Starting or growing your small business requires careful planning. A business plan is a detailed document outlining the goals, strategies, operational plans, and risks associated with starting or running a business. Various types of business plans will be your roadmaps to securing funding, planning for growth, or making big decisions through your business’s lifespan.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through different types of business plans, discussing their format and ideal use cases so you can make the best moves for your business.
Key Takeaways:
- Business plans are not a one-time project when you start your business.
- You may use one or more types of plans in business to make major changes throughout its lifespan.
- The type of business plan you need varies by your industry, business size, and goals.
1. One-page Business Plan
The one-page business plan is for very small businesses like side hustles. A one-page business plan is a great way to get your ideas on paper and work out the fundamentals of the business without doing a bunch of high-level calculations that aren’t relevant to your micro-business.
With this plan, you’ll write a couple of sentences for a few important business sections. Your one-page business plan should include information on your business model (how will your business make money?) and competitive advantage (what will your business do better than competitors?).
You should plan on spending around an hour to write out a one-page business plan. The simplified financial projections will be the most challenging and time-consuming. Most likely, you will need to do research online to get accurate income and expense estimates.
Key Sections
To create a one-page business plan, you’ll need to write one to two sentences to answer the following questions:
- Problem: What problem will your business solve?
- Solution: What will your business provide to solve that problem?
- Business model: How will your business make money?
- Target customers: What type of people will buy your product or service?
- Promotion: How will your target customers learn about your business?
- Competitive advantage: What will your business do better than the competitors?
- Financial projections: How much money do you need to start? How much will you earn every month? And how much will you spend every month?
- Funding required: How much money do you need to start the business?
Best For
A one-page business plan is a great fit for side hustles like dog walking, small handicrafts, and cottage food businesses. If you are helping your child start a business, a one-page business plan is a good exercise to help prepare your child for thinking through their business plans.
Get started writing a one-page business plan by downloading our free template.
2. Traditional Business Plan
The traditional business plan is more thorough than the one-pager. A traditional plan may contain over 40 pages of info about your business. Typically, you’ll use this plan to get funding, such as a larger loan from a bank. You may also use a traditional business plan to attract investors.
You should plan on spending at least 30 hours creating a well-researched business plan. In addition to writing the plan, you will also spend time doing market research and creating financial projections.
Most small business owners can easily do the research and write a traditional business plan. Where most have difficulty is financial projections, which require creating several financial documents. If you don’t have a financial analysis background or interest, it’s a wise strategy to purchase a business plan software that walks you step-by-step through the financial projection process or hire an accountant to assist.
Key Sections
A traditional business plan has many sections and can be 30 to 40 pages (or more) in length. The length of your traditional business plan will vary depending on your business type, industry, and the amount of information you include in your appendix.
- Opening organizational and legal pages: The opening pages of your business plan need to be a cover page, a non-disclosure agreement, and a table of contents.
- Executive summary: This one- to two-page section is a summary of the whole plan, highlighting the key details to encourage potential investors, business partners, or banks to read the full business plan.
- Company summary: Discuss the basics of the company such as its history, location, facilities, ownership, and competitive advantage.
- Products and services: Talk about how your business makes money (business model), its products or services, and future products or services.
- Market and industry analysis: This section analyzes your potential customers and industry. Include any data here about your current (or ideal) customers, business industry, and competitors.
- Marketing strategy and implementation summary: How will you reach your customers? Discuss your marketing, sales, and pricing strategy.
- Management and organization summary: Who will own and operate the business? If your business isn’t open yet, give a compelling reason why your background will make it a success. Include information on any managers in the business as well.
- Financial data and analysis: Here you want to show in charts and graphs how your business will be a success. You will include financial projections such as a profit & loss statement, projected cash flow, and business ratios.
- Appendix: Any documents or information that doesn’t fit in the above categories goes in the appendix. You may want to include documents such as a floor plan, trademark, or marketing materials.
Best For
Small to medium-sized businesses that may need investors, grants, or business loans to get started can benefit from a traditional business plan. Beyond ensuring you get the funds you need, going through the process of writing a traditional business plan will help you refine your idea and answer questions you may not have considered.
3. Business Model Canvas
A business model canvas is a visually dynamic one-page business plan. This business plan model was developed in the early 2000s as a collaborative tool to help fast-moving, customer-focused businesses quickly collaborate on a business plan. The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a strategic tool that lets you visualize your business model.
