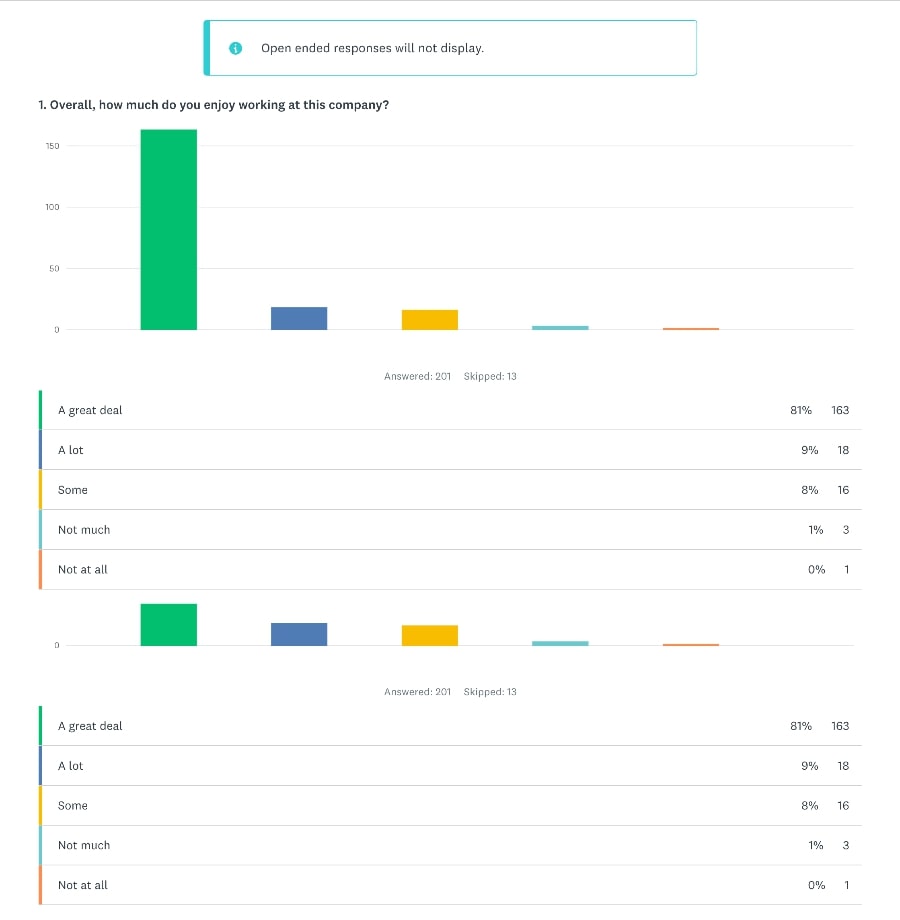
Creating an employee survey involves determining the survey goals, demographics, format, and questions; testing and analyzing the results; and, finally, creating an action plan. An employee survey should measure and improve engagement, evaluate the success of onboarding, or monitor reaction to a specific issue. It should also provide relevant and valuable insights into the employee experience.
