An accounts receivable aging report shows all unpaid customer invoices grouped by the number of days outstanding. Its primary purpose is to keep track of unpaid customer invoices and how long they remain unpaid. A summarized A/R aging report will have one total for each customer broken up by the age of the invoice, which will typically be grouped by: 0 to 30 days, 31 to 60 days, 61 to 90 days, and over 90 days.
Why Is an A/R Aging Report Important?
The A/R aging report is more than just a list of unpaid invoices. It’s a strategic tool that can empower your business to maintain healthy cash flow, manage credit risk, and make informed decisions that contribute to overall financial health and success.
Following are some key aspects that contribute to its value:
How to Read an A/R Aging Report
Compared with other accounting reports, the A/R aging report is fairly easy to understand. Understanding collection patterns and practices can be evaluated by looking at the A/R aging report.
For illustration purposes, below is a sample of an A/R aging report generated using QuickBooks Online. If you’d like to know more about the software’s features and capabilities, read our QuickBooks Online review.
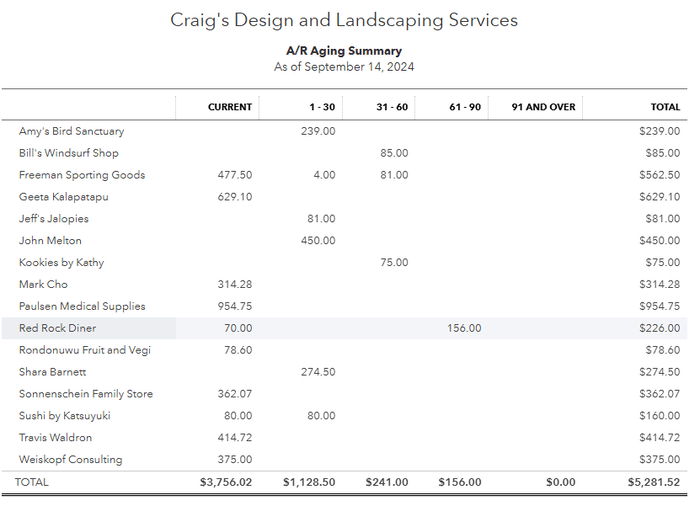
Accounts Receivable Aging Summary Report
The image above shows a total A/R balance of $5,281.52. We can see that $3,756.02 of the A/R isn’t yet due, while the rest of the receivables are overdue one to over 90 days. We can also see that only 4.5% of total receivables are in the 31-60 days age group. Thus, we can derive from this report that the company is doing a good job of collecting balances from customers.
If you want to dig into the details, a detailed A/R aging report can be very helpful. It shows you the age groups as well but provides more information on the receivables belonging to each age group. It’s the one you’ll need to use to follow up with customers because you’ll have more details about particular accounts under each age group.
Below is a sample detailed report from QuickBooks Online.
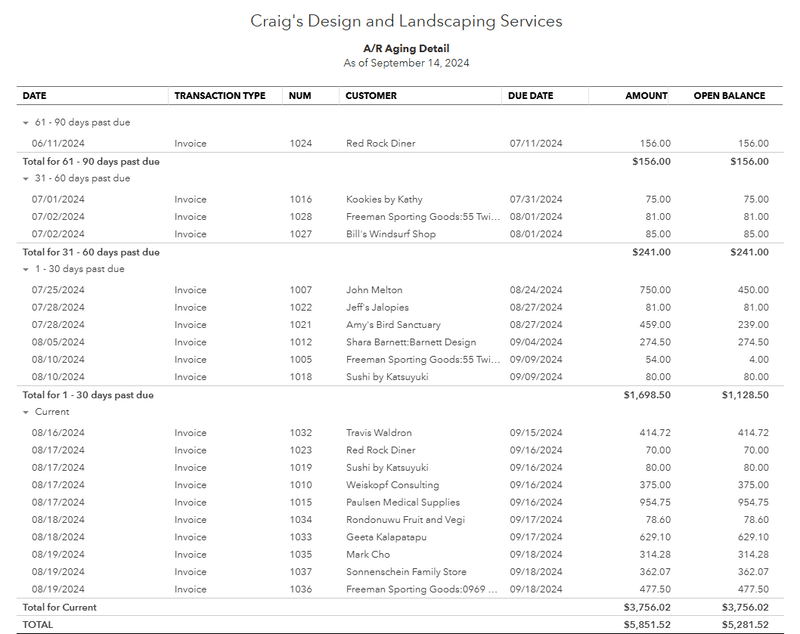
Detailed Accounts Receivable Aging Report
In the sample detailed report above, we can see that most customers are current. There is one customer, Red Rock Diner, that is within the 61-90 days age group; and only three customers within the 31-60 days age group. The total past due within these age groups is $397.
