Generative AI—a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content like text outputs and computer codes—is changing the human resources (HR) landscape. It offers new opportunities to streamline processes, enhance decision-making, and improve employee experiences. It is emerging to be a powerful tool with diverse applications across the field, from recruitment and onboarding to employee engagement and talent development.
Here, we will talk about the roles and impact of generative AI in HR. We will also tackle the challenges and ethical considerations surrounding the implementation of generative AI in HR practices, including data privacy concerns, potential biases in AI-driven decisions, and the need for human oversight.
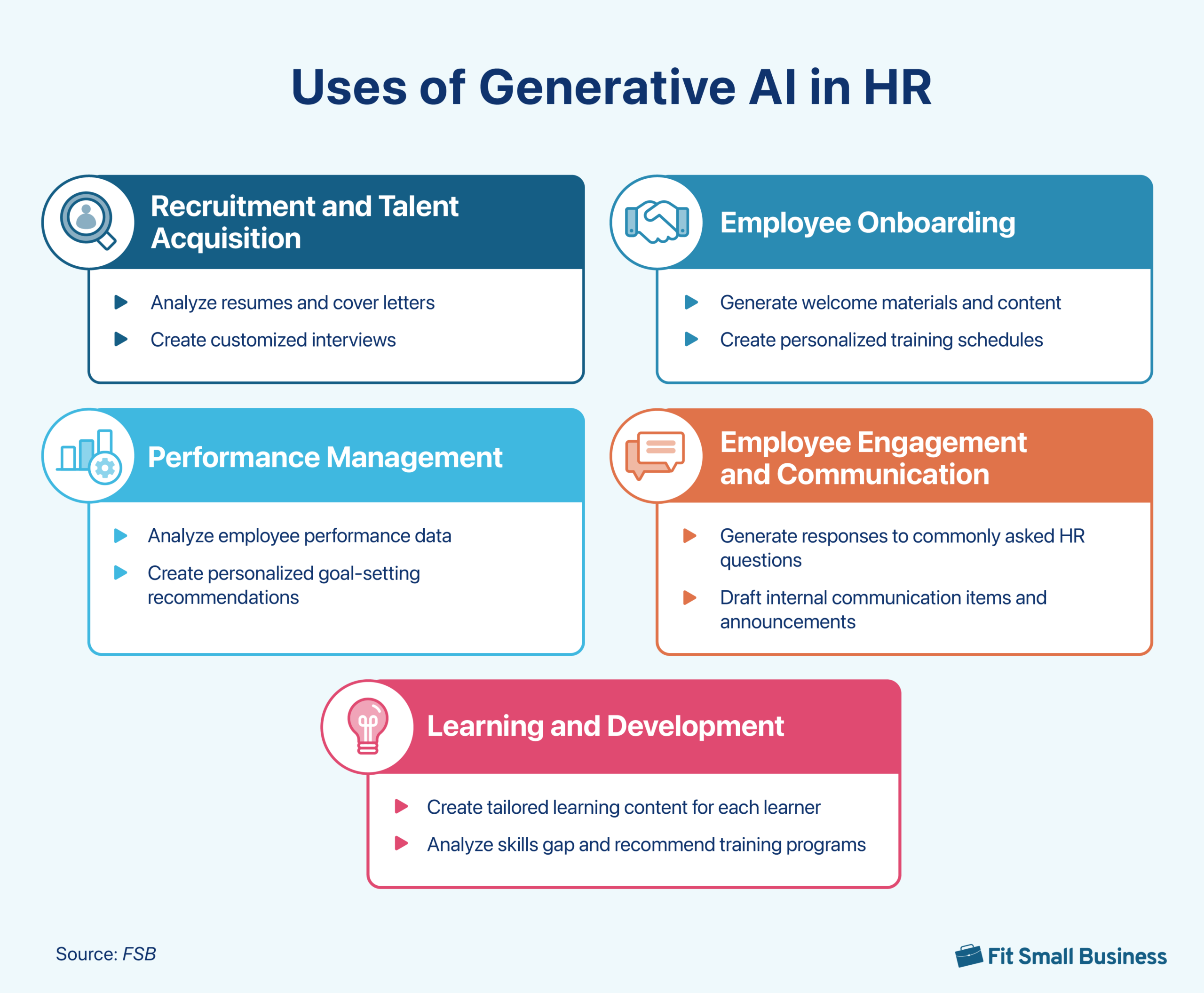
Different Ways of Using Generative AI in HR
In a recent McKinsey report about the future of AI, organizations that adopted generative AI in HR saw a 50% cost reduction and a 33% revenue increase. Below is a closer look at how it is transforming various HR processes:
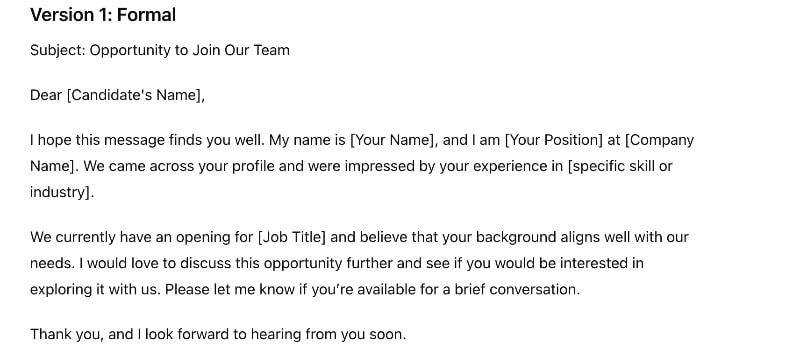
Generative AI has helped talent acquisition teams generate personalized job descriptions that accurately reflect the role requirements while appealing to the target candidate pool. AI tools can craft tailored outreach messages for potential candidates, increasing engagement and response rates. You can also use generative AI to conduct A/B testing for your outreach message by asking the tool to craft different versions of your message.
Here are two versions of an outreach message to a potential candidate generated from ChatGPT:
In the screening phase, talent acquisition managers can use Gen AI to create pre-employment assessment questions and customized interview questions based on the specific job requirements and candidate profiles, ensuring a more targeted and effective interview process. Additionally, it can also create offer letters and other hiring materials, such as media advertisements, flyers, and brochures.
Onboarding new employees can be time-consuming, repetitive, and impersonal for both HR teams and candidates. Generative AI can address these and make the onboarding process smoother and faster. For example, it can create customized plans for new hires, taking into account their role, experience, and the organization’s culture. It can generate welcome materials and orientation content that introduce new employees to the company’s policies, procedures, and culture in an engaging manner.
AI-powered systems can automate paperwork completion through intelligent form-filling, reducing administrative burden and potential errors. An AI assistant can also be available to answer new employee questions, providing instant support during the crucial early days of employment. Furthermore, generative AI can create personalized training schedules based on the new hire’s role and experience, ensuring they receive the most relevant and effective onboarding experience.
