Adding cryptocurrency as a payment method has become increasingly popular among small businesses with the availability of affordable, easy-to-use platforms and apps. To start accepting crypto and bitcoin as a business, you need to sign up for a cryptocurrency account (wallet or payment gateway) and integrate it into your online checkout. You can also use a compatible QR code scanner to accept crypto payments in person.
Here is how to accept crypto as a business in four steps:
Step 1: Understand Cryptocurrency & Its Regulations
Cryptocurrency is a decentralized digital currency built on, secured with, and encrypted by blockchain technology. Unlike traditional physical currencies like the US dollar, cryptocurrency is not regulated by a government or other entity and only exists online. As of June 2022, 30% of cryptocurrency owners use crypto for purchases, and the number is only expected to grow.
Cryptocurrency is a highly debated topic, and the legalities of offering crypto as a payment method for your business will continue to change. However, the basics are as follows:
- Observe state laws for cryptocurrency investors: To accept crypto payments, you must have your own crypto account, which, by default, makes you an investor. This means you are expected to comply with the cryptocurrency regulations for your state.
- Review your cryptocurrency platform policy: Visit your service provider’s website to check for supported countries and review its user agreements. Not all cryptocurrency platforms are legal in the US, even if users can convert (or withdraw) their savings in US dollars. CoinGate, for example, is only legal to use in some states.
Although cryptocurrency owners can trade it for goods and services, crypto is often treated as an investment opportunity. It wasn’t until 2014, when PayPal gave online merchants the ability to accept Bitcoin payments, that small businesses took a serious look at cryptocurrency as a potential alternative payment method to credit cards.
Cryptocurrency vs Credit Card Payments
Cryptocurrency | Credit Cards | |
|---|---|---|
Opening an Account | Does not require approval | Requires approval |
Payment Processing Tool | Blockchain technology | Payment processor |
Transaction Speed | Do not require approval, but speed is based on network activity | Transactions go through real-time verifications but are instant |
Transaction Fees | Ranges from 0.5%–1% | |
Currency Conversion Regulation | Volatile rates but can be managed through certain crypto platforms | More stable conversion value dealing with fiat currency |
Account Security | Merchant is responsible but some crypto platforms offer additional security | Payment processor is responsible, offers advanced fraud and chargeback protection tools |
Chargeback Policy | No chargeback risk on transactions | Susceptible to chargeback and imposes fees |
Additional Features | Additional features are for managing cryptocurrency assets | Additional features such as financing and rewards |
Customer Support | Limited | Available with payment processors |
Fiat money: Government-issued currency, such as the US dollar, that is not made with or backed by a specific commodity, such as gold.
One of the most significant differences between cryptocurrency and credit cards is the former’s volatile value. While credit cards can also be subjected to currency fluctuations, the regulated nature of fiat currencies makes credit cards a more stable payment method than crypto.
On the other hand, using cryptocurrency to accept payments is far less expensive than credit cards because it is not as heavily regulated.
How Cryptocurrency Payment Transactions Work
Cryptocurrency wallets are very similar to your digital wallets, so if you already have Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, CashApp, or Venmo as a payment method, then chances are, you won’t find having crypto payments difficult.