When & How to Generate an A/R Aging Report
You should generate an A/R aging report at least once a month, if not more often. This allows you to stay on top of invoices so that you can remind your customers that an invoice is coming due or notify them of invoices that are past due.
You can generate an A/R aging report using accounting software or manually by reviewing your subsidiary ledgers. However, the manual process is more tedious, as it requires updating all customer accounts before preparing the report. To streamline the process, I strongly recommend that you invest in one of the best small business accounting software.
Using the A/R Aging Report to Get Paid Faster
When you extend credit to customers, it’s good practice to remind them of their outstanding balances. You can use the A/R aging report to send them timely reminders and reduce the occurrence of late payments from them.
Here’s how you can use the A/R aging report when asking for payments:
- Current accounts: An account is current if it’s not yet past the due date—meaning it’s still within the credit period. You should send a payment reminder to customers in the current section of the report when their invoice is within seven days of the due date.
- 1 to 30 days past due: You should call, text, or email a client within two business days of an invoice becoming overdue. I recommend emailing first, because it is the least confrontational of the three. The communication should be informal and a simple reminder to pay their invoice. If the invoice isn’t paid within 14 days of the due date, you should send the first in a series of four collection letters along with follow-up telephone calls. If the invoice is still not paid as the 30-day overdue mark approaches, you should send the second collection letter.
- 31 to 60 days past due: If an invoice has been overdue for more than 30 days, the collection problem has become serious and a third, more strongly worded, collection letter should be sent. In addition to the formal letter, you should conduct weekly phone calls to these customers.
- 61 to 90 days past due: Invoices that are more than 60 days past due can be considered delinquent accounts. You should now send the fourth collection letter, which highlights your planned actions if the customer doesn’t pay. Assuming they haven’t responded to any of the letters or calls, you should freeze their account and stop accepting orders from them until they settle their account. You can also consider legal action or turning the account over to a debt collection agency.
Our related resources:
Estimating Bad Debts Using the Aging Schedule
One of the uses of the aging schedule is to estimate bad debts. Since it classifies customer accounts per age group, you can set a target collection rate per age group, such as 30% collectible for accounts 91 days past due. You can set higher collection rates for accounts that are less than 30 days overdue.
Let’s say that for accounts 31 to 60 days past due, we estimate that 30% will be uncollectible. If total outstanding invoices belonging to this age group is $10,000, the estimated allowance for bad debts is $3,000 ($10,000 × 30%).
Writing Off Uncollectible Accounts
US GAAP Generally Accepted Accounting Principles requires businesses to estimate uncollectible A/R, but small businesses don’t need to follow GAAP unless required by creditors or regulatory bodies. Instead, they can use the direct method to write off bad debts once collection efforts fail. However, for tax purposes, most businesses must use the direct method, as allowances for bad debt aren’t permitted.
For example, a customer has an outstanding invoice of $330 for 92 days. After multiple attempts to contact the customer, it appears they have absconded. The company decides to write off the account as collection now seems unlikely.
The entry to write off an uncollectible account is:
Debit | Credit | |
|---|---|---|
Bad debt expense | 330 | |
Accounts receivable | 330 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
While there’s no single “ideal” percentage, a common benchmark is to aim for 70%-80% of your outstanding invoices to be within the 0-30 days aging period. This suggests that the majority of your customers are paying on time or close to their due dates.
It is recommended to generate it regularly, typically on a monthly basis. This allows you to stay on top of outstanding receivables, identify potential issues early on, and take proactive measures to improve collections.
Yes, most accounting software allow you to customize the report by adjusting aging periods, filtering data by customer or invoice type, and selecting which columns to include.
It is important to set clear credit policies and payment terms and to send invoices promptly and accurately. Be sure to follow up on overdue invoices consistently and professionally. You can also offer an early payment discount to incentivize timely payments and consider using automated payment reminders and working with a collections agency for persistently delinquent accounts.
Bottom Line
An A/R aging report lists everything you’re owed by customers, separated by how many days the amounts are overdue. It can help you to stay on top of unpaid invoices so that you can collect payment on time and avoid the additional costs of hiring a collection agency.


