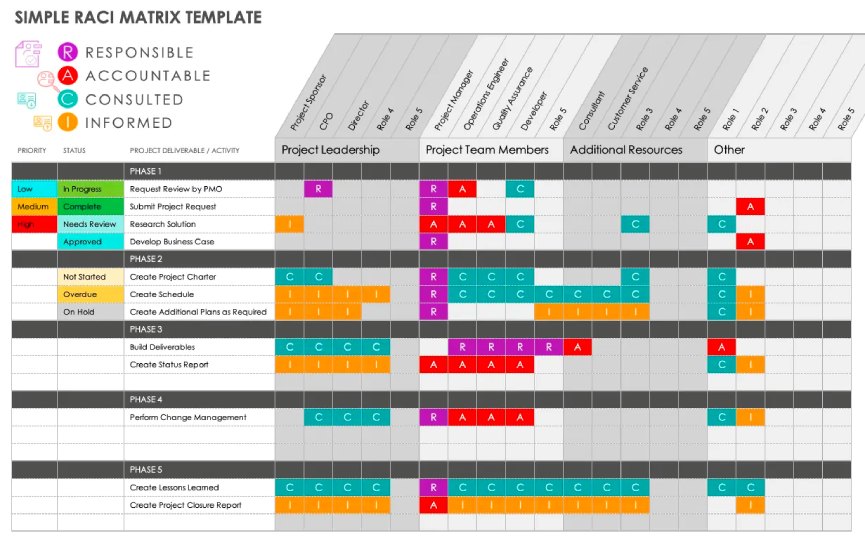
A RACI chart, a type of responsibility assignment matrix (RAM), is a visual tool for defining team members’ responsibilities on specific tasks or outputs. To understand better what a RACI chart is, picture a diagram in a table format. The first column enumerates the project assignments, and the rest of the columns reflect the different stakeholders’ names or roles.
For each task or output under a specific stakeholder, a letter is assigned signifying the team member’s level of ownership or involvement on the deliverable: R is for Responsible, A for Accountable, C for Consulted, and I for Informed. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits and drawbacks of using this visual tool and the best practices for applying it in project management.
The RACI chart defines the responsibility of each stakeholder on every task. (Source: ClickUp)
A Breakdown of the RACI Definition
To explain further what is a RACI chart, let’s drill down into the meaning of the acronym: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed, which represents each team member’s role for each assignment. Find out what the labels mean below:
- R – esponsible: This stakeholder executes the work assigned. It’s possible to have multiple team members labeled R in a matrix. For example, in a software development project, this will be the programmers, user interface/user experience designers, and content writers.
- A – ccountable: This stakeholder delegates the tasks and evaluates the output. In some cases, the person “Responsible” may also be the team member “Accountable.” In most software development projects, the “Accountables” are the team leads and product managers.
- C – onsulted: This stakeholder also reviews the finished tasks, but unlike the “Accountable,” they’re required to sign off on the output before delivery. It’s possible to have multiple stakeholders needing to be consulted in a project. In a software development project, these are the project managers and product owners.
- I – nformed: This is the individual or group of individuals who need to be updated on the progress and completion of the project. They’re often not included in the actual production process. In a software development project, these are the executive leadership or external clients.
Advantages of Using the RACI Chart
Now that you have a rough idea of what is a RACI chart, let’s explore the different advantages of using the matrix in your projects. In a nutshell, the RACI model is an excellent tool for delineating roles and responsibilities, providing a good structure for managing tasks and team members in a project.
When done right, it will increase ownership and accountability among stakeholders, improve communication, and facilitate a more efficient decision-making process in project management. These are the specific ways a RACI chart benefits project teams:
Most people ask, “What is a RACI chart, and why is it useful?” The RACI chart’s primary function is to illustrate the participation of each stakeholder in project activities. As it identifies who’s responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed for each task, it removes any confusion or potential misunderstanding as the project progresses.
On a stakeholder level, this is beneficial as each one understands well what they must do and what’s expected of them. On a team level, knowing who to ask for updates on task progress or approval and sign-off for outputs makes the collaboration process smoother.
Since the RACI chart for project management increases visibility on the responsibilities of each stakeholder, team members have a higher level of task ownership. They are more conscious of the fact that their performance affects others’ work. This increased sense of accountability drives productivity, which contributes to project success.
Another answer to the question “What is a RACI chart used for?” is it’s valuable for speeding up the decision-making process. The diagram outlines the people who need to be consulted for approval, making it easier to identify whom to submit outputs to.
The RACI chart eliminates the frustrating back-and-forth discussion on who gets the final say on deliverables, thus reducing potential delays in project completion. In addition, it allows team members to work on other tasks immediately and gives managers ample time to assess outputs and decide if they’re ready to be delivered.
Most misunderstandings in projects come from confusion about roles and responsibilities. Team members are confused about which managers need a sign-off on specific outputs. Meanwhile, leaders overseeing too many project details sometimes don’t know who exactly in the team needs to be followed up on for updates once the project is rolling.