Here’s an example of a typical cryptocurrency transaction:
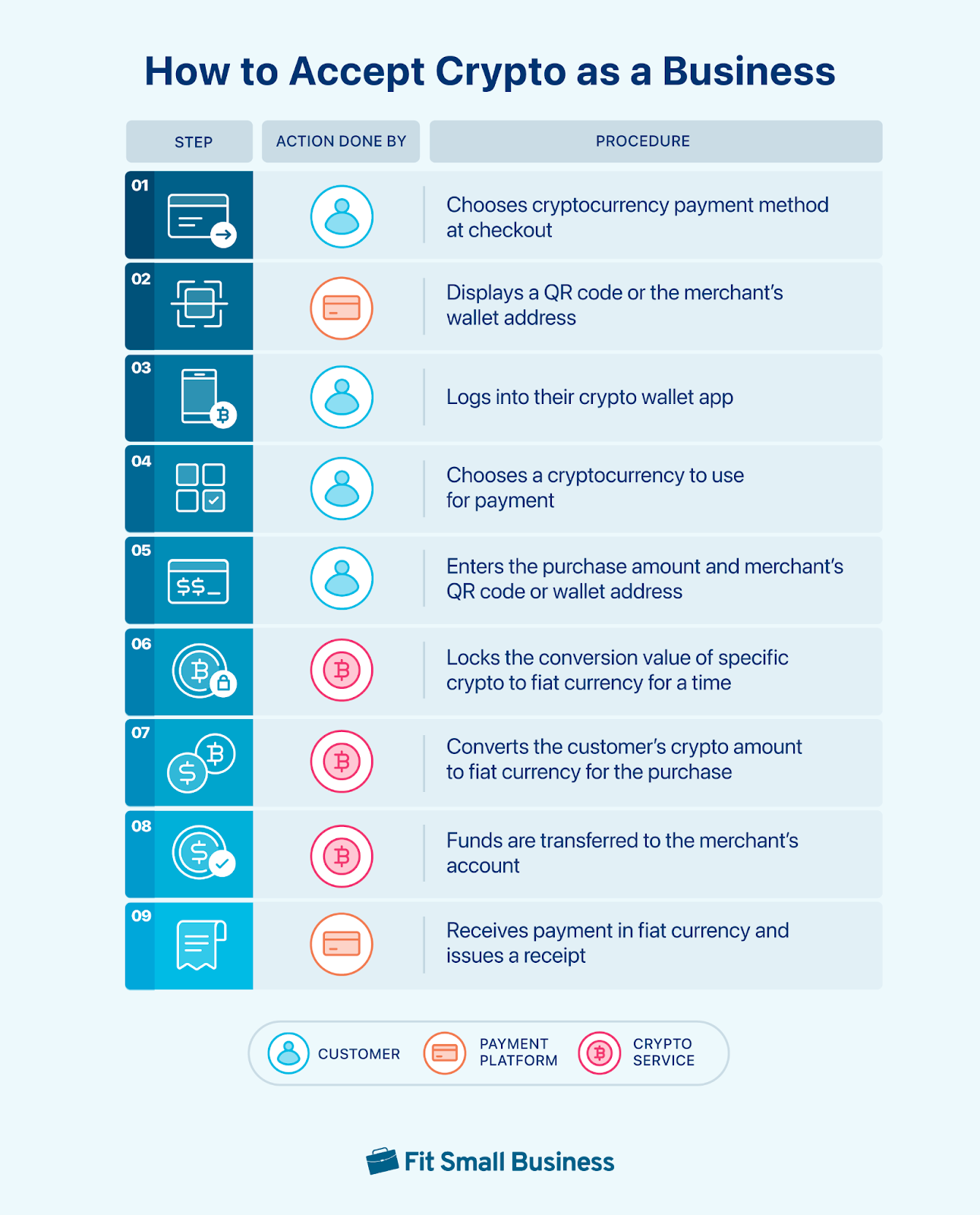
Alternatively, a merchant with its own cryptocurrency account linked to a payment processor, can set up the process so that there is no need to convert the crypto payment into fiat currency. The crypto payment can be added to the merchant’s cryptocurrency balance.
Costs of Accepting Crypto Payments
The standard payment processing transaction fee for crypto payments is about 1%, making it much more affordable than the average credit card processing fee (3%) and even some ACH direct deposit fees (1%–1.5%).
Some providers offer even lower transaction fees (CoinPayments is just 0.5%), while others add a network fee on top of the 1%. Potential additional fees include currency conversion fees and withdrawal fees.
