Upselling is a sales technique or process of suggesting a higher-valued product or service to new or existing customers at a point of sale. The idea is that a customer is already in the buying mindset and could be easily convinced to upgrade to something better at that moment. This technique is generally used just before, during, or slightly after a purchase.
Upselling helps drive overall business growth by directly increasing sales revenue. In fact, most sales professionals practice this and say it accounts for 21% of their company revenue. Here, we define upselling, teach you how to facilitate it, and outline best practices that you can employ in your sales activities. We also provide examples and tips on how to leverage sales tools to support your sales campaigns.
Upselling vs Cross-selling
While both upselling and cross-selling are used to obtain higher value from a sales transaction, they do so using different approaches. The upselling process focuses exclusively on a better version of what the customer is already purchasing. Cross-selling, on the other hand, recommends additional, complementary products or services to what’s being purchased, such as when a sales associate recommends also buying a smart device with a new TV.
How to Upsell in 4 Steps
Around one-third of global business-to-business (B2B) leaders prioritize selling a higher-value product in the buyer journey. It’s safe to say that sales reps can follow the example of these leaders and take time learning the art of this process. Follow these four steps to successfully execute your upselling strategies.
Start the upselling process by giving the customer the product or service that they originally intended to buy. Focus more on the customer than on your products. Find out what pain points they are trying to address with their purchase. Ask them why they need the product and what results they expect from it.
For example, a customer comes in looking for a brand new laptop. During your conversation, you learn that they want a laptop that’s suitable for watching movies and playing video games. You present them with several options that fall within their desired price range.
Now that you know why your customer is buying a product, you are now in a better position to find a good alternative for them. Remember that the solution that you’ll pitch should still provide genuine value to them by addressing their pain points. Find an alternative that has better quality but does not differ greatly from their original purchase. This is also the stage where you’ll decide to cross-sell.
Continuing the scene from the previous step, you remember that the customer wants a laptop for movies and video games. You conclude that the customer needs a product with ample storage and good graphics. At this point, you decide to recommend a higher-priced device with more storage capacity and a better graphics card.
Here, you’ll begin pitching the upgrade to your customer. Refer to your previous conversation and explain why the alternative is more beneficial to them than their original purchase. If your recommendation is well-aligned with their needs, you will be able to earn the customer’s trust, and they will be more receptive to your suggestions.
In our current example, you can mention that the customer might need to pay for additional storage or a new graphics card after a year to better accommodate their movie and gaming needs. Explain that they could save money by purchasing a higher-quality laptop now.
If you have properly explained the benefits of a higher-value product, you should be able to convince the customer to buy it instead of their original intended purchase. However, whether they go for the upgraded product or their original choice, thank them for their purchase. Then, follow up at a later date to see if they are satisfied with their purchase or if you can help them with anything related to the said product.
Keeping in touch with your past and existing customers can eventually help you bring in more revenue. In fact, 72% of revenue comes from existing customers, and only 28% comes from new customers. That said, take time to build a relationship with your customers and ask for their contact information so that you can send them satisfaction surveys, promotional offers, and even referrals.
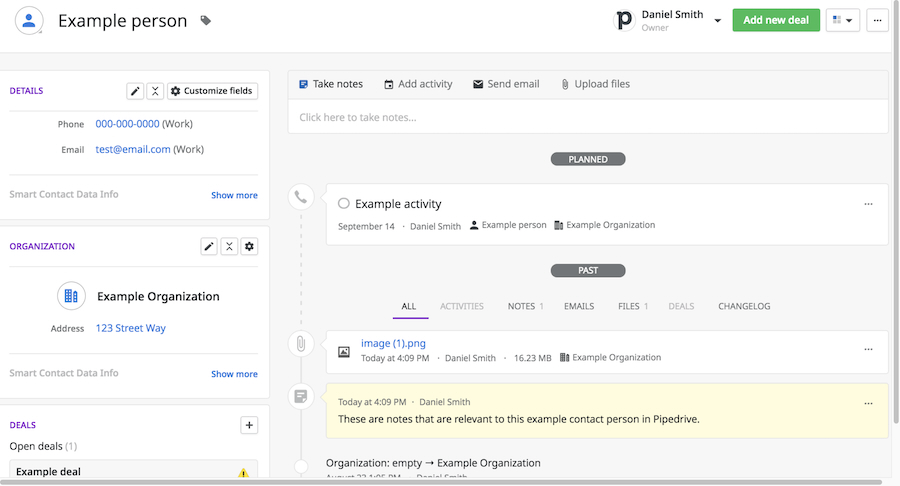
Pipedrive lead profile with notes and activity tracking (Source: Pipedrive)
Upselling Best Practices
Now that you have an understanding of upselling, it’s time to learn how to use it effectively. Sales reps need to tread carefully with this technique and make sure proper sales training is conducted before implementation. If an upsell attempt is made without any regard for the customer’s needs or budget, you risk losing business and being pinned as “pushy.” Follow these best practices to get the most value out of this technique:
For 52% of consumers, a great support experience is fast, personalized, and facilitated by a knowledgeable rep. On that note, make sure your approach lines up with their priorities and preferences for the product or service being purchased. Take a few moments to find out what they really need and what problem they are trying to solve through their purchase.