Follow these general steps to learn how to create an employee survey:
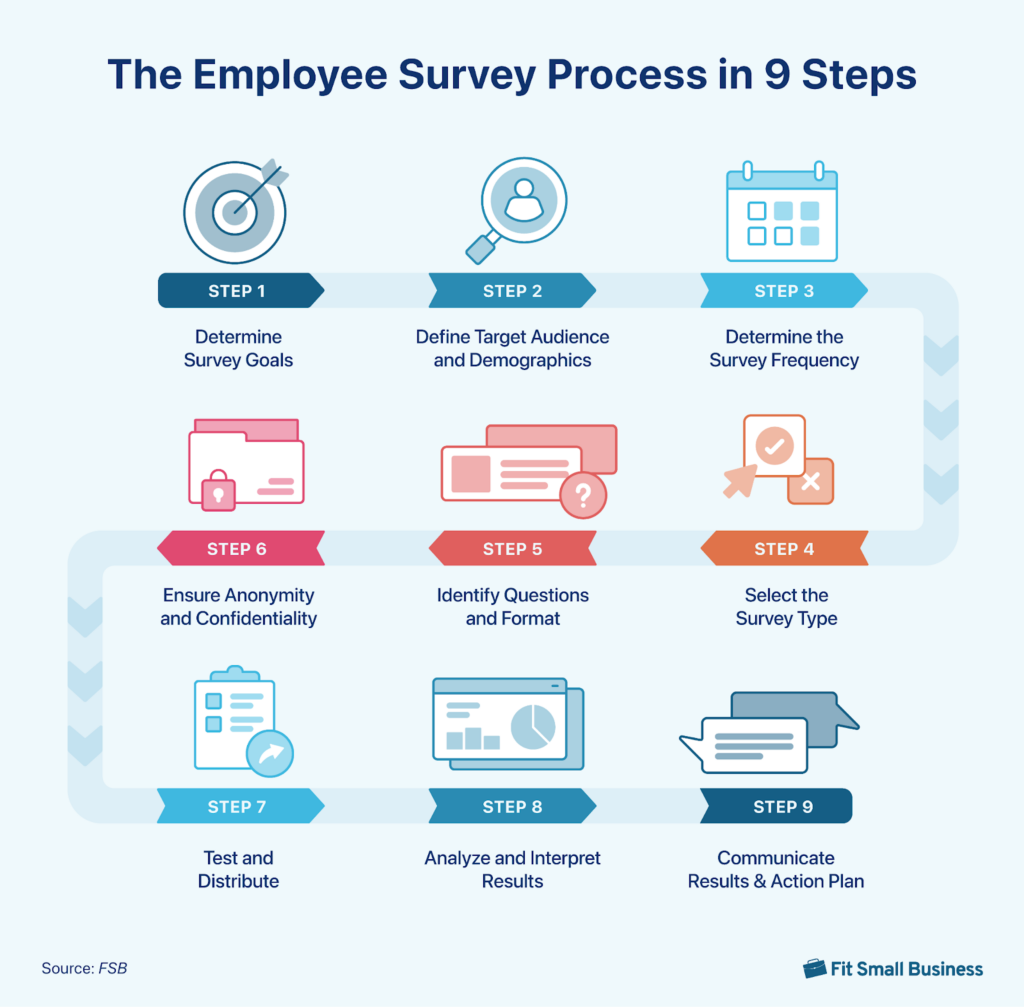
This 9-step employee feedback cycle illustrates the journey from determining survey goals to creating an action plan based on the survey data.
Step 1: Determine Survey Goals
Before creating a survey, you must determine its goals. Identify the key areas you want to cover—i.e., job satisfaction, work-life balance, communication, or management support—and what you want to achieve. Your goals will help you ask the right questions and, consequently, get the right answers. When doing this, follow the specific, measurable, actionable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) rule.
Step 2: Define Target Audience and Demographics
This process involves carefully considering who will participate in the survey and what demographic information you’ll collect. Decide whether the survey will encompass the entire company or focus on specific departments, teams, or locations. Additionally, will you include part-time employees or contractors if they are part of your workforce?
Next, determine the key demographic information you’ll gather. You can use either personal or professional demographics, depending on your goal. These could include the following:
- Age
- Gender
- Race
- Education
- Department
- Tenure
- Pay type
- Position
Step 3: Determine the Survey Frequency
The frequency of your surveys can significantly impact their effectiveness, employee participation rates, and your organization’s ability to act on the results. When determining the ideal survey cadence, consider your company’s size, culture, and capacity for implementing changes based on survey feedback. There’s little benefit if you conduct frequent surveys and can’t address the issues raised promptly.
There are several common approaches to survey frequency, each with its advantages:
- Annual Surveys: They provide a comprehensive view of your organization. They also give you time to implement and see the results of major initiatives.
- Biannual or Quarterly Surveys: They offer more frequent touchpoints and enable you to track the progress of your key metrics throughout the year. They also allow you to create agile responses to emerging issues.
- Pulse Surveys: These are short and frequent surveys focusing on specific topics. They can be conducted monthly or biweekly; thus, providing real-time insights into employee sentiment.