Here are some examples:
Cryptocurrency Platform | Merchant Fees | Accepted Cryptocurrency Types |
|---|---|---|
 | From 1% + 25 cents–2% + 25 cents | 15 including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin |
1% | 150+ including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin | |
$0 | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cronos, USD Coin |
Step 2: Set Up a Crypto Wallet or Crypto Gateway
You first need to decide whether you want to receive your crypto payments as cryptocurrency or fiat money. Once you have chosen a platform, you’ll need to go through the steps to create and set up your account. Specific steps vary depending on the provider, but you’ll likely need to start by downloading the software, whether that’s from a desktop or mobile app.
The general guideline for choosing the type of cryptocurrency app is as follows:
You need a: | If you: |
|---|---|
Crypto Wallet | Want to collect, store, and use cryptocurrency for your business or personally |
Crypto Payment Gateway | Want to accept crypto payments but have them converted to traditional fiat money |
Many popular solutions, like Coinbase and BitPay, have both wallet and gateway functionality.
You will need a crypto wallet to collect or store cryptocurrency. You do not need a separate crypto wallet if you plan on using a gateway to transfer the funds from your sales into US dollars or similar currency before depositing them into your business checking account.
There are three kinds of crypto wallets; you can use one or multiple:
Description | Responsible for security | Platform features | |
|---|---|---|---|
Hosted wallets | Out of the box app | Wallet service provider | Buy, store, trade, and sell crypto |
Self-custody wallets | Customizable software | Merchant | Buy, trade, sell, stake, lend, borrow, and more |
Hardware wallets | Secure, physical device | Merchant | Buy, sell, trade, lend, borrow, and more |
Hosted wallets are “out-of-the-box” solutions that require minimal setup and technical skill. As such, it’s also the most common type of crypto wallet and a great entry-level option.
Self-custody wallets provide the software you need to store your crypto assets, and gives you more flexibility and control over your account. However, the merchant is responsible for the security, so if you forget your crypto credentials, there’s no way to recover them—or your assets
Hardware wallets are the most secure way to maintain your crypto wallet, but it requires possessing a physical device that you’ll have to keep track of and store securely.
Some of the most popular crypto wallet platforms include:
- Coinbase: One of the most popular and reliable digital wallets that is both secure and beginner-friendly
- MetaMask: Another popular option ideal for those using Ethereum
- MyEtherWallet: A customizable open-source platform that can be great for businesses with budget
Did you know? PayPal consumer apps have their own crypto wallet allowing customers to pay for purchases using crypto currencies. With over 400 million active accounts, PayPal’s adoption of crypto is a huge boost in getting this type of payment method to become more mainstream.
When choosing your crypto wallet, consider which types of cryptocurrencies it works with. Bitcoin is, by and large, the most popular cryptocurrency, with around 83% of US consumers alone owning some form of this currency.
Other players are also emerging; the more currencies you can cover, the more sales you’ll likely capture. You should also consider the level of crypto/bitcoin payment security that wallets provide.
Cryptocurrency payment gateways function similarly to crypto wallets, but with added functionality. They typically come with a hosted or noncustodial wallet, which stores funds from customer purchases made with crypto until you choose to convert those funds into fiat money like US dollars and transfer them to your bank account.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Easier to set up | Less secure than crypto wallets |
| Provides conversion loss protection | Costs more |
Knowing how to accept cryptocurrency payments through gateways is convenient if you don’t want to invest a lot of time or energy delving into the world of crypto.
Gateways also mitigate risk, as you are paid the market rate at the time of the transaction. If the value of the cryptocurrency decreases while the transaction is being verified, you won’t lose out.
On the other hand, using a payment gateway in your cryptocurrency transaction introduces a third party, which by nature, crypto is meant to avoid. Adding in a third party also comes with additional fees.
Transaction fees and markups are typically higher if you use a gateway versus a crypto wallet. While standard crypto transaction fees are around 1%, some gateways charge as high as 5% for currency conversion.