For example, if someone goes to your clothing store to buy a suit because the one they currently have is uncomfortable, don’t upsell them on a suit made of a higher-quality but still uncomfortable material. The needs of the buyer have to be front of mind. You can use these questions to discover their needs and tailor an offer for them:
- “What are you looking to get from this product/service?”
- “Is there a specific feature or product attribute you’d like to see in our product/service?”
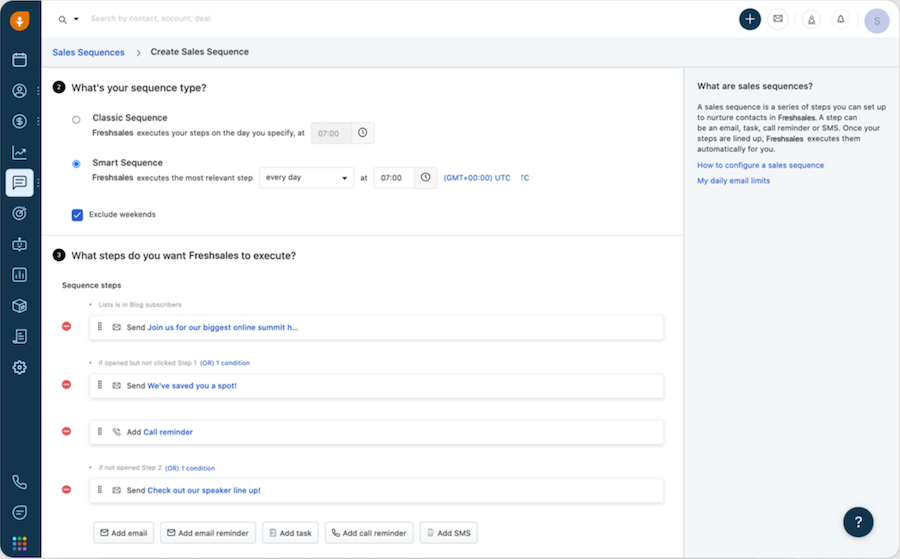
Freshsales creating smart sales sequences for a personalized campaign (Source: Freshworks)
It’s essential that reps always keep the customer’s budget in mind when selling higher-value products. Pushing a product that a person cannot afford is downright unethical. During the early phase of the buying process, use probing questions such as, “What’s your budget range looking like for this type of product/service?” to find out a person’s spending capabilities. You can present the upgraded options that give them the most value based on their response.
One of the most effective emotional selling techniques that you can also use in upselling is honing in more on the benefits of a product rather than merely enumerating its features. Explain to the customer how the higher-value product can improve their life or offer a better solution to their pain points. For instance, an insurance agent can highlight how a company can attract top talent by offering a wide range of benefits that include health insurance and retirement plans.