Using a RACI chart template prompts you to define who’s in charge of what. It guides you on stakeholders’ roles and responsibilities as the project progresses. Moreover, it helps you avoid overloading or underloading team members with tasks. Since responsibilities are laid out, you’ll be able to strike a balance in assigning work to specific stakeholders.
Disadvantages of Using the RACI Chart
Although the RACI chart is great for defining roles and responsibilities, it’s not a foolproof tool. It comes with disadvantages that you should be aware of to know whether it’s worth adopting in your organization and project. Below are some disadvantages of using the RACI chart:
Creating a RACI matrix is tedious as it requires plotting every activity in the project, conducting meetings and negotiations with stakeholders, and finalizing who’s in charge of specific tasks. It’s part of the project planning stage and may cause you to delay project execution if you haven’t completed the matrix yet. In the case of urgent projects, the intricateness of creating a RACI chart may compromise timely delivery.
Since the RACI chart highlights a hierarchical structure in project teams, it’s not for all. Organizations that aim to practice innovation might not see team members introducing new ideas as their roles are restricted. They may be reluctant to share new ways of doing things for fear of overstepping their assigned responsibilities.
At the same time, the RACI chart fails to recognize the informal roles that develop in team relationships. While there are official project managers and product owners who would need to be consulted about work quality, there are team members, particularly the senior ones, who don’t have formal titles but are referred to because of their expertise. They’re usually not acknowledged in the RACI matrix.
As mentioned in our answer to the question, “What is a RACI chart in project management?” the tool requires assigning letters indicating the role of each stakeholder. This shouldn’t be a problem for simple projects. However, for large initiatives with various stakeholders, the diagram quickly becomes tedious and intricate, making it harder to keep track.
Moreover, complex projects often see frequent changes. This requires you to update the matrix every now and then to ensure that it accurately reflects each person’s responsibilities. This administrative task may be overwhelming in the long run.
How to Create a RACI Chart
While there are plenty of RACI chart templates you can use to get started quickly, the process of creating a matrix from scratch is rather simple. Follow these easy steps on how to create a RACI chart:
- List the tasks and activities the project requires. This task column is your first column.
- Plot the names or roles of team members as the next column headers.
- Populate the table with R, A, C, and I labels, according to the responsibilities of each team member. Start with the people “Responsible” for the tasks, as this helps determine what roles other team members will play.
- Discuss the chart with team members.
- Sign off on the document.
Examples of a RACI Chart
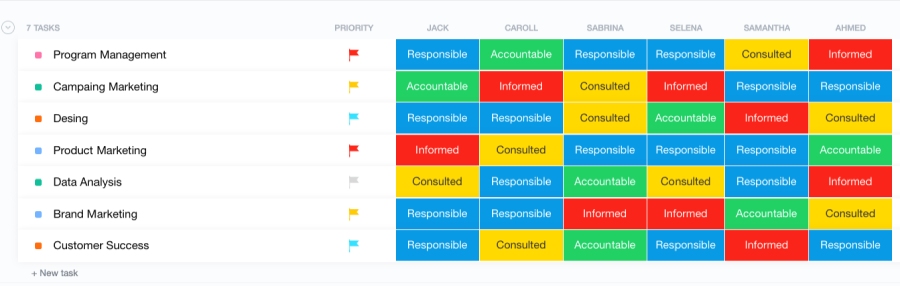
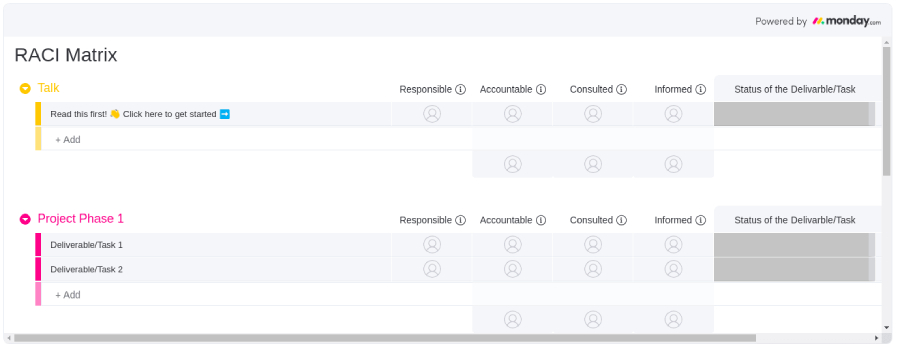
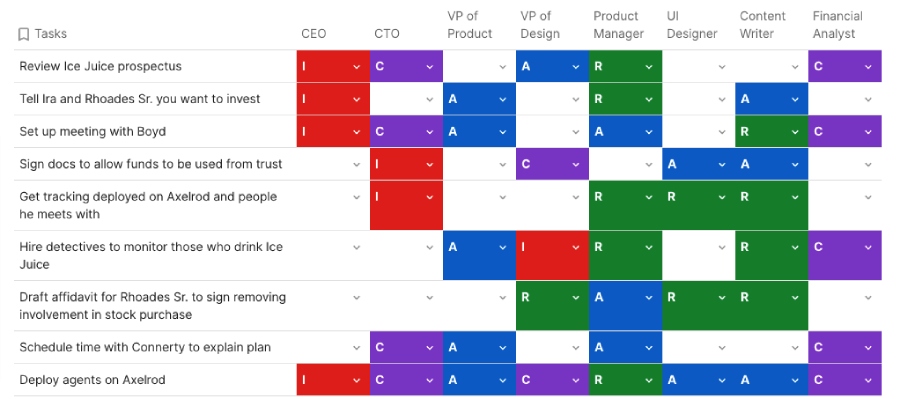
Now that you understand well what is RACI matrix, let’s delve into the actual diagrams to help you better visualize how it’s created. Various project management solutions provide templates to make the plotting of tasks and team member roles and responsibilities easier. Here are some RACI chart examples from different project management systems that you may consider in project planning:
Rules for Using the RACI Chart
To make the most of the tool, users are encouraged to follow a few general guidelines when using the RACI chart. These are the rules to remember:
- There should only be one “Responsible” and “Accountable” person per task: Having multiple people assigned to the responsible and accountable duties will create confusion. One team member might disregard the task, assuming that the others designated will work on it. On the flip side, this could also result in duplicate work, wasting team members’ efforts and time.