Many business owners prefer to use the BMC because it can be done as a visual exercise with the leadership team. Together, the team can go through each section and provide high-level input. Once you create the basics of the BMC, it’s easy to share with others. The contents can be summed up on one page, whereas the traditional plan above will likely be at least 40 pages.
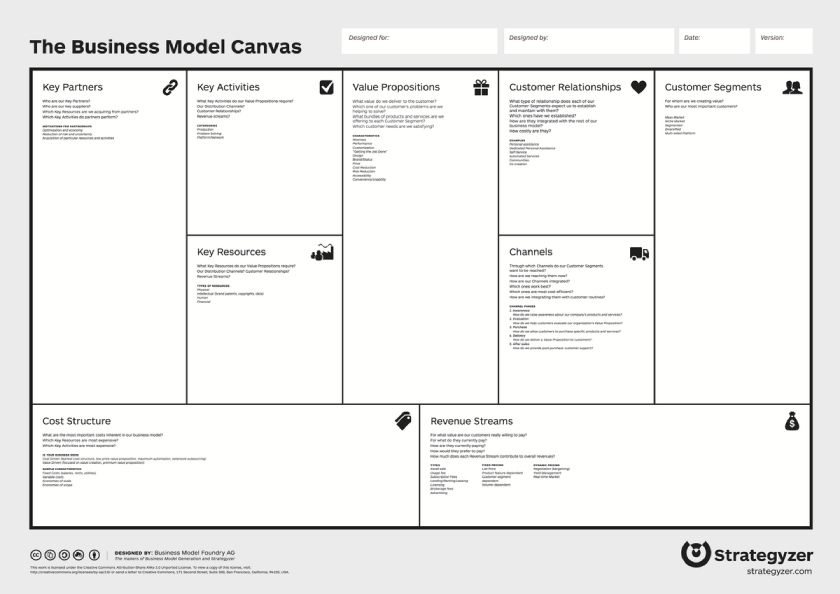
Source: Strategyzer
Key Sections
- Key partners: What people or organizations (outside of the business) help your business operate such as suppliers or referral sources?
- Key activities: What crucial activities need to be done in the business so that you can serve your customers?
- Key resources: Who are the key people (inside the business), and what are the patents, places, and machines that the business couldn’t operate without?
- Value proposition: What value will you be delivering to customers? What customer problems are you trying to solve?
- Customer relationships: How will you maintain relationships with your customers?
- Channels: What channels will you use to reach customers and maintain relationships?
- Customer segments: Who are the most important types of customers or businesses that will be buying your products or services?
- Cost structure: What are the largest expenses in your business? List at least seven.
- Revenue streams: In what ways will your business earn money? If possible, list specific numbers such as the average earned per product or service performed.
Best For
The Business Model Canvas is great for team collaboration. It is a great business plan for startups and businesses that need agility. If you need to raise funds for your business, you’ll need to supplement your BMC with financial projections.
4. Startup Plan
A startup plan is similar to a traditional business plan. However, startups tend to be larger, more complex businesses than the typical small to midsize business. A startup business plan will have many of the same sections as a traditional business plan, but the financial projections for a startup plan will typically include many more dynamic visualizations to dramatically illustrate the idea. Startups are characterized by fast growth and a need for large initial investments, so startup business plans tend to focus a lot of energy on finding funding.
Key Sections
You’ll see a lot of the same sections in a startup business plan as in a traditional business plan, though the key sections may have a different focus.
- Opening organizational and legal pages: A non-disclosure agreement is standard for a startup business plan. This section also includes business information like the addresses and contact information of key owners and partners.
- Executive summary: This is a high-level summary of the entire business plan that enables potential investors and business partners to quickly understand the key elements of your proposed business.
- Company description: This section covers your business mission, vision, and goals. It should also list your legal structure (i.e. sole proprietorship, LLC, corporation), and briefly describe what sets your company apart from competitors.
- Market research and analysis: Demonstrate your understanding of the market size, trends, competition, and customer demographics. Potential investors want to feel confident that you know the industry you are entering.
- Organization and management: Introduce key team members, including a brief description of their roles, responsibilities, and qualifications. If you have an advisory board (not uncommon for startups) list those key stakeholders, too.