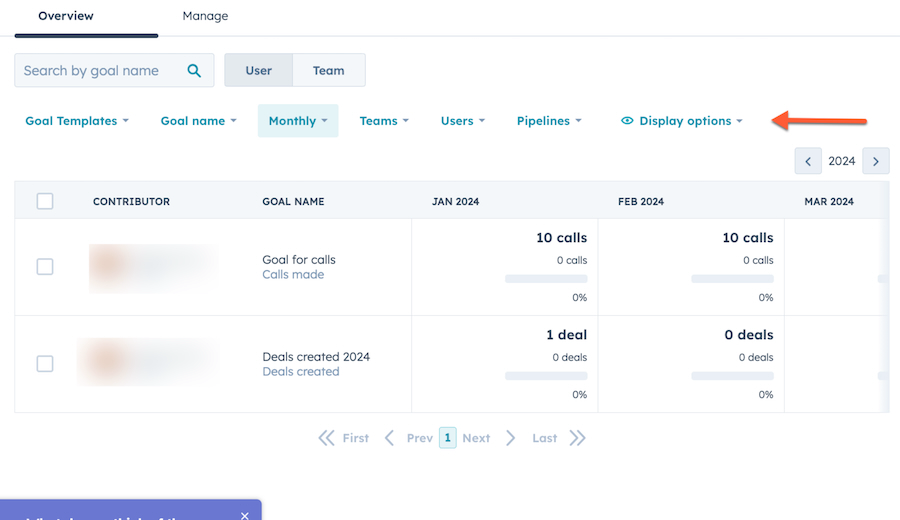
HubSpot CRM sales goal management system (Source: HubSpot)
Upselling Examples by Industry
A sales rep is often involved in an upsell, but on marketing channels such as websites or emails, there is no need for an agent. There’s no rule of thumb as to how this process must occur, just as long as there’s some form of communication to encourage a customer to upgrade. Click on the options below to see some examples of upselling in various industries.
For SaaS products such as CRM software, it’s common to have a tiered system and provide upselling opportunities using comparison charts. Zoho CRM, for instance, offers a free version plus four subscription tiers that have feature comparisons on the website.
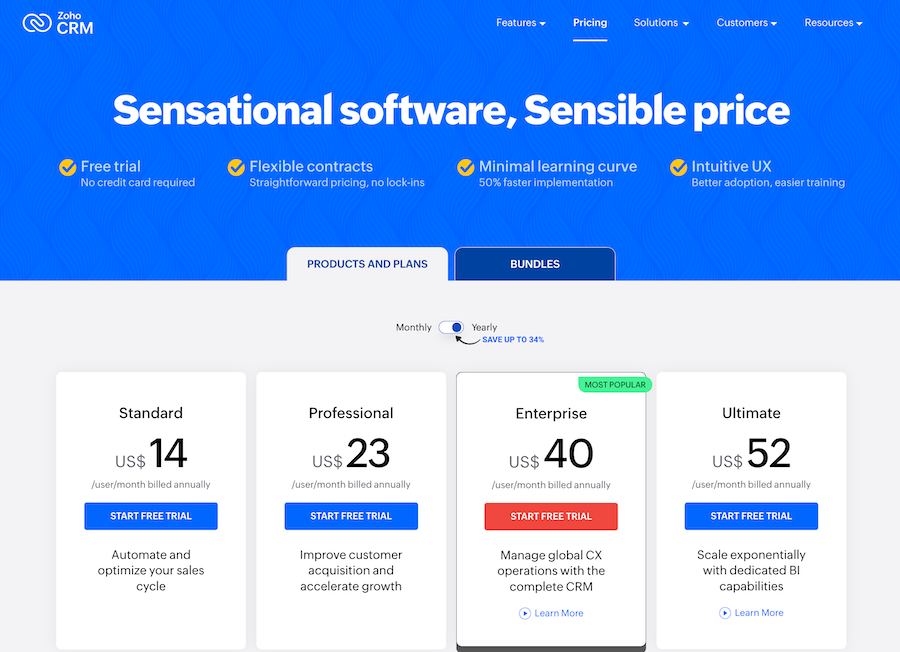
Zoho CRM subscription packages comparison
When a customer goes to an Apple Store to buy a new iPhone, the sales associate can recommend the latest model with newer and more advanced features. On the Apple website, the newest models are displayed more prominently. The pricing page also contains a link to a demo video of the iPhone 15 and iPhone 15 Pro. Customers who want to buy older models have to scroll down a drop-down menu and manually select their desired unit.
