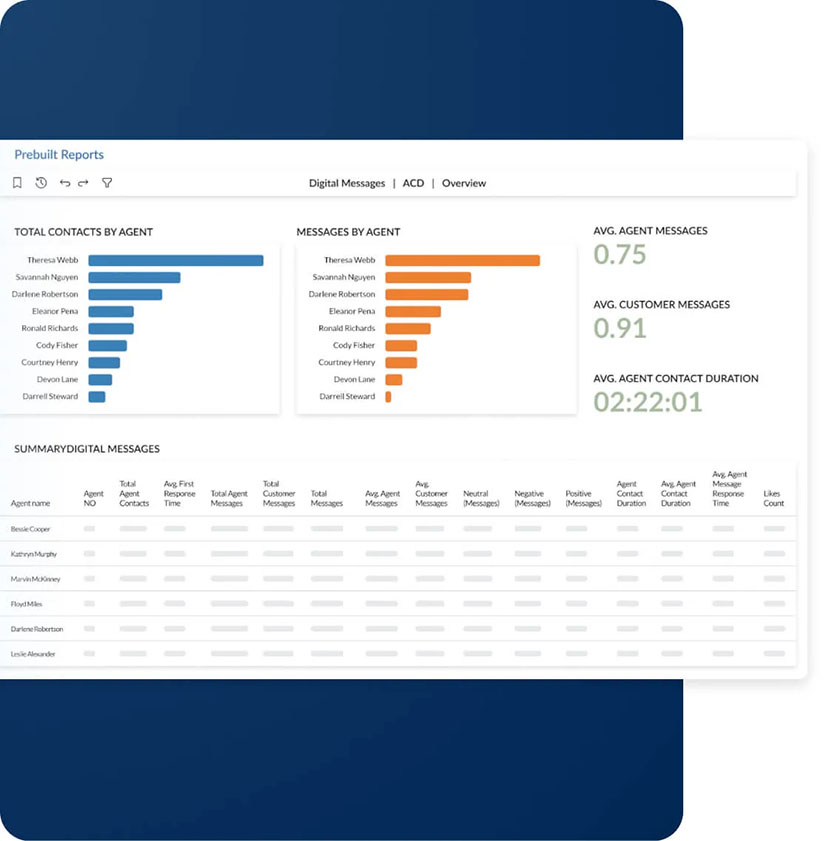
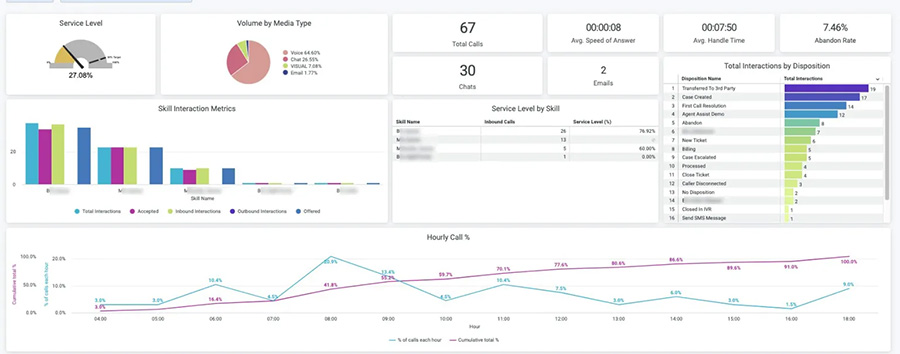
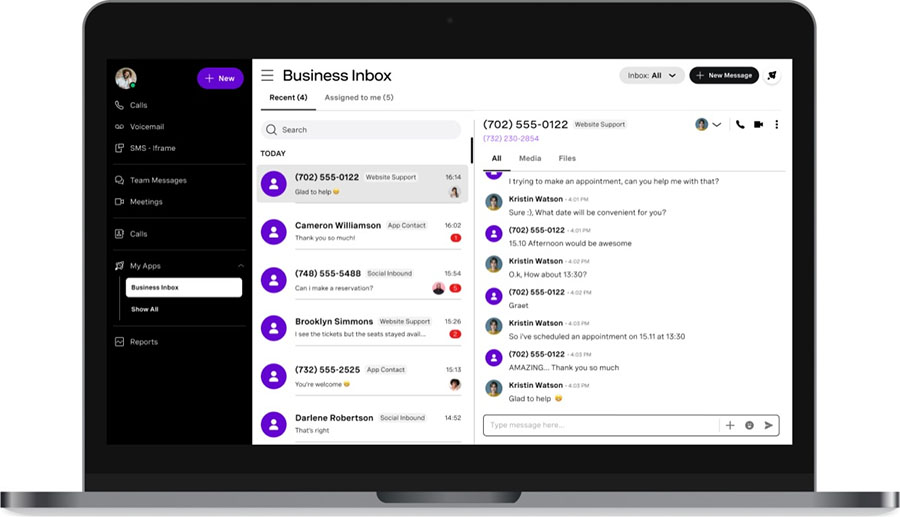
The terms “call center” and “contact center” are often used interchangeably, as they both contribute to delivering quality customer service and generating sales. However, their primary difference lies in the channel or medium used. If you’re deciding between contact center vs call center and want to determine which is better, know that it depends on what you need. Call centers focus on phone communications, while contact centers provide support through various channels like phone and live chat.