- Products or services: Explain how your product or service solves a problem or meets a market need. Include specific mention of any intellectual property or proprietary technology you have or will develop.
- Marketing and sales strategy: Outline your plan for attracting and retaining customers. Include details about your pricing strategy, sales tactics, and distribution channels.
- Financial projections: It can be tricky to generate accurate financial projections if you are proposing a new business model or developing a disruptive technology. Financial projections in a startup business plan are generally more speculative than in a traditional business plan and are based on hypotheses about customer acquisition, market penetration, and growth. Startup plans may only include one-, three-, and five-year projections and leave off longer-term 10-year projections.
- Funding request: Detail how much money you need and what you’ll use it for. Startups tend to have multiple funding “rounds,” so list the timeline and requested funds for each funding round here.
- Appendix: As with a traditional business plan, any documents—like design plans, licenses, or patents—that don’t fit in the categories above, add them to your appendix.
Best For
A startup business plan is the right fit for technology-based and industry-disrupting businesses. If your product or service is novel and expected to grow quickly, a startup business plan can also work for you. Any business with a focus on quickly raising lots of initial capital from investors or banks can benefit from following this business plan format.
5. Lean Canvas
The Lean Canvas combines the Business Model Canvas template with the focus of a lean business plan. A Lean Canvas is ideal for startups that want a more focused, streamlined business plan. The Lean Canvas is great for quickly recording a business idea based on a gut feeling or instinct.
A Lean Canvas plan focuses on the customers’ problems and the solution your business will provide. Unlike a traditional business model, a Lean Canvas is not heavy on financial projections. Like all canvas-based business plans, the Lean Canvas is also great for collaborating with other stakeholders or business partners to create a business plan.
Key Sections
These are the major sections of a Lean Canvas business plan. As with a Business Model Canvas, these sections are all laid out in a tile formation on a single page.
- Problem: This section lists the one to three major problems your business will solve. It also typically includes a short list of one to three businesses that already exist to solve this problem.
- Solution: These are the top features of your product or service that will solve the problems you listed in the first section. It should provide a clear vision of how your solutions directly solve the problems.
- Key metrics: This is a short bulleted list of the key performance indicators you’ll track to measure your business’s growth and success. Customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, customer retention, and sales per customer are all common KPIs.
- Unique value proposition (UVP): Describe what makes your business unique compared to your competitors.
- Unfair advantage: This goes beyond your UVP to list exactly what your business can provide that other competitors cannot replicate. Many people think of this as the “moat” around your business.
- Channels: These are the pathways you will use to reach your customer segments. Depending on your business type, you might list direct sales, social media, partnerships, government contracts, ecommerce platforms, or more.
- Customer segments: Define the specific customer types or groups that will benefit from your business. Include a brief description of the likely “early adopters.”
- Cost structure: List the major fixed and variable costs required to get your business started (permits, licenses, rent, etc.) and keep it running (marketing, salaries, etc.).
- Revenue streams: List the ways your business will make money—subscriptions, direct sales, consulting fees, licensing, ecommerce sales, etc.
Best For
The Lean Canvas emphasizes agility and a customer-centered approach. It is great for startups that focus on experimentation and direct problem-solving for customers, like software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies. It’s not the greatest fit for a brick-and-mortar business like a retail or restaurant operation.
6. Strategic Plan
A strategic plan is a business plan that you write after your business is already operational. These plans are designed to help your business plan for growth in a specific area while staying aligned with your mission and core values.
A strategic plan will focus on long-term goals and objectives, laying out your path to achieving strategic milestones. Depending on your business type, those milestones might be growing sales in a specific region or obtaining a business certification, like a B Corp designation. Medium to large businesses commonly write strategic plans. But it can also be a good fit for small businesses that operate in challenging or quickly changing industries.
Your strategic plan needs to be clear, concise, and easy to understand. It should simplify your decision-making process, not complicate it. If you need support writing a strategic plan, contact a small business advisor at your local Small Business Development Center (SBDC), or book some time with a business consultant in your industry to get additional guidance.
Key Sections
- Vision and mission statements: Starting with your vision statement or mission statement ensures you keep your strategic plan focused and design solutions that demonstrate your business values.