Some of the most popular crypto payment gateways include:
- Coinbase Commerce: Connects with Coinbase wallet and works with popular ecommerce platforms such as Shopify and WooCommerce
- BitPay: Accepts 13 cryptocurrencies on your website, through invoices or email, and in-person through the BitPay Checkout app
- Coinspaid: Gateway that accepts over 30 cryptocurrency payment options and can deposit funds as US dollars, euros, and British pounds right into your bank account
Step 3: Integrate Crypto Payments into Your Online Checkout
Now that you have your crypto wallet and/or gateway set up, it’s time to add crypto into your website.
How to Integrate Crypto Wallets
You can integrate your crypto wallet on your website and enable it as a payment option in the checkout process. There are two main approaches to doing this.
1. Open source API: If you use a crypto platform that offers an open source API, as you’ll often find with self-hosted wallets, you can integrate this with your website using custom HTML code. The upside here is that you have more control over the look, feel, and functionality, though it requires technical resources that not every small business can access.
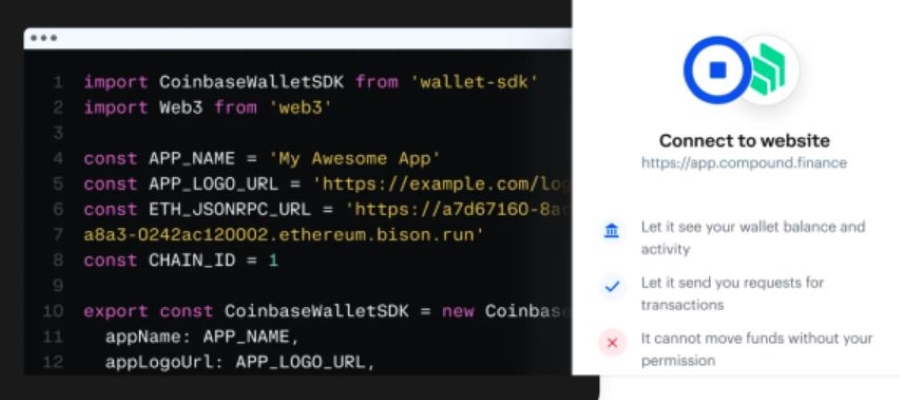
2. Plugin/app: Depending on your ecommerce platform, an integration may be available. Crypto integrations make it easy to set up because they cover all the technicalities for you. It’s simply a matter of downloading the plugin or app and installing it on your website.
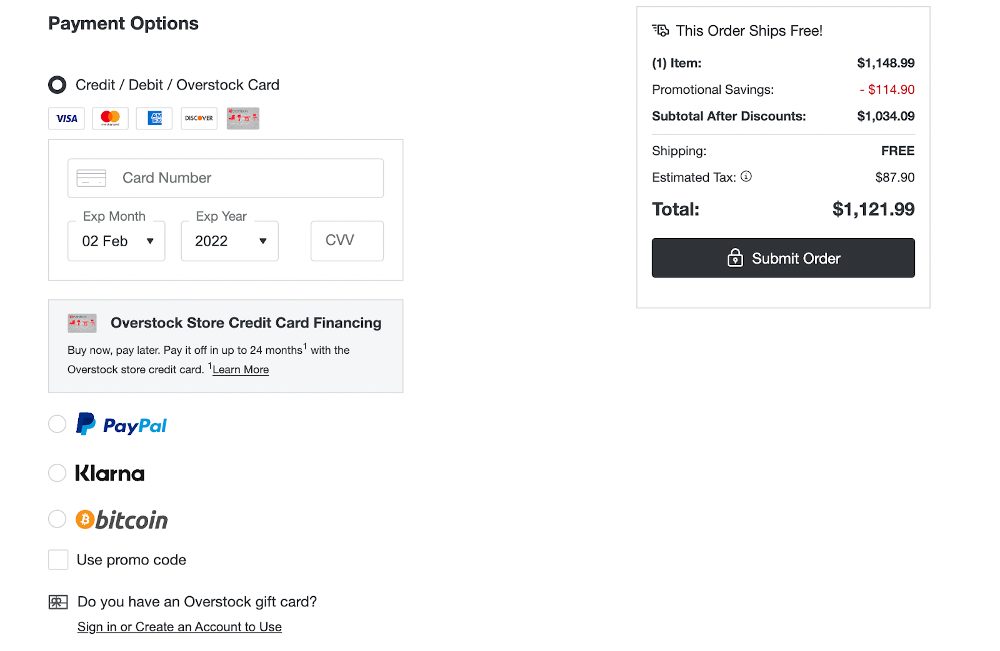
How to Integrate Crypto Payment Gateways
For your online stores, the ease of adding a crypto payment gateway will depend on the ecommerce platform you use. For example, while both WordPress and Shopify come with built-in integration for cryptocurrency payments, Shopify has an easier step-by-step guided setup process for crypto payment integration compared to WordPress.
