Ethical consumerism involves buying products and services produced in a way that minimizes social or environmental harm, while avoiding purchases that could negatively affect society or the environment. This approach has become a key aspect of today’s retail landscape, representing a significant shift in consumer values and priorities.
Ethical consumerism for retailers is a vital element to consider when planning your sourcing, branding, marketing, and internal operations to align with evolving consumer expectations. In this article, we’ll provide a detailed list of the causes consumers care about, what you can do, and how your business can engage with ethical consumers.
What Is Ethical Consumerism?
At its core, ethical consumerism is about making purchasing decisions based on ethical principles—such as fair trade practices, environmental sustainability, and social responsibility. It’s a type of activism that allows shoppers to “vote with their dollar” to drive positive change.
Consumers are increasingly mindful of their purchasing impact, seeking ethical products that align with their values like sustainability, fair labor, and animal welfare. Adapting business models to these ethical considerations is not just about meeting demand, but also about contributing to a more responsible and sustainable marketplace.

Buying from small and local businesses is a notable form of ethical consumerism, with 71% of shoppers reporting that they go out of their way to support local businesses.
Why Does Ethical Consumerism for Retailers Matter?
In a landscape where 82% of consumers prefer brands that mirror their values, ethical consumerism is vital for businesses. This retail trend demands a commitment to ethical sourcing, transparency, and environmental stewardship. Retailers embracing these values not only contribute to sustainability but also attract a loyal, value-driven customer base.
However, as 72% of consumers are skeptical about brands overstating their ethical efforts, authenticity in promoting ethical standards is crucial. Retailers must be transparent and trustworthy in their practices to build consumer confidence.
The digital age has empowered consumers to easily research products and company ethics on platforms like Ethical Consumer, The Green Directory, and People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA). Similarly, the impact of social media has caused Millennial and Gen Z shoppers to frequently share their favorite ethical retailers and publicly criticize brands they don’t support due to their ethics.
Ultimately, today’s consumer looks beyond the product—scrutinizing sourcing, labor conditions, and environmental impact. This informed approach is shaping consumer expectations, making ethical consumerism a core factor in business operations.
Benefits of Ethical Consumerism for Retailers
Adopting ethical consumerism allows retailers to align with current market trends and contribute positively to global welfare, but it also serves to strengthen your brand and your business as a whole. Here’s how:
- Enhanced Brand Reputation and Trust: Adopting ethical practices improves a retailer’s brand image, making it more attractive to consumers who value transparency and corporate responsibility.
- Increased Customer Loyalty and Retention: Ethical consumerism fosters strong connections with customers, leading to repeat business and word-of-mouth promotion from satisfied customers.
- Attracting a Broader Customer Base: By embracing ethical values, retailers can appeal to millennials and Gen Z, expanding their market reach to include these increasingly conscious consumer groups.
- Differentiation in the Market: Ethical practices set retailers apart from competitors, attracting consumers who seek brands that align with their personal values.
- Resilience and Long-term Sustainability: Ethical approaches, such as sustainable sourcing, can lead to a more resilient business model, reducing risks and costs related to resources and environmental regulations.
- Positive Workplace Environment: Fair labor practices and a company culture that aligns with the ethical values shared by employees create a better work environment, enhancing employee satisfaction and retention.
- Positive Impacts: Retailers committed to ethical practices contribute to societal and environmental well-being.
- Innovation and Adaptability: The pursuit of ethical consumerism drives innovation in product development and operational efficiency, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability.
Factors That Ethical Consumers Care About
Ethical consumers today are discerning and informed, looking beyond mere products to the values and practices of the companies they support. Here’s a comprehensive look at the key factors they consider:
Animal Rights & Cruelty
A significant number of consumers, especially those interested in veganism and cruelty-free products, base their buying decisions on animal welfare and ethical treatment. By prioritizing these values in their products and practices, businesses can not only attract a niche audience but also appeal to the broader public.