- Organizational goals: Write down where you hope to see your business in three, five, and ten years. If you foresee changes on the horizon for your industry, include a brief description of the challenge and how you plan to react to it. Mention how you will grow your business and reach new customers at each milestone.
- SWOT analysis: A SWOT analysis is a list of your business’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- PESTEL analysis: This is typically a table that illustrates the external forces that influence your business. To create your table follow the acronym and list the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal influences.
- Current state: This is a description of the current state of your business performance and business operation. This section provides a baseline to compare your future business states, so you can more easily see your business growth.
- Future state: This is a detailed description of the future state you see for your business, or where you hope the business will go.
- Key objectives: This is a list of your major projects, initiatives, or goals; whatever activities you’ll need to undertake to get your business where you want it to be.
- Strategies: Describe what needs to happen for your business to meet your stated goals. List what resources you will need (and when) to get there. This section should include a one-page action plan that summarizes each key action you plan to take and the planned timeline for each shift.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): List the KPIs or metrics you will use to measure your business’s progress toward your long-term goals. What will you measure, and how will you measure it?
Best For
Strategic plans are a great fit for established businesses that need to grow or refine operations and for businesses pivoting due to disruption from third parties or market forces (like supply chain disruption or inflation).
7. Feasibility Plan
A feasibility study is like a rough draft of a business plan; it’s a “business plan lite.” A feasibility plan focuses on answering a single question: is this business idea viable? A feasibility plan or feasibility study helps you determine if a business idea will be profitable before you expend too much time or money to get the business off the ground.
Key Sections
- Executive summary: As with other business plan types, the feasibility plan starts with a one-page executive summary. This lists the key takeaways from your whole plan, so you and other stakeholders can get the main information quickly.
- Business idea: Clearly and succinctly detail your business idea. This is the foundation for the rest of the document, so make sure it is clear how your business will make money.
- Demand analysis: This section is a summary of how many people, and what specific types of customers are likely to purchase your proposed product or service. List who they are, where they are located relative to your business, and other defining characteristics.
- Market research: This section lists competitors in your market and looks at how your proposed business idea compares.
- Risk analysis: This section should include foreseeable legal concerns (like any permits or licenses you’ll need to obtain), logistics issues (like supply chain logistics), and technical challenges (like needing to design an app).
- Financial feasibility: This section includes costs like marketing, required staff, rent, and other costs as compared to your projected profits. These
- Recommendations: This section is the “TL;DR” section of this feasibility plan. After considering all the information in the plan document, does the business idea get a thumbs up or a thumbs down? If the recommendation is that the business idea is not feasible, you should offer alternative ideas that may work instead.
Best For
Feasibility plans are a great first step before committing to writing a full, traditional business plan. Feasibility plans, or feasibility studies, are ideal for startups and any business that is offering novel products or services.
8. Operations Plan
A lot of these business plans have focused on big questions like your business vision, the big problems your product will solve, and your projections for the future. An operations plan is focused on the day-to-day logistics and workflows that keep your business running. If other business plans focus on the “why” and the “what,” your operations plan is all about the “how.”
Key Sections
An operations plan is much shorter than a typical business plan. Key sections of an operational plan include:
- Product (or service) delivery: This section describes how you deliver your product or service to customers. It covers every step of the process, from sourcing raw materials to final delivery. Service-based businesses should detail how services are scheduled and managed. Product-based businesses should include details about their manufacturing, inventory management, and distribution processes.
- Supply chain management: This section focuses on the source of your raw materials. It lists your key suppliers, explains your purchasing strategy, and details how these materials arrive at your location.
- Facilities and equipment: Provide information about your physical business spaces, along with the equipment and technology that you use to run your business. Depending on your business type, you might list office space, warehouses, retail locations, or manufacturing facilities. If you plan to schedule upgrades or additional equipment when you reach key milestones, mention that here.
- Staffing and organizational structure: List your business’s personnel needs and management structure. Explain the key employee roles, the number of each employee you need, and how you plan to recruit, train, and manage these team members.
- Operating model: Describe your typical work tasks and their workflows. How do customers place orders or book appointments? How are those orders communicated internally amongst your staff? How do you handle customer inquiries or complaints?
- Quality control: Explain how you’ll monitor the quality of your products or services. Will you inspect and test products? Will you use secret shoppers?