In performance management, generative AI can create performance review templates tailored to specific roles, ensuring comprehensive and relevant evaluations. For example, it can get bulleted lists compiled by managers, praise received on Slack, customer-generated performance reviews, and other sources. Then, managers can input it in a generative AI tool like ChatGPT and use a good prompt/command. The tool can transform all that information into a comprehensive performance review.
The technology can generate suggestions for performance improvement, offering actionable advice based on individual strengths and weaknesses. AI can assist in creating personalized goal-setting recommendations and aligning individual objectives with organizational goals. Additionally, generative AI can compile and analyze feedback from various sources to generate comprehensive performance reports, offering a more balanced and data-driven approach to performance evaluations.
When it comes to employee engagement and communication, generative AI can help HR professionals by drafting internal communications and announcements, ensuring consistent messaging across the organization. It can also create personalized employee engagement surveys, tailoring questions to specific departments or roles for more meaningful insights.
AI-powered systems can generate responses to common HR-related queries, providing employees with quick accurate information. By analyzing communication patterns, AI can also offer suggestions to improve team collaboration and overall organizational communication. On top of these, sophisticated chatbots powered by generative AI can handle routine HR inquiries, freeing up HR professionals to focus more on complex, strategic tasks.
In the area of learning and development, generative AI is transforming how organizations approach employee growth. It can create personalized learning paths for employees based on their current skills, career aspirations, and the organization’s needs. AI systems can generate tailored training content, adapting the material to individual learning styles and preferences for maximum effectiveness.
Interactive learning modules and simulations can be developed using AI, providing engaging and practical learning experiences. The technology can also be used to analyze skill gaps across the organization and recommend training programs to address them efficiently. Finally, AI can generate quizzes and assessments to evaluate learning outcomes, providing immediate feedback and adjusting future learning recommendations based on performance.
How Generative AI Will Impact HR
Despite the job security concerns raised by many individuals, 34% of HR leaders who participated in Gartner’s 2024 benchmarking session said that they are exploring generative AI use cases and opportunities. In the same session, 76% of HR leaders believe that if they do not adopt or implement AI solutions in the next two years, it will greatly affect the success of their organizations.