- Always-on Feedback: These are continuous feedback mechanisms that allow employees to share their thoughts at any time.
It’s worth noting that you can adopt a hybrid approach, combining different frequencies for various purposes. For example, you might conduct the following:
- An annual comprehensive engagement survey
- Quarterly pulse surveys on specific topics
- Monthly check-ins on key performance indicators
Step 4: Select the Survey Type
Select the survey type that aligns with your goals and the frequency at which you want to conduct the survey. Some different types of employee surveys include pulse surveys, onboarding surveys, and annual workplace culture surveys.
Step 5: Identify Questions and Format
The survey questions should align with the survey’s goals. You can also use preexisting survey questions and adapt them to your organization’s specific needs.
You can use a combination of open- and close-ended questions in your survey. Close-ended questions allow employees to choose from a list of options, while open-ended questions allow employees to provide their own responses. Here are some samples:
Open-ended Questions | Close-ended Questions |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 6: Ensure Anonymity and Confidentiality
Guaranteeing anonymity and confidentiality in your employee survey is crucial for fostering trust and encouraging honest, unfiltered feedback. When employees feel secure in expressing their opinions without fear of repercussions, they’re more likely to provide candid responses, leading to more valuable and actionable data.
To ensure anonymity and confidentiality, consider implementing the following measures:
1. Use a Trusted Third-party Survey Platform
Choose a reputable survey platform with robust security measures. Confirm that the chosen platform supports anonymous submissions. Also ensure that the system prevents tracing individual responses back to specific employees.
2. Limit Demographic Data Collection
When gathering demographic data, focus solely on essential information to maintain anonymity. Be cautious about combining demographic categories that might unintentionally identify individuals.
For instance, while data on age group, gender, department, and years of service alone might not identify anyone, combining them can reveal an individual’s identity. If your survey results show responses from “a female employee, aged 40-50, working in the IT department for 10-15 years”, it might point to a specific person, especially if there’s only one female in that age group with that length of service.
To avoid this, use ranges instead of exact figures and limit the number of demographic questions to further protect employee privacy.
3. Set Minimum Response Thresholds
Response thresholds, in the context of employee surveys, are the minimum number of responses required before data is reported or analyzed for a particular group or category. Establishing a minimum response threshold safeguards individual anonymity, particularly in smaller teams or departments.
By only producing reports when a certain number of responses are received, you reduce the risk of accidentally identifying specific employees through their feedback and demographic information.
4. Communicate Your Commitment to Anonymity
To build trust and encourage honest participation in employee surveys, it’s essential to communicate your commitment to privacy and data protection. Clearly outline the specific measures implemented to safeguard employee identities, such as using secure platforms and limiting access to raw data.
Also provide a transparent explanation of how survey responses will be handled, stored, and used, including any data retention policies and the purposes for which the information will be used.
5. Train Managers and Leaders
During training, it should be emphasized why maintaining confidentiality is essential for getting honest feedback and fostering trust within the organization. Along with this, provide clear guidelines on how to appropriately discuss and act upon survey results without attempting to identify individual respondents.
6. Handle Open-ended Responses Carefully
When handling open-ended responses in employee surveys, it’s crucial to carefully review and process the comments before sharing them. Remove any information that could potentially identify the respondents, such as names, specific projects, or unique situations. You can either do this manually or use text analysis software like Drumroll AI to ensure thoroughness and accuracy.
7. Secure Data Storage and Transmissions
Implement robust encryption measures to safeguard the information during both transmission and storage, preventing unauthorized access or data breaches. Additionally, establish strict access controls to limit who can view the raw survey data. Only essential personnel, such as key HR staff or designated analysts, should have access to this sensitive information.
Step 7: Test & Distribute
Before distributing the survey to employees, test it with a small group to ensure that the questions are clear and easy to understand. After that, choose a suitable method for distributing the survey to employees, such as email or an online survey tool. Ensure that employees understand the purpose of the survey and that their responses will be anonymous.
