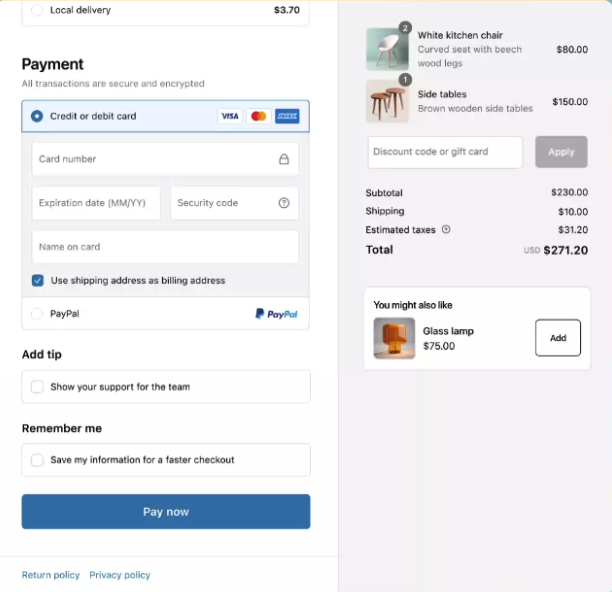
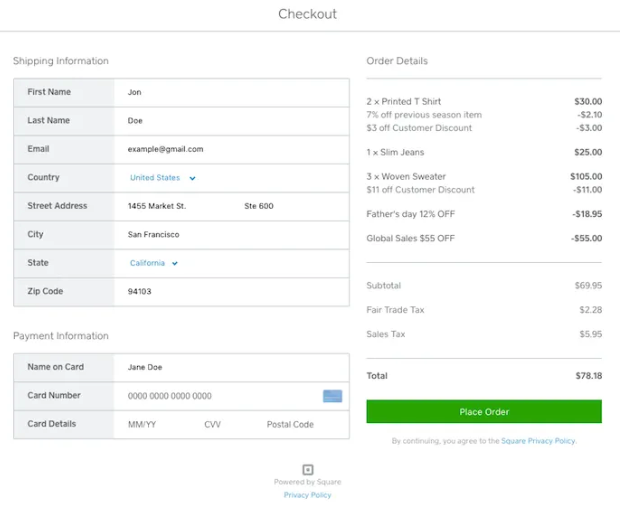
Embedded payments are a convenient way for businesses to accept payments directly within their websites or apps—without having to deal with different providers—while simplifying the checkout process for customers.
Understanding the dynamics and intricacies of embedded payments is important for small businesses that want to streamline transactions, improve customer satisfaction, increase operational efficiency, and drive business growth.
Key takeaways:
- Embedded payments allow businesses to accept payments directly within their websites or apps, increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs.
- By letting customers pay directly on websites or apps without being redirected, embedded payments make online buying faster and smoother for customers (potentially lowering abandonment rates).
- The use of embedded payment solutions is projected to continue increasing in the coming years, with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and contactless payments.
Embedded vs Integrated Payments
Embedded payments involve the seamless direct integration of payment processing within the platform (such as a website or app). One example is Shopify Payments. Merchants on the Shopify platform do not need to sign up with a separate payment processor if they choose to use Shopify Payments.
Meanwhile, integrated payments are an older solution and involve the integration of a third-party payment processor into an existing infrastructure (such as an ecommerce platform). Some ecommerce platform providers require merchants to sign up with a separate payment processor to handle payment processing on their website.
Here’s a quick overview of these two payment technologies:
Embedded Payments | Integrated Payments |
|---|---|
Seamless payment processing directly within the website or mobile app | Third-party payment processing solution integrated into ecommerce platform or mobile app |
Customers complete transactions without being redirected to an external payment gateway or website | Customers are asked to leave the website or app temporarily to complete the transaction through a separate payment gateway or portal |
Businesses deal with one provider only | Businesses deal with at least two separate providers |
Faster, more streamlined, cohesive user experience | More disjointed customer experience |
Businesses have everything within one platform | More flexibility for businesses in choosing a payment processor |
Payment redirection, which sometimes happens with integrated payments, increases the risk of losing customers. When a customer gets redirected to a different page during checkout, it can cause confusion and drive them to abandon their cart.
Using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) with a third-party payment processor means businesses have to deal with different providers and would likely have to pay separate fees. Although using APIs with a third-party payment processor will provide the same seamless transaction on the customer’s side, it is not a fully embedded payment solution for the business because the merchant still has payment processing as a separate service.
How Do Embedded Payments Work?
A payment transaction facilitated by embedded payments involves several steps to ensure smooth processing while maintaining security and convenience for both the customer and the business. Here’s how the process typically works:
- Initiation of Payment: The customer decides to make a purchase or payment within the platform or service. This could involve adding items to a shopping cart on an ecommerce website, subscribing to a service, or making an in-app purchase.
With non-embedded payments, the customer gets redirected to another website at this point, and the next steps are handled by the payment service provider, not the ecommerce platform or service. - Selection of Payment Method: The customer selects their preferred payment method from the available options—credit or debit cards, digital wallets, bank transfers, or other alternative payment methods.
- Encryption of Payment Data: When the customer enters their payment information, such as credit card details or account credentials, the data is encrypted using advanced encryption algorithms. This encryption ensures that the payment information remains secure during transmission over the internet.
- Tokenization of Payment Information: To enhance security, the payment information is often tokenized, where sensitive data is replaced with unique tokens. These tokens are meaningless to unauthorized parties and are securely transmitted and stored within the platform’s environment.