- “Responsible” and “Accountable” roles are mandatory: The “Responsible” and “Accountable” roles must be explicitly specified. Even in tasks that can be automated, there should be someone responsible or accountable for ensuring that the work is completed successfully.
- Communication with the consultant must be a priority. The “Responsible” and “Accountable” team members must coordinate closely with the “Consulted” to ensure that deliverables comply with quality standards.
- All stakeholders must be informed: Everyone must be aware of the progress and developments made on the project.
Best Practices for Using the RACI Chart
Now that you know the basics of what a RACI matrix is, the next step is to understand the best practices to help you maximize the chart’s effectiveness. Below are some strategies you may incorporate in your project management process:
No stakeholder should have too many “Responsible” tasks designated to them. Being overworked will lead to burnout, compromising the quality and timely delivery of outputs. On the flip side, ensure that team members have enough assignments. You’ll waste your manpower’s skills and potential if they are underworked.
Moreover, the project stalls when there are not enough resources dedicated to completing the tasks. Thus, when you develop a RACI chart, always double-check if there are too many or too few “Responsible” tasks assigned to individuals.
The stakeholders must own the role that they’ve been assigned to. Before coming up with a matrix, conduct discussions with team members. Brief them on what their role entails for the assignments and ask if they’re willing to participate in such a manner.
Ideally, when you get their buy-in, it should be put in writing and included in the project charter, the document that outlines the project’s purpose, objectives, scope, and stakeholders. This should make the team members’ acceptance of the role official.
Avoid listing administrative to-dos, such as booking meetings or creating reports, as these could overwhelm the matrix. Instead, concentrate on the most important project activities and deliverables. This should help your team be focused on critical tasks that move the project along to completion. Refer to your project plan that clearly states your project goals to properly filter through tasks.
To ensure that you have the right people on the job, review the roles you entrusted to team members, ensuring they are skilled and experienced to handle what’s assigned to them. This reduces the likelihood of outputs being repeatedly revised and passed around the team, which considerably delays project completion.
As the project progresses, you’re bound to see changes in some roles and responsibilities. These should be reflected in the chart to guide team members accordingly. Before making any changes, though, ensure that the involved parties are informed.
Alternatives to the RACI Chart
Given the disadvantages of the RACI chart, you may find it useful to explore alternatives to this responsibility assignment matrix. These alternatives are in table formats as well, but they’re structured to be simpler, focus less on tasks, or provide other role options outside the traditional.
Below are the RACI chart alternatives you may explore:
RACI Alternative | Definition |
|---|---|
RAS |
|
RASCI |
|
RAPID |
|
CARS |
|
DACI |
|
CLAM |
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, there should be no blank spaces in a RACI chart. Every team member must have a role, even if it’s only to be informed of the developments in the project. Remember, the RACI chart is designed to facilitate effective and maximum participation among team members. In most organizations, when there’s no person identified under the “Responsible” role, it’s assumed that the “Accountable” person will work on the task.
Yes. Simple tasks may entail having one person only for both the “Responsible” and “Accountable” roles.
There’s no strict rule as to how many team members or leaders must be consulted, but the golden rule is to limit the number, as too many parties may complicate the decision-making process and hold up the approval or sign-off, resulting in a project delay.
Bottom Line
A RACI chart is an effective responsibility assignment matrix that defines whether a project stakeholder is “Responsible,” “Accountable,” “Consulted,” or “Informed” for specific tasks. It’s beneficial to businesses as it clarifies roles and responsibilities, makes team members more accountable, speeds up decision-making, and helps resolve conflicts faster.
Now that you know the basics of what a RACI chart is in project management, remember that the key to maximizing this visual tool is to adopt best practices, including ensuring tasks are assigned to different roles equitably and focusing on key assignments only. Adopt project management software solutions and use their RACI chart templates to get started on this tool easily.