number doesn’t inherently indicate fraud, it could signify a new check-writing entity, especially if the checking account is less than a year old. Be cautious of check numbers in the low three digits for personal checks and low four digits for business checks, as these might be associated with higher risk. Keeping an eye on these check number intricacies adds an extra layer of diligence in safeguarding against potential fraudulent activities.
3. Routing Number
The routing number, a nine-digit code located at the bottom left of a check, uniquely identifies the financial institution involved in the transaction. This code facilitates seamless fund routing and automated processing through systems like the Automated Clearing House (ACH). Use the routing number to verify check authenticity by confirming that it matches the correct bank that issued the check.
4. Visual Appearance
Visually examining the check is equally important. Authentic checks typically have clear and relevant memos, and any vague or nonsensical notations in the memo area may raise suspicions. Also, stains or discolorations on the check can be a cause for concern. Legitimate checks are printed on high-quality paper, and any unusual marks may suggest potential tampering or fabrication.
5. Check Details
Beyond the check number, various other details require careful examination to identify potential signs of a fake check. Here are some crucial signs that may indicate a fake check:
- No authorized signature
- Incorrectly spelled or missing name and address
- Incorrect account number
- Notations such as “void” or “nonnegotiable”
- Mismatched numerical and written amounts
- Missing bank logo
6. Watermarks
Legitimate checks employ advanced security measures, often including intricate watermarks seamlessly integrated into the paper. When scrutinizing a check’s authenticity, hold it up to the light and meticulously examine it for subtle imprints or changes in texture. Authentic watermarks are designed to be nearly imperceptible under normal conditions but become apparent when exposed to light, serving as a reliable indicator of a genuine financial instrument.
7. Security Threads
Legitimate checks frequently incorporate embedded security threads, an additional safeguard against counterfeiting. Thin, metallic strips running vertically through the paper are intentionally woven into the check’s fabric to deter replication. When examining a check, holding it up to a light source reveals these security threads, with genuine checks displaying distinct and continuous features that confirm their authenticity. Attempts to replicate this characteristic often introduce irregularities, making it easier to identify potential counterfeits.
Additionally, authentic security threads may showcase dynamic reflections or color changes under varying lighting conditions. Thoroughly examine the check by tilting it to observe any shifts in color or reflective properties.
8. Holograms
Holograms function as a sophisticated security feature in many checks to help prevent counterfeiting. These three-dimensional images or patterns are integrated into the check’s design to create a visually striking element that is challenging to replicate. When inspecting a check, pay particular attention to holographic elements, which often include intricate details or shifting colors. Tilt it at different angles to observe any changes in color or pattern within the holographic elements. Genuine checks with holograms will exhibit fluid transitions and dynamic shifts
9. Special Inks
Authentic checks also use special inks that help identify them as legitimate ones. These inks possess unique properties, such as the ability to undergo color changes when exposed to varying light conditions. During the examination of a check, it is prudent to scrutinize the ink for any anomalies in color patterns. Authentic checks utilize these specialized inks precisely to create challenges for counterfeiters, maintaining consistent and vibrant colors as a hallmark of legitimacy.
10. Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) line
The Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) line is a critical component of legitimate checks, facilitating efficient processing through automated systems. This specialized line, typically found at the bottom of the check, contains magnetic characters that hold essential account information. When verifying the authenticity of a check, carefully inspect the MICR line to ensure clarity and accuracy in the printed characters.
Legitimate checks feature a well-defined MICR line. It will contain the account number, routing number, and check number, which should align accurately with the number displayed on the check. Any disparities may indicate a fake check.
What to Do If You Spot a Fake Check
Discovering a fake check requires prompt and decisive action to mitigate potential risks. Here’s a step-by-step guide on what to do if you suspect a check may be fraudulent:
- Step 1: Cease Further Transactions. Cease any ongoing transactions involving the suspect check. Refrain from depositing it or using it for any financial activities.
- Step 2: Contact the Issuing Bank. Reach out to the bank listed on the check using a verified contact number. Report your concerns and seek confirmation regarding the legitimacy of the check.
- Step 3: Document Details. Document key information about the check, including payer details, the check amount, and any other relevant particulars. This documentation can be valuable for potential investigations.
- Step 4: Inform Your Bank. Notify your bank promptly and provide them with comprehensive information. Your bank can guide you on the appropriate steps to take and may implement additional safeguards.
- Step 5: Report to Law Enforcement. File a report with local law enforcement agencies. Share all gathered details about the fraudulent check to aid their investigation efforts.
- Step 6: Warn Others. Share information about the incident with other businesses in your community. Collective awareness can help prevent similar incidents and protect fellow business owners.
8 Tips on How to Avoid a Fake Check Scam
Navigating the risks associated with fake check scams requires a proactive approach and a set of robust practices. Here are key tips to safeguard your business:
- Set a policy for accepting check payments: Establish clear policies for accepting check payments within your business. Communicate and enforce guidelines to ensure consistency in check verification across transactions.
- Educate Your Staff: Ensure your staff is informed about the situation and conduct training sessions on identifying signs of fake checks. Empower them to contribute to fraud prevention efforts.
- Take note of different banks’ check security features: Familiarize yourself and your team with the security features specific to different banks, especially the biggest banks in your area. Understanding these features makes it easier to spot irregularities and increases the accuracy of your check verification process.
- Wait for a check to clear before releasing a product or performing a service: Exercise caution by waiting for a check to clear before fulfilling a product order or providing a service. While the process may take time, it adds an extra layer of assurance that the check is legitimate.
- Call the issuing bank: When in doubt, contact the issuing bank directly using a verified contact number. Confirm the legitimacy of the check and gather additional information to make informed decisions.
- Consult professionals: Seek guidance from legal or financial professionals with expertise in fraud prevention. Their insights can be instrumental in navigating the aftermath of a potential fraud incident.
- Stay vigilant: Maintain a heightened level of vigilance in future transactions. Stay informed about the latest security features and fraud prevention techniques to stay ahead of evolving scam tactics.
- Offer other payment methods: Diversify your payment methods and consider alternatives that offer additional layers of security. Offer other ways to pay when a customer presents a check. While checks are a common form of payment, exploring electronic and secure payment options can minimize the risk of falling victim to fraudulent activities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Click through the sections below for common questions on how to spot a fake check:
To verify if a check is real, carefully examine security features such as watermarks, holograms, and the MICR line. Confirm the check number and inspect for an authorized signature. If in doubt, contact the issuing bank using a verified contact number to confirm the check’s legitimacy.
Depositing a fake check can lead to serious consequences. Initially, the bank may make the funds available, but once the check is discovered to be fake, the deposit will be reversed, and the account holder may be held responsible for the full amount. Additionally, individuals may face legal actions, fees, and damage to their financial reputation.
Fake checks often lack genuine security features found in authentic ones. These may include missing watermarks, holograms, or security threads. Additionally, irregularities in the check number sequence, absence of an authorized signature, and discrepancies in the MICR line are common features that can indicate a check is fake.
Bottom Line
Spotting fake checks is important for businesses to avoid financial pitfalls and protect their reputation. Fake checks, whether counterfeit, altered, or fraudulent, pose substantial risks, making it crucial for businesses to be vigilant and well-informed. Recognizing security features like watermarks, holograms, and the MICR line, setting clear policies for check acceptance, and educating staff will help businesses avoid fake checks.