While there are still many people who expressed their concerns about AI taking over their jobs, 78% of executives believe that Gen AI’s benefits outweigh its risks. HR has been discovering a wealth of benefits that are reshaping how they attract, develop, and retain talent. Below are the top three benefits of AI in HR:
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
Generative AI boosts productivity by automating time-consuming tasks. A GitHub survey showed that 60% to 75% of developers who used a Gen AI tool not only improved their productivity but also their sense of fulfillment. That’s because the tool automated repetitive tasks and allowed them to focus on more satisfying work.
From an HR point of view, HR professionals can also focus on more strategic initiatives as generative AI automates mundane HR tasks, like generating documents and providing instant responses to common queries. This significantly reduces manual workload and accelerates HR processes.
Personalized Employee Experiences
By leveraging vast amounts of data, generative AI can create tailored experiences for employees at every stage of their journey. From customized onboarding plans to personalized learning paths and career development recommendations. AI helps deliver more relevant and engaging experiences that can boost employee satisfaction and retention.
Data-driven Decision Making
Generative AI can analyze complex patterns in HR data—such as patterns that may lead to employee turnover—to provide valuable insights and predictions. This capability enables HR leaders to make more informed decisions about workforce planning, talent management, and organizational strategy. AI-generated reports can highlight trends, identify potential issues, and suggest proactive measures, leading to more effective HR policies.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While generative AI offers immense potential for revolutionizing HR practices, it also presents significant challenges and ethical considerations. As organizations increasingly adopt AI technologies, it’s crucial to address these concerns to ensure fair, transparent, and responsible use of AI in the workplace.
Let’s explore some of the key considerations and challenges associated with implementing generative AI in HR.
AI algorithms are only as unbiased as the data they’re trained on and the humans who design them. In HR contexts, biased AI can perpetuate or even amplify existing inequalities in hiring, promotion, and other decision-making processes.
A real-world example of this can be found in a Bloomberg experiment where they tested whether ChatGPT has a bias or not. After feeding GPT 3.5 with resumes and asking it to rank the resumes 1,000 times, the tool favored names from some demographics. For example, names that are commonly associated with Asian women ranked first, while names associated with Black women ranked eighth.

A Bloomberg experiment revealed that AI is not free from hiring biases. (Source: Bloomberg)
Generative AI requires vast amounts of data to function effectively, raising significant privacy concerns. HR departments handle sensitive personal information, from social security numbers to health records and performance evaluations. The use of AI introduces new risks of data breaches or unauthorized access. GDPR and CCPA laws emphasize individuals’ rights to privacy and control over their personal data, requiring organizations to obtain explicit consent and be transparent about data collection and usage.
Moreover, employees may feel uncomfortable with AI systems analyzing their personal data because it could potentially expose sensitive information, such as their SSNs or HIPAA PHI (protected health information). Additionally, using gen AI tools can compromise a company’s proprietary information. Organizations need to implement robust data protection measures, obtain clear consent for data use, and be transparent about how employee data is collected, stored, and analyzed by AI systems.
The “black box” nature of many AI algorithms can make it difficult to understand how they arrive at their conclusions or recommendations. Then, there’s also the danger of AI hallucinations where AI generates incorrect or fabricated information, which can mislead users. This can be particularly problematic in HR, where decisions significantly impact people’s careers and livelihoods. Employees may question the fairness of AI-driven decisions if they can’t understand the reasoning behind them.
HR departments need to prioritize explainable AI models and develop clear communication strategies to help employees understand how AI is used in decision-making processes. This includes providing avenues for employees to challenge or appeal AI-driven decisions.
As AI takes over more HR tasks, there are concerns about its impact on HR professionals’ roles. While AI can automate many routine tasks, freeing up HR staff for more strategic work, it may also lead to job displacement in some areas. For instance, AI chatbots might reduce the need for HR support staff, while advanced analytics could decrease demand for certain HR analyst roles.
Organizations need to carefully manage this transition, focusing on reskilling and upskilling HR professionals to work alongside AI systems effectively. It’s also crucial to maintain a balance between AI efficiency and the human touch that is often critical in HR functions, especially in areas like employee relations and conflict resolution.
Best Practices for Using Generative AI in HR
Here are six best practices for using generative AI and creating a strategy in HR:
1. Align AI Initiatives With Business Objectives
Start by clearly defining your organization’s HR goals and overall business strategy. Identify specific areas where generative AI can add the most value, such as improving recruitment efficiency, enhancing employee engagement, or streamlining performance management. Ensure that every AI initiative directly supports these objectives. This alignment will help prioritize AI projects, secure leadership buy-in, and measure the impact of AI implementations effectively.