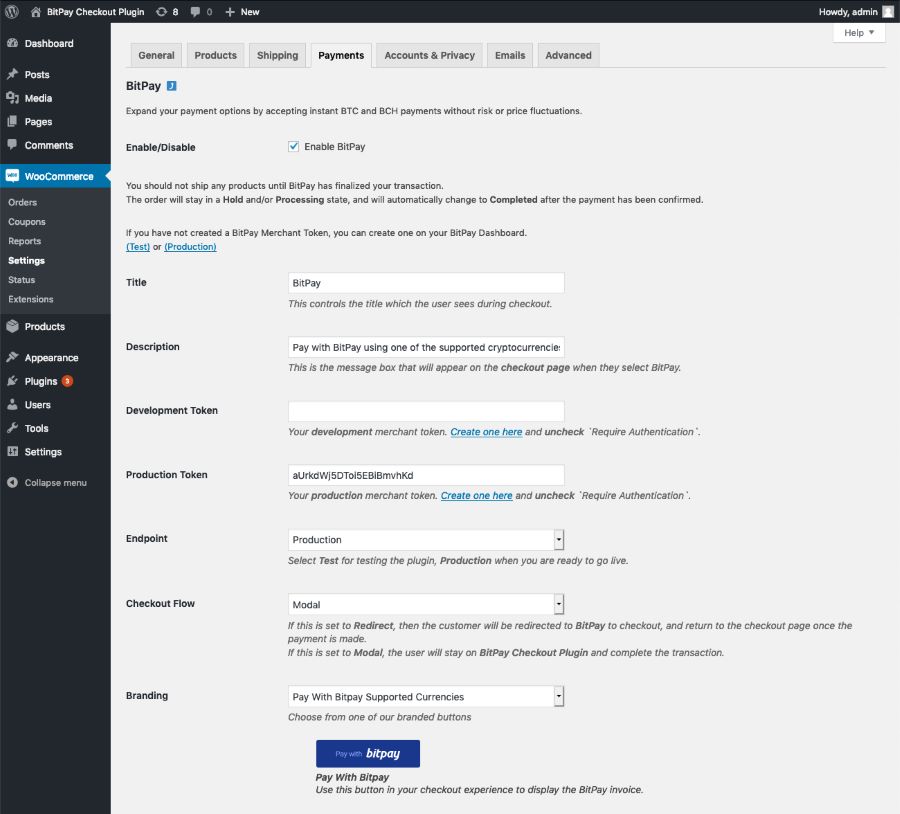
You can integrate BitPay to your online store through a WooCommerce plugin that’s readily available in WordPress. (Source: WordPress)
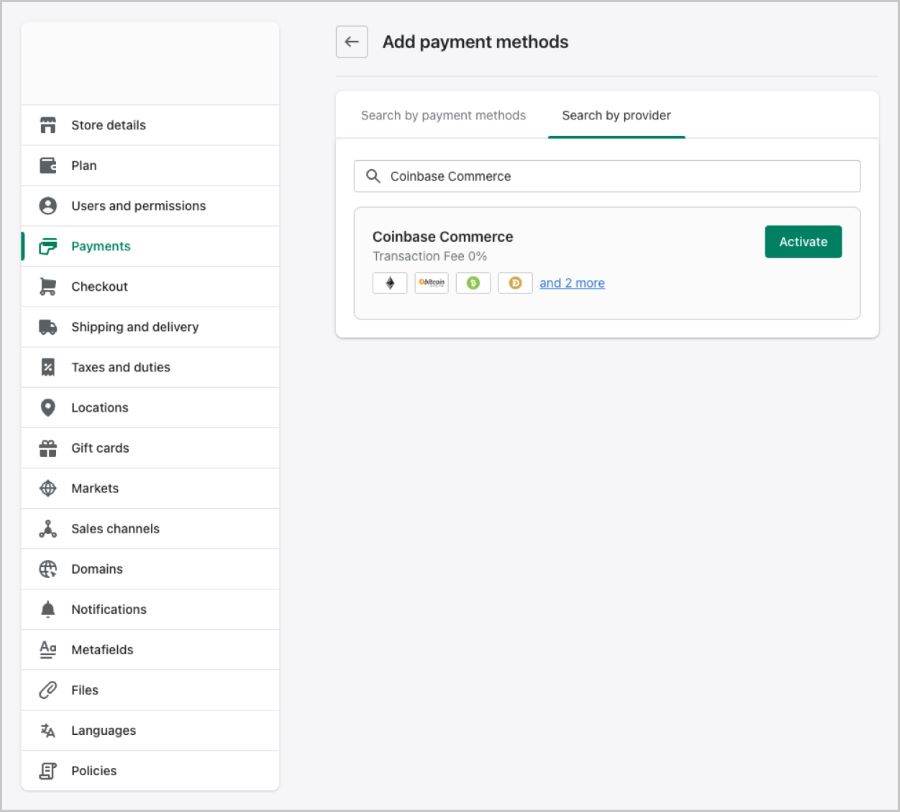
Shopify also uses plugins to integrate crypto payment methods, but its guided activation process is much easier to follow. (Source: Coinbase)
Step 4: Offer In-person Crypto Payments
In-store shoppers can also reap the benefits of being able to pay in cryptocurrency—if you let them. There are a number of ways to use some of the platforms mentioned earlier to handle in-person crypto payments.