Step 8: Analyze and Interpret Results
Analyzing the results will help identify areas of strength and weakness in your organization. Here are a few tips on how to do that:
- Review the Response Rate: Determine how many employees responded to the survey to calculate the response rate. A low response rate may indicate a lack of interest or engagement in the survey.
- Identify the Key Themes: Look for common response themes and patterns. For example, you can group similar responses to identify the most common concerns or issues that must be addressed.
- Review Individual Questions: Examine the responses to each question. Look for questions where the responses are particularly positive or negative. This will help you identify areas of strength and areas that need improvement.
- Segment the Data: Analyze the results by different demographic groups, such as job level, department, or location. This will help you identify any disparities in the engagement levels between different groups of employees.
- Benchmark Against Industry Standards: Compare your results against industry benchmarks or previous survey results. This will help you determine whether the engagement levels are improving or declining over time.
Step 9: Communicate Results & Action Plan
Once you have reviewed and shared the employee survey results, the next step is creating an action plan to address the key issues identified. Creating an action plan is crucial for improving engagement levels and fostering a positive work environment. Here are some key considerations when creating an action plan:
1. Identify Areas of Improvement
Start by reviewing the survey results and identifying areas where employees are dissatisfied or have provided suggestions for improvement.
2. Prioritize Opportunities for Growth
Prioritize growth opportunities based on the areas for improvement you identified. Consider their impact on employee engagement levels, the feasibility of addressing them, and the resources available.
3. Set SMART Goals
Like survey goal-setting, your action plan should have goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
4. Develop Action Steps
Develop specific steps to achieve each goal. These steps should be concrete, actionable, and easily delegated to specific individuals or teams.
5. Allocate Resources
Identify necessary resources to be allocated to support the action steps. This may include financial resources, time, and personnel.
6. Establish a Timeline
Establish a timeline for implementing the action steps and achieving the goals. The timeline should be realistic and take into account the resources available.
7. Monitor Progress
Monitor progress regularly and make adjustments as needed. This may involve gathering employee feedback, revisiting the action plan, and adjusting timelines or action items as needed.
8. Celebrate Successes
Celebrating success is an important part of an action plan because it reinforces positive behaviors and outcomes. When employees are acknowledged and rewarded for their efforts and achievements, it reinforces the behaviors that led to those successes. This can encourage employees to continue to exhibit those positive behaviors and strive for further success in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When writing an employee survey, you should focus on key areas like job satisfaction, work environment, company culture, work-life balance, and professional growth opportunities. Analyze each aspect of your workforce to determine if it aligns with the company’s goals and values. These areas collectively provide a comprehensive view of the employee experience and organizational health
To create an effective employee exit survey, focus on key areas such as reasons for leaving and overall work experience. You can also include topics like relationships with management, company culture, and job satisfaction. Ensure the survey is easily accessible, most probably through an online platform, and consider conducting a brief in-person exit interview to complement the survey results.
To design an effective employee satisfaction survey, start by clearly defining your objectives and the key areas you want to assess, such as job satisfaction and company culture. Use a mix of question types for quantitative data and qualitative insights. Keep questions clear, concise, and unbiased to ensure accurate responses. Also, consider the survey’s length and aim for a completion time of 10-15 minutes to maintain engagement.
Here are a few simple steps on how you can create an anonymous survey:
- Start by selecting a secure online survey platform that doesn’t collect identifying information.
- Craft questions that focus on general feedback without asking for specific details that could reveal an employee’s identity.
- Use broad categories for demographic questions to protect anonymity.
- Avoid using unique links or requiring logins that could be traced back to individuals.
- Consider using randomized response techniques for sensitive questions.
When analyzing results, ensure you don’t isolate responses in a way that could identify participants.
An employee engagement survey is a strategic tool used by organizations to measure and assess the level of emotional commitment, motivation, and connection employees have to their work and the company. These surveys typically cover job satisfaction, workplace culture, leadership effectiveness, career development opportunities, work-life balance, and overall organizational health.
Bottom Line
Learning how to create an employee engagement survey allows organizations to uncover areas for improvement and boost business performance. You can conduct them annually, quarterly, or whenever you deem necessary. No matter the frequency, being consistent can keep your employees committed and satisfied.