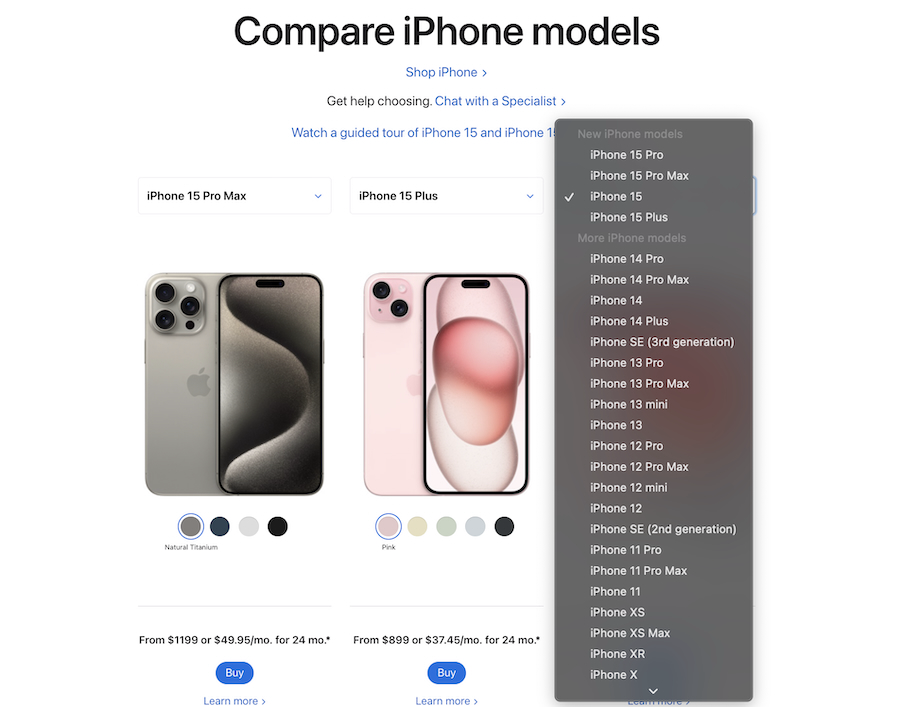
Apple iPhone 15 models pricing comparison with guided tour option
Let’s say a customer is considering buying a 2016 BMW X1. After finding out that the customer likes listening to music while on the road, a car salesperson can invite them to check out a 2020 BMW X1 with better speaker systems.
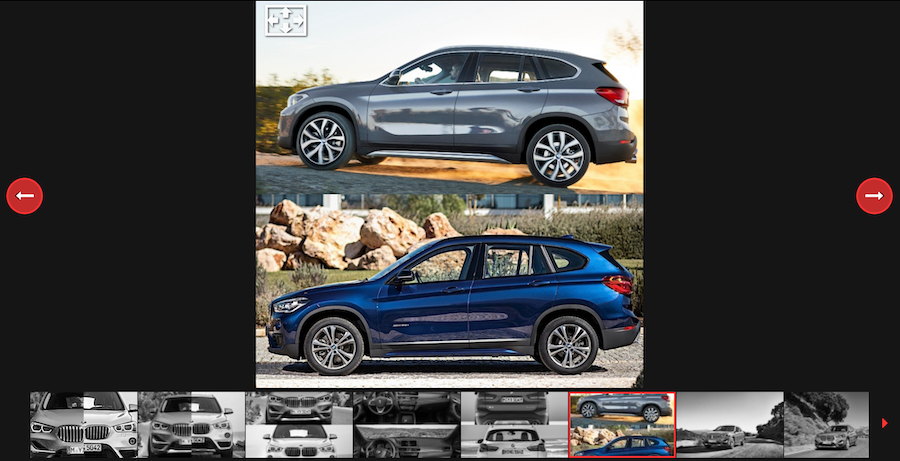

2020 BMW X1 vs 2016 BMW X1 (Source: autoevolution)
A business owner looks to subscribe to a free version of the web-design platform Weebly. While on the website, the business owner sees the more premium subscription options and realizes that they can get more value from a paid plan compared to the free version.