Consider adding a crypto-compatible QR code scanner or NFC terminal for in-store checkout. If you use a mobile POS, you may also be able to integrate crypto payments with your existing system—if it supports them. Coingate, for example, comes with a full crypto/bitcoin POS system.
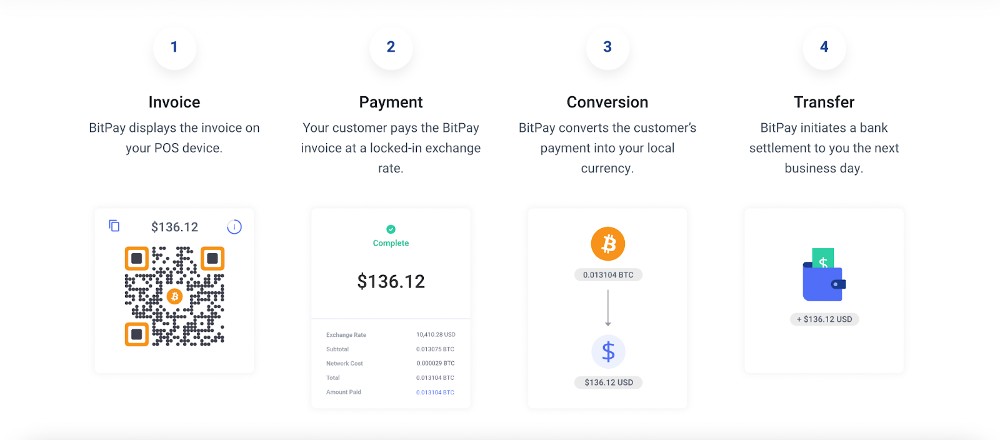
Use the BitPay Checkout app to display QR payment links for in-person payments. (Source: BitPay)
The Latest in In-person Crypto Payments
Though crypto is still relatively new, it has been on the payments industry’s radar for some time, and leading payment services providers are developing methods to allow merchants to accept cryptocurrency payments.
