Every aspiring entrepreneur should have a roadmap—a strategy for growing their business from a core idea to a profitable venture. A business model defines an entrepreneur’s overall plan for making a profit, identifying its core product (or service), target market, value proposition Identifies what makes a business unique from its competitors , and strategy for sustainability.
This guide will introduce you to the basics of a business model and help get you started on creating your own.
Key Takeaways:
- A business model is a company’s overall growth strategy.
- Business models focus on building, delivering, and growing the company’s unique value proposition.
- The business model is the foundation of a business plan.
- A business model canvas is a helpful tool for creating a successful business model.
Business Model Types
Business model types determine the focus of the entrepreneur’s venture. Some of the most common business models are listed below:
Retail
Retail is the most common business model. This model starts with buying products from suppliers at wholesale prices and then selling directly to customers with a markup, also referred to as reselling. The markup includes the business’s cost to handle and operate plus the owner’s profit margin.
Examples:
- Clothing stores
- Supermarkets
- Gas stations
Manufacturing
A manufacturing or product business model involves sourcing raw materials in bulk to process and create a new product. Manufacturers earn profit by selling large volumes of the product to wholesalers and retailers. While this is considered wholesale pricing, operating costs are significantly low for the business owner to still earn a profit.
Examples:
- Coca-Cola
- Procter & Gamble
- Ford
Service-based
In a service-based business model, owners earn profit by providing a service for a fee instead of a physical product. These services are sourced from a skill or skills that consumers need help accessing. Consultation with lawyers and doctors, home repairs and maintenance, food produced by chefs, and convenience provided by restaurant servers fall under this category.
Examples:
- Restaurants
- Clinics
- Salons & spas
Subscription
A subscription is a business model in which consumers (called subscribers) pay a recurring fee in exchange for continuous delivery of a product or service. The subscription-based model includes everything from magazines and monthly gift boxes to software access and streaming services.
Examples:
- Netflix
- Spotify
- Peloton
Freemium
Freemiums are similar to subscriptions in that they offer a recurring product or service for a fee. However, unlike subscriptions, a freemium business model includes a forever-free subscription option, where the same product or service can be offered minus key features that can only be accessed with a paid plan.
Examples:
- YouTube
- Zoom
- Uber
Bundling
This business model offers a unique value proposition where products or services are grouped together based on certain criteria. The business attracts consumers by showing that purchasing the bundle is more cost-effective or more convenient than buying each product or service within the bundle separately.
Examples:
- McDonald’s Happy Meal
- Computer hardware and OS
- Gift sets
Marketplace
A marketplace provides an online platform for other businesses to sell their products or services. Similar to its physical counterpart, the owner earns by charging its clients a fee for “renting” a space on the platform. Marketplaces vary in features, services, and even niches that help make them attractive to clients.
Examples:
- Amazon
- Airbnb
- UpWork
Affiliate
In an affiliate business model (also called click-through business model), an ecommerce merchant enters a contract with marketers (individuals or other businesses), forming an affiliate network, to promote their products or services in exchange for a commission. The ecommerce merchant can widen its customer base while keeping its marketing cost to a minimum. Most online marketplaces have an affiliate marketing program in place.
Examples:
- Amazon affiliate marketing
- eBay affiliate marketing
- Etsy affiliate marketing
Bait-and-Hook
The bait-and-hook or razor blade business model works by selling a valuable product at cost (sometimes even below cost) in exchange for recurring sales of a related disposable item. The major characteristic of these valuable products is that they require a top-up or a refill of the complementary item to work.
Examples:
- Xerox
- HP Printers
- Nespresso
Reverse Bait-and-Hook
As the name suggests, this business strategy is the opposite of bait-and-hook. The merchant assigns a premium price on the main product and offers the companion items for free or at a discount. Also called the reverse razor blade, this business model offers an attractive line of complementary products to encourage an upfront investment in a premium item.
Examples:
- Apple iPhone
- Amazon Kindle
- Toys & accessories
Franchise
A franchise business model is where an established company expands its customer base by allowing other entrepreneurs to use its brand and product or service in return for an initial franchise fee and regular royalty payments. The franchisee benefits from the parent company’s well-known brand and proven procedures.
Examples:
- McDonald’s
- Starbucks
- Walmart
Pay-as-You-Go
The pay-as-you-go business model allows a merchant to earn from actual service rendered or actual usage rather than a fixed fee paid for subscriptions. Some businesses include a base rate on top of a metered fee.
Examples:
- Utilities
- Mobile Plans
- Cloud storage
Brokerage
A brokerage business model is where a merchant serves as a middle person between a buyer and a customer and earns a commission based on a percentage of the total transaction value. A broker does not have its own product or service but would have a wide network or platform to find a transaction match. Real estate, stock, and art brokerage firms are the most common examples.
Examples:
- ReMax
- JP Morgan
- Christie’s
Creating a Successful Business Model
A business model is the building block of a company’s revenue strategy, and a proven, successful business model is characterized by a clear outline of goals to help with decision-making.