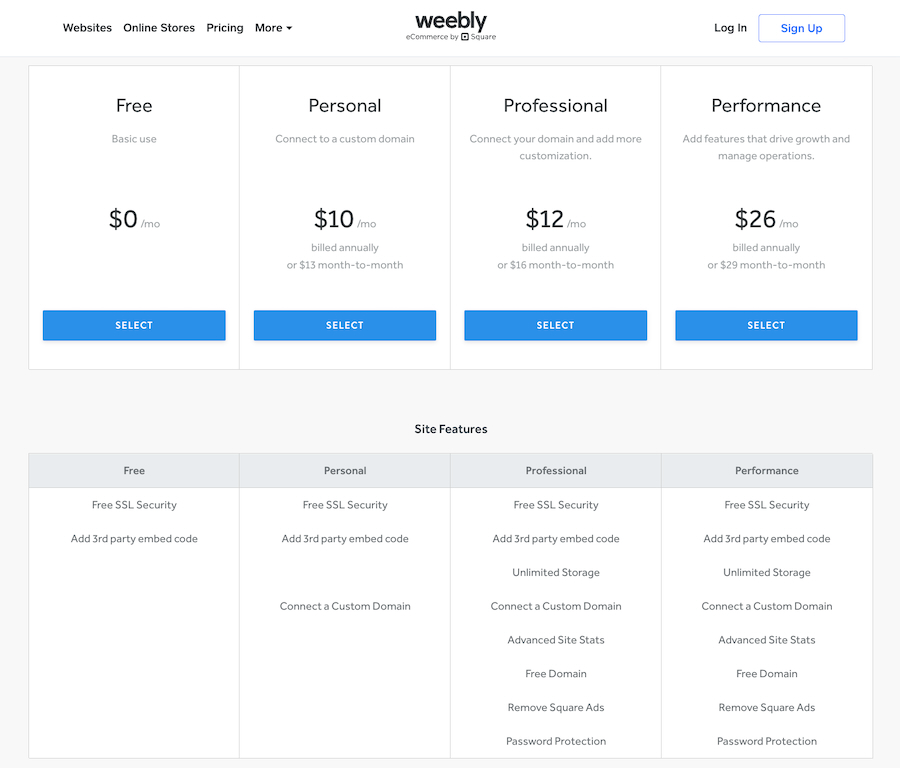
Weebly pricing plan comparison
A customer goes to a Starbucks restaurant to order a Tall cup of cold coffee. The cashier asks if they want to upgrade to a Grande for just $1 more. Interestingly, Starbucks’ online menu automatically selects the Grande option when you click on a drink, and you’ll have to manually select Tall if you want a smaller cup. There are also a lot of customization options like additional flavor, cold foam, toppings, and sweeteners, which all come with added costs.
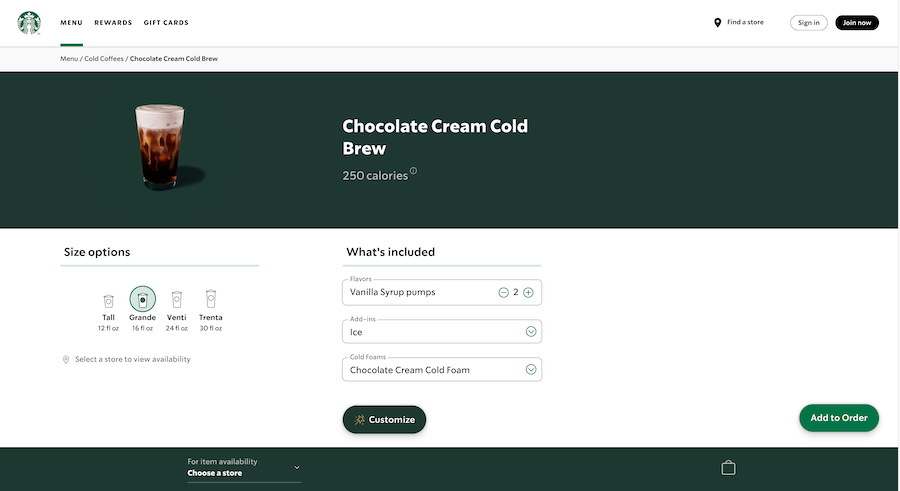
Customization options for Starbucks Chocolate Cream Cold Brew
An insured business is about to purchase a business owner’s policy (BOP). The insurance agent recommends they upgrade to a different carrier, which offers higher coverage limits.

Fit Small Business’ list of the top BOP insurance companies (Source: Fit Small Business)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Promoting a higher-value product is beneficial to both the company and the customer. The benefits of upselling include an increased customer lifetime value (CLV) and revenue through the sale of higher-priced products or services. Customers also benefit from it by addressing their basic needs and delivering more value by presenting them with a better alternative to their original purchase.
Upselling is good when salespeople honestly and carefully consider the needs of the customer. However, it can be considered bad if done aggressively. Pressuring customers to buy a premium product can backfire as it not only erodes their trust but discourages them from making any purchase.
To upsell without sounding too pushy, sales reps can say, “Did you know we’re running a special offer? You can get [mention benefits of the product/service] and it will help you with [mention pain points].” Another phrase that they can use is, “If you like [mention feature],” you might really love [mention the premium product/service] …” and continue outlining the benefits of the alternative product or service.
Bottom Line
Upselling is a cost-effective strategy to increase revenue with every purchase, catalyzing business growth. Those in sales management and leadership positions should find various ways to promote premium solutions. Understanding this technique and following its best practices will help you reap upselling benefits such as increased revenue and higher lifetime customer value.