This article explores the differences between a traditional call center based on legacy on-premise systems and a modern contact center powered by the latest technologies.
Contact Center vs Call Center at a Glance
Contact Center | Call Center | |
|---|---|---|
Best For | Businesses offering omnichannel communications wanting to integrate inbound and outbound interactions | Teams needing software to manage inbound and outbound calls |
Monthly Starting Price (per User) | $20 to $140 | $20 to $100 |
Objective | Serve as a customer service hub providing a variety of communication channels | Provide quality service over the phone |
Communication Channels | Omnichannel: Phone, email, text, live chat, social media | Phone |
Agent Skills | Proficient in channel-agnostic interactions | Proficient in voice-based communications |
Key Features |
|
|
Usage | Customer relationship management, customer service, technical support, telemarketing, and sales | Customer service, technical support, telemarketing, and sales |
Scalability | Highly scalable across multiple communication channels; compatible with future media channels | Highly scalable but limited to one communication channel; incompatible with future media channels |
Unified Customer View | 360-degree view of customer profile, interaction, and history | Limited to phone history and customer profile |
Customer Self-service | IVR | IVR, chatbots, FAQ pages |
Contact Center vs Call Center: What’s the Difference?
The main difference between call centers and contact centers boils down to their communication channels. Call centers rely mainly on legacy or voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) phone systems, while contact centers leverage calling technology and other (often digital) channels.
Here’s a closer look at some of the primary contact center and call center differences:
- Interaction channels: Call centers typically just handle phone calls, but contact centers interact with customers and colleagues through a range of channels like text, social media, chat, and email.
- Available customer data: Call center software gathers phone call data, but contact centers can collate and analyze data from different sources of customer engagement.
- Self-service technology: Both business communication systems have self-service options like IVRs and automatic call distribution (ACD). However, with more communication channels, contact centers can use other tools like website support, visual IVR, and live chatbots.
Traditional call centers remain one of the most popular avenues for customer support, but with technological advances, call centers have evolved into contact centers—a business unit that connects customers across different contact methods.
What Is a Call Center?
Call centers are composed of customer service specialists and agents who help field and respond to client calls about a company’s products, services, or technical support. These offices provide customer support over the telephone and often act as knowledge bases for billing inquiries, technical support, and account information and/or modifications. Call centers usually focus on quick client resolution and enhanced agent productivity.
These centralized systems manage inbound and outbound calls via traditional phone lines or VoIP. Centers can employ anywhere from a small group of agents to sizable teams supporting multinational corporations. Call centers often focus on providing comprehensive customer satisfaction, increasing lead generation, acquiring new customers, or streamlining the order processing and payment workflow.
Whether the center is focused on customer service or sales, it is integral to providing a great customer experience. People often imagine large office spaces filled with cubicles and agents accepting calls one after another. Still, while many setups remain this way, modern call center software allows for more flexibility and can be set up for remote teams.
Benefits of Using Call Center Technology
Communicating with customers—whether you’re providing support or proactively engaging your market—is an essential aspect of any business. Establishing one may not be a priority for small businesses and startups, but having this set up and running as soon as possible is advantageous. Here are some key benefits you gain by integrating a call center into your business operations:
- Provides employee flexibility: Businesses can offer employees more flexibility thanks to advanced call center software with hot desking and VoIP technology.
- Decreases overhead costs: Leveraging technology helps businesses reduce operating costs, and using third-party software to automate tasks lowers labor costs. Using cloud-based services reduces physical infrastructure requirements.
- Boosts customer satisfaction: Reliable call centers translate to a smoother customer journey, leading to higher satisfaction and brand loyalty.
- Enhances competitive advantage: Gain an edge over competition by giving customers a reliable communication channel that can provide information quickly.
What Is a Contact Center?
To understand the difference, you need to know that a contact center is the modern adaptation of a call center. Contact centers offer customer service channels beyond phone calls. They allow businesses to engage customers through voice, email, social media, messaging, and live chat. This responds to the growing trend of customers expecting businesses to adopt the communication channels most often used in their everyday lives.
Contact centers are centralized systems that manage a business’ omnichannel strategy. With advanced cloud-based contact center features like visual interactive voice response (IVR), automated routing, and artificial intelligence (AI), contact center agents can manage multiple conversations on varied platforms simultaneously. This saves companies money by reducing labor expenses and utilizing lower-cost digital channels.