A successful business model should have a:
- Sound foundation: A successful business model provides a business foundation that does not waver even with changes within the industry.
- Strong value proposition: It supports the company’s unique value, allowing it to assign a price that consumers will be willing to pay.
- Well-planned strategy: This clearly outlines how a business will be structured to successfully deliver a company’s value and how this unique value will generate revenue.
- Identified target market: The business model should clearly identify the customer segment the business plans to serve.
Business Model vs Business Plan
A business model is a high-level plan that covers the entrepreneur’s vision and mission, while a business plan is a roadmap for executing a business model. Read our business plan guide for step-by-step advice on crafting an expert business plan.
The Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas is a template that helps visualize an entrepreneur’s business strategy. It focuses on how to build on and deliver the company’s value proposition as well as ensure that this strategy sustains and grows the business.
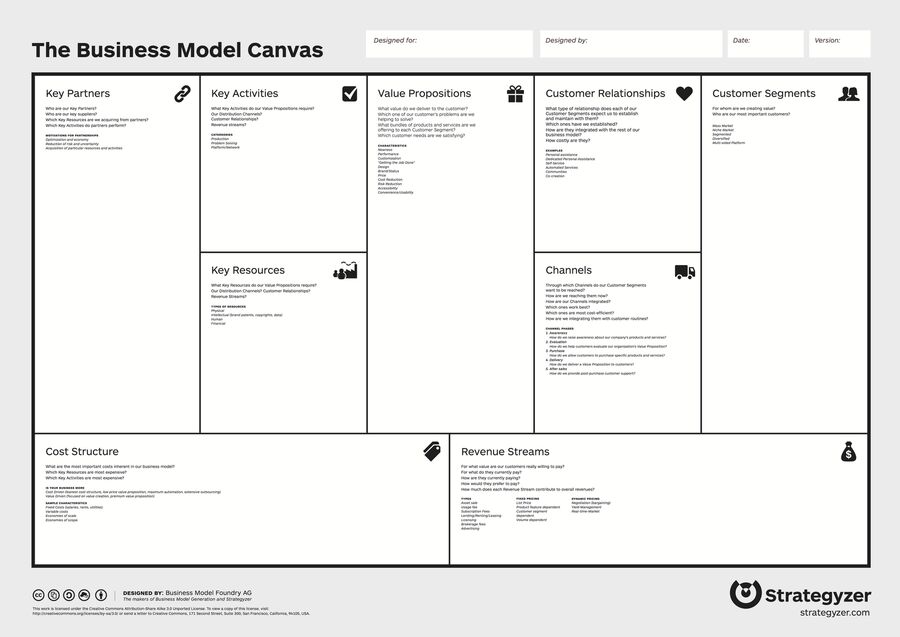
The Business Model Canvas is based on Alexander Osterwalder’s PhD work in 2005 on business model ontology which has been modified for different niches. (Source: Wikipedia)
Since its introduction, many business model templates have been developed to fit different business types. While each business model is unique, every template is comprised of nine building blocks which are as follows:
- Key partners: Identifies suppliers of needed resources and partners for key activities that build the business value
- Key activities: Activities that build the company’s value proposition
- Key resources: Human, financial, physical, and intellectual assets needed to build the business value
- Value proposition: Combination of products and services that makes a business unique from competitors
- Customer segments: Lists the business’ target set of customers based on certain categories
- Customer relationships: Business strategy for nurturing, keeping, and expanding customer base
- Channels: Delivery strategy for the business’ products and services
- Cost structure: Identifying the business strategy for operational costs
- Revenue streams: Lists the business’ primary and secondary sources of income
For a complete guide, download our Free “How to Start a Business” e-book:

Thank you for downloading!
Quick Tip:
As you’re starting your business, it’s wise to register it as a legal entity, like an LLC. Doing this will protect your personal assets if a lawsuit were to occur against the business. You can register your business as an LLC through an online legal service.
IncFile is an online service that handles and files the paperwork so your business can become an LLC quickly.
Start your business today with IncFile for as little as $0 plus state fees with no contracts and no hidden fees.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
These are some of the most common questions we encounter about business models.
A business model is an overall strategy for growing a business, identifying key components such as value proposition, partners, cost structure, and target market. It is at the core of every company’s business plans.
Retail, manufacturing, and service are some of the most basic examples of a business model. However, as market demand and technology evolved, other business models such as pay-as-you-go, subscriptions, and freemiums have been developed over the years.
Yes, every entrepreneur should start by creating a business model to keep decision-makers focused on the company’s overall goals.
Bottom Line
Every business, whatever its size, should start with a business model. A business model is a company’s roadmap to success—establishing a concrete strategy for developing and delivering its products and services to its customers. It guides decision-makers through roadblocks and innovations within the chosen industry, so the company remains focused on its short- and long-term growth goals. Using a business model canvas will help you get started in creating your own.