- Authorization Request: An authorization request is sent to the customer’s bank or financial institution to verify the transaction and ensure that the customer has sufficient funds or credit available.
- Authentication: Depending on the payment method and security measures in place, the customer may need to authenticate their identity to authorize the transaction. This could involve entering a one-time password (OTP), using biometric authentication, or other methods to verify their identity.
- Transaction Approval: Upon successful authorization and authentication, the customer’s bank or financial institution approves the transaction, indicating that the funds can be transferred to the merchant’s account. Upon completing the payment, customers receive immediate confirmation within the platform, providing reassurance and transparency throughout the transaction process.
- Settlement and Funds Transfer: The funds from the customer’s account are transferred to the merchant’s account, according to the process set by the platform.
For businesses, using a platform that offers embedded payments means that they simply have to sign up with the platform, and payment processing is handled by the platform.
Benefits of Embedded Payments
Embedded payments offer a range of advantages for both customers and businesses. Here are some of them:
For Customers
- Convenience: Embedded payments allow customers to complete the transactions seamlessly within the platform or service they are using, eliminating the need to navigate to external payment portals or re-enter payment information.
- Faster Checkout: With embedded payments, customers experience quicker checkout processes, reducing wait times and friction for the whole transaction.
- Enhanced Security: Embedded payment systems prioritize data security, employing encryption and tokenization techniques to protect sensitive payment information from unauthorized access and fraud. Also, all data is handled securely by one entity instead of two. Learn about secure payment systems.
- Improved User Experience: When payment processing is directly embedded into the platform or service, the overall effect for customers is a cohesive and user-friendly experience.
For Businesses
- Increased Conversion Rates: A simpler checkout process can lead to higher conversion rates because customers are more likely to complete the transactions, especially if the payment process is seamless and convenient.
- Streamlined Operations: Since most embedded payment solutions also offer services for other business systems such as inventory management and accounting software, business operations are more streamlined. Businesses can reduce the need to sync or maintain different systems.
- Reduced Costs: Businesses only need to get one provider for different services. For example, instead of paying separately for an ecommerce platform and a payment processing solution, businesses can go with a service that offers embedded payments within its ecommerce platform. Any overhead costs associated with data reconciliation are also eliminated.
- Improved Customer Insights. Embedded payment systems often provide businesses with valuable data and insights into customer behavior and preferences, such as their preferred payment methods, since the complete customer journey happens within the platform.
- Stronger Security: Many embedded payment solutions come with strong fraud detection and protection tools that help protect both businesses and customers. This may result in lower fraud risk and fewer chargebacks for businesses.
Related: How to Dispute a Chargeback
Future of Embedded Payments
In 2023, embedded payments were expected to hit $32 billion. According to a study by Juniper Research, embedded payments are projected to reach $59 billion in 2027, which is a growth of 84%. As payment technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the future of embedded payments holds promising opportunities for innovation and growth.
Several trends are shaping the trajectory of embedded payments and are poised to shape the way businesses and consumers interact with financial transactions.
Integration With Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are expected to play a significant role in embedded payments. These technologies will enable more personalized and contextual payment experiences, as well as facilitate innovative use cases such as voice-activated payments and smart connected devices.
Related: AI in Ecommerce: Small Business Guide
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the future of embedded payments will prioritize enhanced security measures and robust fraud prevention mechanisms. Advanced authentication methods, biometric verification, and real-time fraud detection algorithms will become integral components of embedded payment systems to safeguard sensitive payment data and mitigate risks.
Related:
Seamless Omnichannel Experiences
The focus of embedded payment providers will be on delivering seamless omnichannel experiences, allowing customers to initiate and complete transactions across multiple channels and devices seamlessly. Whether online, in-store, or via mobile, embedded payment solutions will enable consistent and frictionless payment experiences throughout the customer journey.
Related:
Integration With Digital Wallets & Cryptocurrencies
Digital wallets and cryptocurrencies are gaining traction as alternative payment methods, offering greater convenience and security for customers. There will likely be increased integration with digital wallets and support for cryptocurrencies, providing customers with more choices and flexibility in how they pay.
Related:
- What is a Digital Wallet & How Does it Work for Merchants?
- How to Accept Cryptocurrency Payments as a Business
Regulatory Compliance & Standard
The evolving regulatory landscape surrounding payments and data privacy will lead to greater emphasis on compliance with industry standards and regulations. Payment service providers and businesses will be expected to strongly adapt to changing regulatory requirements to ensure the security and integrity of embedded payment systems.
Related:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Click through the sections below to find answers to common questions on embedded payments:
An example of an embedded payment is when a customer makes a purchase directly within a mobile app or website without being redirected to an external payment gateway. Some examples are when you buy a product from an online retailer like Amazon, make in-app purchases in a mobile game, or pay for services through an app like Uber.
Embedded finance refers to the integration of various financial services into non-financial platforms or applications. Embedded payments is one aspect of embedded finance, as well as embedded insurance, banking, lending, and investing.
Embedded payments offer numerous benefits for customers, including streamlined checkout experiences, possibly leading to increased conversion rates and customer satisfaction. For businesses, embedded payments simplify payment processing, reduce operational costs, and provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Bottom Line
Embedded payments represent a significant evolution in digital transactions, offering seamless and secure payment experiences directly within websites and apps. Eliminating the need for redirection and integrating payment processing into the platform helps businesses enhance customer satisfaction, streamline operations, and potentially increase conversion rates.
As the future of embedded payments continues to unfold with advancements in technology and regulatory compliance, businesses that embrace this innovation stand to benefit from improved efficiency, reduced costs, and a competitive edge in the evolving digital landscape.