Benefits of Using Contact Center Technology
Contact centers use modern technology to interact with customers, track client data and communications, and measure performance across various channels. It presents plenty of advantages for small businesses, such as better customer support, a streamlined communications journey, and quicker resolution and handling time. Below are some ways contact centers can contribute to growing your business:
- Improves brand consistency: Ensure you have a consistent message across each touchpoint. Contact center software lets your agents field questions from different channels, ensuring consistency and clarity of message.
- Enhances customer experience: Customers have come to expect lightning-fast responses and effortless resolutions from businesses they transact with. A digitally integrated company can provide excellent customer support by providing a frictionless experience.
- Boosts sales and revenue: Optimizing conversations with customers allows businesses to provide better, personalized service. With higher satisfaction levels, clients are more inclined to patronize a business, emphasizing that customer service is an investment, not merely an operating expense.
- Elevated brand image and reputation: Being available on all communication channels emphasizes a business’ genuine interest in what customers have to say. Being proactive regarding customer support goes a long way to creating a brand image that resonates with customers.
When to Use a Call Center
Often, customers associate the term call center with a hotline that they’ve experienced being on perpetual hold or passed around from agent to agent or through an IVR. Because of these experiences, call centers have been given a bad reputation. However, with advancements in technology, business phone systems have evolved.
When deciding between a contact center vs call center, consider a call center if:
- The primary focus of your communication strategy is managing call flows.
- Your sole contact mode with customers is through phone calls.
- You have inconsistent or weak internet connectivity.
Here are some examples of how call centers are used in different industries:
The healthcare industry uses call centers for medical consultations between patients and physicians. They can be used to call healthcare institutions like hospitals and inquire about appointments, prescription refills, and billing inquiries.
Banking is an area that uses call center technology quite heavily. Phone systems with IVR are commonly used for issues like fraud. For example, banks can use outbound voice response tools to raise awareness of fraudulent efforts or any doubtful transactions in accounts. They can also be used for loan applications where callers can call your number and an agent can check an applicant’s eligibility for loans and other financial products.
Customers can use phone call centers to ask about flight updates, train schedules, and weather conditions for upcoming travels. Travel agencies can also use call centers to accept new bookings or receive calls from clients experiencing challenges while traveling.
While shopping has moved to the digital world, consumers still use call centers to ask about product availability, request a refund, or get shipping updates.
When to Use a Contact Center
There are many ways to interact with customers besides the phone. Businesses can use contact centers to deliver technical support via chat or video, provide status updates via text messages, or send sales invoices and inquiries by email directly to the customer.
When deciding between a call center vs contact center, consider a contact center if:
- Your customers are using multiple digital channels to reach your business.
- You’re looking for cross-channel reporting.
- Your business is expanding and ready to scale.
Here are some examples of how contact centers are used in different industries:
The finance industry is highly regulated at federal and state levels, requiring secure software. Several service providers offer AI tools that can help in terms of data collection and recovery while ensuring data privacy. Consider conversation AI outbound calls with a live agent handoff or conference calling with clients.
Interact with customers in different ways, from messages to phone calls to websites and mobile applications, and provide prompt responses to increase sales revenue. Chatbots respond to common requests like price lists and standard business information like operating hours and shipping information. It’s great for businesses lacking the resources to employ agents 24/7. Chatbots on Messenger and social media ensure all inquiries receive a timely response.
Open multiple communication channels so customers can easily place food orders and send payment details. Use contact center technology to ensure quality control through customer feedback. Contact centers can also handle client complaints about food issues, allowing you to provide timely and effective solutions.
Best Contact Center Providers
While comparing call center vs contact center for small businesses, we recommended choosing a contact center platform to expand your customer support systems. Contact centers provide robust customer support across many channels, allowing you to streamline systems and operations. This leads to quicker and more optimized customer support and engagement. Here are our three suggested contact centers for small businesses:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Call center agents handle incoming or outgoing customer calls for a company or professional. The key call center agent duties include handling customer engagement, identifying customer needs, and upselling products. Many don’t realize that working in a call center isn’t just taking calls all day—the position also entails writing emails, taking notes, updating client information, making reports, and doing follow-through.
Companies involved in client servicing, like healthcare firms or service providers, use call and contact centers to ensure issues raised are addressed and handled quickly and efficiently. The industries that use outbound call centers the most include real estate, banking, telecommunications, tourism, and finance.
The difference between an inbound and outbound call lies in who initiates the call. Inbound call centers handle incoming calls, often made by consumers, while outbound call centers reach out and dial the consumers. However, many call centers are hybrid and handle both inbound and outbound call center services.
Bottom Line
In this contact center vs call center comparison, we outline both technologies’ definitions, benefits, and use cases. Traditional call centers assist customers or respond to inquiries by phone, while contact centers offer seamless customer touchpoints, improving customer experience and operational efficiency.
Businesses must consider how their chosen customer service solution will drive them toward the future. By using contact and call center technology, companies can offer secure and reliable remote working solutions for their staff while lowering communication costs and contributing to improved customer support.