- According to the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA), over 70% of stores carrying humane products report increased sales over three years
- 45% of stores that stock humane products have done so for over two years, indicating steady demand
- About 30% of supermarket managers show interest in expanding their inventory to include more products that emphasize the humane treatment of animals
This concept encompasses the overall treatment of animals in product creation. Even if a business deals in animal-derived goods, making efforts to prioritize or improve animal welfare can attract consumers who are concerned about humane treatment. Examples include sourcing materials from suppliers who use humane slaughter practices and donating to wildlife conservation funds.
Many consumers either prefer or exclusively buy products made from cruelty-free, synthetic, or plant-based materials—especially in industries like fashion, beauty, and food. Businesses address this by obtaining certifications like cruelty-free or vegan, providing transparency in their sourcing practices, and offering alternatives to animal products.
Some popular brands express their values and appeal to ethical consumers by building their business around animal-free products, such as NuReveal Skincare and vegan footwear brand Taylor + Thomas. Other brands, like Amy’s Kitchen, offer vegan or vegetarian options to supplement their usual offerings, diversifying their product lines to cater to a wider range of ethical consumer preferences.

Amy’s Kitchen sells vegan versions of its popular non-vegan products.
(Source: Amy’s Kitchen)
The practice of testing products on animals to ensure safety for human use is most prevalent in the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries and often causes significant animal suffering.
Businesses can avoid animal testing by using alternative testing methods, such as in-vitro (test tube) experiments or computer-simulated models. These alternatives not only prevent harm to animals but are also often more cost-effective and reliable.
Factory farming, or intensive animal farming, involves raising large numbers of animals in confined spaces to optimize production and reduce costs. This method often leads to poor animal welfare and potential human health risks due to practices like the overuse of antibiotics and inadequate living conditions.
Ethical consumers typically look for products from free-range, pasture-raised, or organic farms. However, the definitions of these labels can vary, ranging from basic space requirements to access to natural environments, and informed buyers are increasingly looking for truly ethical products. Retailers can meet this demand by sourcing from farms with humane practices and transparent operations, alongside recognized, third-party-backed certifications.
Environmental Impact
As environmental concerns gain prominence, there has been a significant shift toward eco-friendly shopping habits. Seventy-seven percent of consumers now believe that sustainability is important when selecting products to buy, and are seeking out retailers who actively reduce their carbon footprint. As a result, many brands have adapted by incorporating green practices into their operations, making it important for businesses to improve their environmental efforts to keep pace with market trends.
Public awareness of climate change is growing, and shoppers are seeking retailers committed to reducing their carbon footprint, aiming to also reduce their own through the products they use. Businesses can help by adopting energy-efficient practices, optimizing logistics to decrease fuel usage, and engaging in carbon offsetting initiatives (such as investing in renewable energy projects or reforestation).
Renewable energy, sourced from natural elements like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, aids in reducing dependency on fossil fuels and addressing climate change. These alternative forms of energy preserve natural resources and minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
Opting to install renewable energy systems or purchase green energy demonstrates a strong commitment to sustainable practices, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Waste reduction and recycling are increasingly important to consumers who are aware of the impact of waste on landfills and ecosystems. They look for retailers that use recycled materials, design items for easy recycling or reuse, offer products with minimal or reusable packaging, or take part in the circular economy by selling pre-owned goods. These practices not only conserve resources but also resonate with eco-conscious consumers and make for highly visible sustainability efforts.

Grocery retailer Ocado labels its products to showcase its certifications and recyclable content.
(Source: B&B Press)
For businesses, water conservation mostly involves minimizing water usage in production processes, particularly in industries with high water demands, such as textile and agriculture. Retailers can contribute by using water-saving technologies (like low-flow fixtures) and sourcing from suppliers who employ water-efficient practices.
Pesticides, used widely in agriculture and certain manufacturing processes, pose risks to ecosystems, wildlife, and human health. Reducing or eliminating pesticide use involves sourcing materials produced with fewer or no chemical pesticides and promoting organic or low-impact farming practices. Retailers focusing on low-pesticide or pesticide-free products can cater to both eco-minded consumers and health-conscious shoppers.
Company Ethos & Business Practices
The spotlight on companies’ core values and business practices is more intense than ever. Consumers are increasingly aligning their spending with their personal beliefs, compelling businesses to adapt and redefine their strategies.