- Square users can now receive Bitcoin payments through the Cash App’s latest integration.
- The recent upgrade to PayPal’s payment app now allows users to hold and then convert crypto to USD to pay for purchases.
- Brick-and-mortar shops can now integrate their POS systems with NOWPayments to start accepting crypto for in-person transactions.
- Coingate is launching a POS app that supports more than 70 cryptocurrencies.
Pros & Cons of Accepting Bitcoin & Other Crypto Payments
You could argue that accepting cryptocurrency can boost average transaction value and encourage shoppers to make larger purchases and spend more money, though the data varies depending on the demographic, such as the consumer’s age.
That said, there are several benefits and challenges that are more straightforward when it comes to accepting crypto payments in your small retail business.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Capture more sales by accommodating more payment types | May be subject to capital gains tax |
| Fast and easy online transactions, which helps to get better conversion rates | Limited regulation |
| Low payment processing fees; competitive with other payment types | Volatile and unpredictable valuation and exchange rate |
| No risk of chargebacks | Susceptible to cybersecurity threats |
| Allows for simplified international selling and currency conversion | Requires additional tech stack and setup |
In addition to appealing to crypto owners, since cryptocurrency is unregulated, it appeals to cannabis and other high-risk businesses that banks and traditional merchant accounts decline to work with.
See our picks for the best crypto-friendly business banks.
State of Cryptocurrency Adoption
Consider the following news on the state of cryptocurrency adoption before deciding to add a crypto payment method:
- Ethereum (ETH) leads cryptocurrencies under the decentralized Finance (DeFi) and is projected to reach 22 million users by 2028.
- However, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is currently looking into classifying Ethereum as a security instead of a digital asset which will result in delisting ETH and losing 20% of the cryptocurrency market.
- Thirteen percent of cryptocurrency owners acquired crypto for the purpose of making purchases online.
- The issue of cryptocurrency in the US is highly debated by legislators, causing adoption into the retail industry to slow down.
- Some crypto currencies are issued by central banks. At present, 11 of the G20 member countries (which includes Brazil, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea) have already launched a pilot of their own Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs).
CBDCs are government-issued digital currencies issued by central banks, so this type of crypto is more stable than others but at the same time, more regulated.
Meanwhile, DeFis are composed of digital currencies and other financial products that use a decentralized blockchain network. Here, transactions are faster because there are no intermediaries like the central bank, but the currency values are less stable.
Accepting Crypto as a Business Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To accept cryptocurrency payments as a business, you need to set up a cryptocurrency account, then integrate your cryptocurrency account to your online store or in-store POS system using a crypto wallet or payment gateway.
Generally, yes. Cryptocurrency payments are safe from chargebacks so you don’t need to worry about fraudulent transactions or chargeback fees. Also, during transactions, there are crypto payment gateways that offer a number of ways to protect your cryptocurrency from changes in valuation during transactions.
The average transaction fee for accepting cryptocurrency payments is 1%, which is considerably lower than credit card processing fees.
Businesses accepting cryptocurrency payments are required to report income earned based on the fair market value of the currency at the time of the transaction. Note however, that if you hold the crypto currency instead of converting it to fiat currency right away, the IRS may also require you to declare any capital gains (increase in the value of the cryptocurrency) earned when you eventually sell the crypto.
Bottom Line
While cryptocurrency is still largely viewed as a futuristic trend that’s not here to stay, others are going all-in on the new digital currency. Data shows that nearly half of US merchants have started accepting cryptocurrency as a payment method in 2022, yet only a very small portion of these are small businesses.
Regardless of which camp you’re in, learning how to accept bitcoin payments and other cryptocurrency can help boost conversion rates and keep your business ahead of the competition. Cryptocurrency is becoming more widely accessible, and early adopters are uniquely positioned to reap the benefits early on.