2. Develop a Transparent AI Policy
The AI policy should define and ensure how AI tools are used within the company and ensure that all stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities. To ensure transparency, these policies should include:
- Purpose and scope: Clearly define the purpose of AI use within the organization and the areas where it will be applied.
- Ethical guidelines: Outline ethical principles, including fairness, bias mitigation, and data privacy, that guide AI development and deployment.
- Data usage policies: Specify how data will be collected, used, stored, and protected, including user consent and anonymization practices.
- Accountability and responsibility: Define roles and responsibilities for AI oversight, including who is accountable for decisions made by AI systems.
- AI system transparency: Describe the transparency measure in place, such as making AI decision-making processes understandable to users and stakeholders.
- Bias and error monitoring: Establish protocols for regularly monitoring AI systems for biases, errors, and unintended consequences, and how these will be addressed.
- Compliance with regulations: Ensure that AI practices comply with relevant laws and industry standards, including regular audits and updates as regulations change.
- Training and awareness: Include training programs to educate employees on AI use, ethical considerations, and the company’s AI policies.
3. Prioritize Data Quality and Ethical AI Use
Implement robust data governance practices to ensure the quality, accuracy, and representativeness of the data used to train and operate AI systems. Regularly audit your data for biases and errors. Develop clear ethical guidelines for AI use, addressing issues such as fairness, transparency, and privacy.
For example, AI systems should only use data that has been ethically sourced with strict protocols in place to protect user privacy. Also consider forming an AI ethics committee to oversee the development and deployment of AI solutions in HR, ensuring they align with your organization’s values and comply with relevant regulations.
4. Invest in AI Literacy and Upskilling
Provide comprehensive training to HR staff and other relevant employees on AI concepts, capabilities, and limitations. This will enable them to work effectively alongside AI systems and make informed decisions about AI use.
Develop a continuous learning program to keep the team updated on the latest AI advancements and best practices. Additionally, identify and nurture AI champions within the HR department who can drive adoption and serve as go-to resources for AI-related questions.
5. Implement AI Solutions Incrementally
Adopt a phased approach to implementing generative AI in HR. Start with pilot projects in specific areas where AI can deliver quick wins and demonstrate value. Use these initial successes to build confidence and gather insights before scaling to more complex applications. This incremental approach allows for learning and adjustment along the way, reducing risks and increasing the likelihood of long-term success.
6. Maintain Human Oversight and Intervention
While generative AI can automate many tasks, it’s crucial to maintain human oversight in HR processes, especially those involving critical decisions about employees. Design your AI systems with clear touchpoints for human review and intervention. These touchpoints should be placed at the following key stages:
- Data input and pre-processing: Before data is fed into the AI models, humans should review and validate quality, relevance, and ethical sourcing data.
- Decision-making process: For AI systems making critical or high-stake decisions, human review should be integrated before final decisions are implemented, especially in areas like healthcare, finance, and legal matters.
- Post-deployment monitoring: After AI systems are deployed, continuous human monitoring should be established to detect and correct any biases, errors, or unintended consequences in real time.
- User feedback and incident handling: Touchpoints should be available for humans to intervene based on user feedback or when AI systems malfunction, ensuring that issues are addressed promptly and effectively.
There should also be a regular assessment of the balance between AI automation and human judgment, adjusting as necessary to ensure that empathy, context, and ethical considerations remain central to HR practices.
Regular assessments should be conducted whenever there are significant updates to AI systems or changes in business processes. Develop clear guidelines for when and how human HR professionals should review or override AI-generated decisions or recommendations.
Top Generative AI Tools for Each HR Process
HR Process | AI Tool | How It Helps |
|---|---|---|
Recruitment and Talent Acquisition | Paradox |
|
Fetcher |
| |
Employee Onboarding | Enboarder |
|
Leena AI |
| |
Performance Management | Lattice |
|
15Five |
| |
Employee Engagement and Communication | Slack |
|
Leapsome |
| |
Learning and Development | Docebo |
|
EdCast |
|
Bottom Line
Generative AI is poised to transform the landscape of Human Resources, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance efficiency, personalization, and strategic decision-making across all HR functions. While the benefits are significant, organizations must navigate challenges such as bias mitigation, data privacy, and maintaining the human touch in HR processes. By embracing best practices and developing thoughtful strategies, HR departments can harness the power of generative AI to create more dynamic, responsive, and effective workplaces that benefit both employees and the organization as a whole.