Businesses’ political practices, including lobbying efforts and donations, are under increasing scrutiny from consumers. Many are choosing to support businesses whose political activities and contributions align with their own values and beliefs.
For retailers, being open about their political stances or affiliations can create a strong bond with like-minded consumers, but it also runs the risk of alienating others. As a result, some brands choose to remain neutral, while others actively engage in political discussions and action, aligning their brand with specific causes or movements that resonate with their target market. In contrast, companies that take an opposing approach often face criticism and backlash, causing a negative reputation and lost sales.
Example In The News: Japanese Beauty Brand DHC Under Fire Following CEO’s Discriminatory Comments
As Asian beauty products gained worldwide popularity, Japanese skincare brand DHC faced widespread boycotts following comments from its CEO that were regarded as nationalist and racist toward Koreans.
The public perception of a company’s leadership is becoming an important factor for shoppers, especially in terms of pay equity.
Ethical consumers care about how businesses compensate their top executives, especially when it comes to the stark contrast between executive salaries and those of regular employees. This issue has gained more attention in recent years, with examples like Amazon drawing criticism for the immense wealth of its CEO compared to the challenging working conditions experienced by its lower-level employees.
In the realm of retail and ecommerce, marketing strategies play a pivotal role in influencing consumer behavior. However, some marketing tactics can be deemed irresponsible, primarily when they exploit consumer insecurities or misrepresent the true nature of products. Two notable forms of irresponsible marketing are:
- Greenwashing: This involves companies falsely advertising their products or policies as environmentally friendly or sustainable, when in reality they may not meet these claims. Greenwashing misleads consumers who are making conscious efforts to choose eco-friendly products, undermining their trust and the genuine efforts of truly sustainable brands.
- Insecurity Marketing: This strategy, commonly in the beauty and health sectors, links personal success and happiness to appearance, promoting products as fixes for perceived flaws. It often leads to negative self-image and unrealistic standards, seen in advertising that uses extremely thin models or objectifies individuals. For small business owners in these sectors, focusing on positive, inclusive marketing is vital.
Employee Treatment
Many ethical shoppers look at how businesses value and support their workforce, with an emphasis on fair wages, healthy work environments, and equitable treatment. By promoting fair employee treatment, businesses not only foster a positive workplace but also strengthen their appeal to considerate customer bases.
Example In The News: Nike is facing a new wave of anti-sweatshop protests
Many consumers still associate Nike with its past allegations of sweatshop and labor rights violations—including wage theft, harsh working conditions, and factory closures—which derailed the brand’s image in the late 1990s and again in 2017.
Fair working conditions are essential for the well-being of employees and are a key focus for ethical consumers. This includes safe work environments, reasonable work hours, and the absence of exploitative practices.
Consumers are increasingly aware of and concerned about the conditions under which the products they purchase are made. Retailers who ensure and openly communicate their commitment to maintaining fair working conditions in their operations and supply chains can gain the trust and loyalty of a growing base of socially conscious consumers.
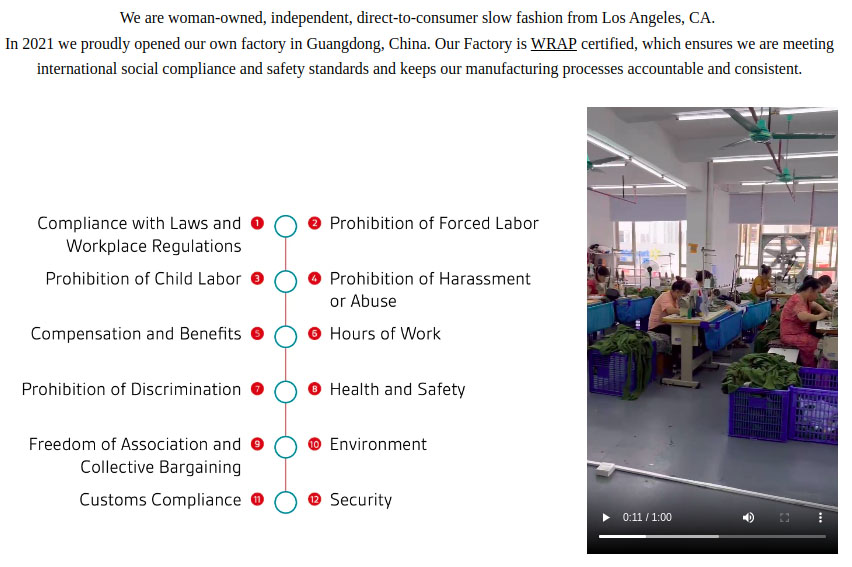
LA-based clothing retailer Fashion Brand Company communicates its commitment to ethical treatment of employees on its website, complete with a video tour of its manufacturing facility.
(Source: Fashion Brand Company)
Living wage refers to a salary that allows employees to afford a decent standard of living, covering basic needs such as housing, food, healthcare, and education. Ethical consumers increasingly favor retailers who ensure their workers, both domestically and in supply chains abroad, receive wages that meet these standards.
Retailers committed to paying living wages are often viewed as more responsible and caring, attracting consumers who prioritize the well-being of workers in their purchasing decisions. This approach not only fosters a positive company image but also contributes to a more equitable and sustainable economy.
Diversity and inclusion within companies are not only a matter of social justice but also a point of evaluation for ethical consumers. Ensuring a workforce that includes a wide range of individuals from various backgrounds and providing equitable treatment and opportunities for all employees are key factors.
Brands that actively promote diversity and inclusion are often seen as progressive and socially responsible, appealing to consumers who value equality and representation in the businesses they support.

Labels distinguishing businesses as “Women Owned” and “Black Owned” are common ways for brands to demonstrate how they empower underrepresented entrepreneurs and promote diversity in the marketplace.
(Source: Onyx Brands)
Unions play a critical role in protecting workers’ rights, advocating for fair wages, and ensuring safe working conditions—making them an important aspect of worker treatment in the eyes of ethical consumers.
Retailers that recognize and support their employees’ rights to unionize, or at least maintain a neutral stance on union activities, are often viewed more favorably by consumers who are concerned about workers’ rights.
Example In The News: Costco takes responsibility for workers’ decision to unionize
Costco’s acknowledgment of a “failure on their part” in response to workers’ unionization efforts signals that the company recognizes the importance of fair employee treatment and the impact it has on its reputation among consumers.
Supply Chains
Supply chains are crucial in retail and many other business operations, with every stage holding substantial ethical weight. These steps offer chances to either make a positive difference in communities or engage in less ethical practices, risking consumer trust and loyalty. Understanding these dynamics is key:
Fair Trade practices are at the forefront of ethical sourcing, ensuring that goods and materials are produced in conditions that respect workers and the environment. This approach emphasizes fair payment, safe working conditions, and sustainable practices for producers, often in developing countries.
Consumers are increasingly opting for Fair Trade-certified products, knowing these purchases help improve workers’ lives and their communities. Retailers who adopt and promote Fair Trade practices not only support ethical production standards but also align with the values of a growing segment of consumers who are conscious about the global impact of their purchases
Local sourcing means obtaining products and materials from local producers to minimize the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation. This practice supports local economies, reduces emissions, and often results in fresher, more sustainable products. By adopting local sourcing, retailers can reduce their environmental impact and appeal to consumers who value supporting local businesses.
The sourcing of raw materials is a key aspect of ethical retail practices, with shoppers becoming increasingly aware of the origins of the materials used in the products they buy—such as whether they’re sustainably sourced or contribute to environmental degradation.
Retailers focusing on ethically sourced raw materials, such as organic cotton, recycled metals, or sustainably harvested wood, cater to consumers who are concerned about the environmental footprint and ethical implications of their purchases.
Supporting Small & Local Businesses
Events like Small Business Saturday and busy farmers markets around the country prove that consumers are devoted to supporting small and local businesses. This commitment comes from a number of factors, largely rooted in the desire to enrich their own communities. Many shoppers even willingly pay more for local products, showing that it’s a worthy cause to pursue when it comes to ethical consumerism.
Supporting local businesses is a key factor in strengthening economies at a community level. For consumers, this means prioritizing goods manufactured within their own country or region, which is particularly relevant for US consumers with ‘Made in America’ products.
This approach helps sustain nearby jobs and industries and is often seen as a mark of community support. Retailers who stock and promote locally made products appeal to a broad base of consumers who value the quality, authenticity, and the idea of contributing positively to their local community and national industries.

The FTC requires all products carrying the classic ‘Made In America’ label to go through their final assembly or processing in the United States and rely on domestic sources for significant processing and ingredients.
(Source: Thompson & Associates)
The practice of promoting local artisans and craftspeople is an impactful form of community development commonly used by businesses and helps attract customers as well. It not only helps preserve local crafts and cultural heritage but also boosts the local economy by providing livelihoods to local creators.
Consumers are increasingly drawn to unique, handcrafted products that carry a story and a touch of personal craftsmanship.
Consumers and businesses alike are aware that fair competition practices are essential in ensuring a healthy market where small and local businesses can thrive alongside larger corporations. This involves advocating for and adhering to regulations that prevent monopolistic practices and ensure a level playing field for all businesses.
Example In The News: FTC Sues Amazon for Illegally Maintaining Monopoly Power
Amazon’s repeated illegal actions hinder fair competition, giving it the power to raise prices, reduce product quality, and limit innovation—leading to increased government scrutiny and a negative response from consumers.
How to Improve Your Business’ Ethics and Attract Ethical Consumers
In today’s market, ethical consumers don’t just value transparency, but a genuine effort towards ethical improvement. More and more, savvy consumers are doing their homework, and retailers who provide clear and honest information are rewarded with their business and loyalty.
Even retailers with limited operational flexibility or tight budgets can take meaningful steps to improve their business ethics and effectively communicate these practices to consumers. Here are some actionable strategies:
- Small Steps in Sustainability: Start with small, budget-friendly initiatives. This could be as simple as reducing energy usage in stores, improving recycling methods, or opting for more eco-friendly packaging.
- Labeling: Showcase your sustainability efforts with clear and effective branding. For instance, prominently feature eco-friendly packaging on product labels, demonstrating your dedicated commitment to environmental responsibility.
- Community Engagement: Participate in community events and collaborations with local businesses, and use this as part of your brand’s story in marketing materials, on your website, and in social media posts. This showcases a commitment to local welfare and can be a strong part of your brand’s identity.
- Ethical Marketing and Brand Messaging: Shift to marketing strategies that focus on positive, ethical messages. Use social media, email newsletters, and website content to convey your brand’s ethical stance and values.
- Support Employee Well-being: Treating employees well and ensuring fair working conditions can often be a matter of policy and culture rather than budget. Simple steps like ensuring fair work hours, fostering a respectful work environment, and recognizing employee efforts can go a long way in building a positive brand image. You can also openly share stories or testimonials from employees to showcase the company’s positive work environment.
- Ethical Sourcing with Certifications: Where possible, obtain certifications for ethical sourcing (like Fair Trade) and display these certifications on product packaging, your website, and in marketing materials to validate any ethical claims.
- Customer Feedback and Involvement: Engaging with customers to understand their values and feedback can be a cost-effective way of aligning business practices with consumer expectations. This can be done through social media, surveys, or community forums.
- Educate and Inform: Use your online presence to educate consumers about ethical practices, sustainability, and how consumer choices can make a difference. Blog posts, social media content, and marketing campaigns can discuss the importance of ethical consumerism and how your business is contributing.
- Leverage Storytelling in Branding: Share your journey towards ethical practices through storytelling in marketing and branding. This could include the challenges faced, the successes achieved, and the impact on the community and environment.

“On their website or main page, where their statement is loud and clear, and also as part of the focus of the company. On my website, I clearly state that 10% of my sales at the end of the year go to a specific charity and that all of my food is vegan on purpose. It’s a good thing to advertise, as more people will gravitate toward what they believe is building a better and safer future.”
- Alyssa Dufresne, Dufresne’s Vegan Treats
Bottom Line
Shoppers are more motivated than ever to consider ethics in their buying decisions, making ethical consumerism for retailers a critical component to work into your business strategy. By doing so, brands can not only attract a loyal customer base but also align their brand with their own values and create a positive impact.