- Risk management: Identify common risks you encounter and your plans for mitigating those risks. Risks might include supply chain disruption, employee workplace injuries, customer injuries, equipment failure, or natural disasters.
- Key metrics: List the major performance indicators you will track to measure your operational performance.
Best For
An operations plan is a great tool for businesses in complex industries and those with complicated supply chains. If your business combines any configuration of manufacturing, distribution, sales, and services, an operations plan will help you identify bottlenecks and keep you organized.
9. Contingency Plan (What-if Plan)
A contingency plan (also called a “What-if Plan”) helps your business prepare for unexpected events like changes in customer demand or market downturns. You can write a contingency plan at any stage in your business journey, whether you are a new or existing business. A contingency plan can help your business weather crises from natural disasters to cyberattacks.
Key Sections
- Risk assessment: Identify the potential risks that can impact your business. Cyberattacks, data breaches, supply chain disruptions, and equipment failures are common small business risks.
- Impact assessment: Evaluate the potential impact of each risk you identified. Consider revenue, employee, customer, and safety impacts. Prepare for both short- and long-term impacts.
- Response strategy: Outline the specific steps your business will take to respond to each risk you listed. Be detailed and include alternatives to ensure your business is prepared for all variables. List the resources you’ll need for each strategy to ensure they are easily accessible if the worst happens.
- Chain of command: Clearly articulate who should take responsibility for key tasks in your business in the event that you need to implement any of your response strategies.
- Communication strategy: Describe how information about your business response to crises will be communicated to your team, your suppliers, customers, and the general public.
- Training plan: Include a schedule and training details for how you plan to get your whole team on the same page for each response strategy.
- Monitoring and updating: How will you monitor risk development? How often will you update your contingency plan?
Best For
Businesses in volatile industries (like ecommerce or technology) or those with complex supply chains (like manufacturers) have long created contingency plans. In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic and multiple armed conflicts around the world, though, it’s clear that even small businesses can benefit from creating contingency plans.
10. Expansion Plan
An expansion plan will guide your business as it grows, laying out a strategic plan for expanding your existing operation. Whether you are opening a new location, launching new products, or expanding your services, an expansion plan will keep you focused and keep your costs in line.
Key Sections
An expansion plan is shorter than a traditional business plan, but it still has some key elements to include.
- Executive summary: Like all the other business plan types, your expansion plan should start with an executive summary to highlight the key points of the complete plan.
- Market analysis: This is a detailed analysis of the market for the new audience you hope to attract or the new competitors your business will encounter by expanding.
- Expansion strategy: Outline the specific steps you need to take to complete your expansion, from locating additional storage or operational space, obtaining or creating new products or services, entering new markets, or building new locations. Include a timeline for each phase in your expansion plan.
- Operational adjustments: Will you need to hire additional staff or retrain existing ones? Will you need to secure additional suppliers, forge relationships with new vendors, or improve your customer service bandwidth to meet increased demand?
- Marketing and sales strategy: How will you draw new customers or inform existing ones of your expansion? Include plans for advertising, partnerships, and other promotional efforts.
- Risk assessment: Include a clear assessment of the risks of expanding your business, including your plan for mitigating those risks.
- Financial projections: As an existing business, you should have some historical data to draw from to create future projections for this expansion. Use this information, along with your expectations of the expansion, to generate projections of your expected costs, cash flow, and how much capital you will need to fund your expansion. This is particularly important if you need to seek funding in the form of loans or investments to fund your expansion.
- Metrics and KPIs: Define the metrics you’ll use to measure the success of your expansion, from revenue growth to customer ratings and retention.
Best For
An expansion plan is a great idea for any growing business to strategically plan to grow their business and measure impacts. Even the smallest businesses should comprise an expansion plan to ensure they maintain profitability as they grow.
11. Nonprofit Business Plan
A nonprofit business plan is different from a traditional business plan because it focuses more on mission and longevity than profit. Unlike for-profit businesses that create plans to appeal to investors, nonprofit business plans need to appeal to donors and grant-awarding agencies. A nonprofit business plan needs to show how a nonprofit organization will achieve its mission while remaining financially stable.
A nonprofit business plan may be 12 to 30 pages long, depending on the organization’s mission, the number of staff, and the impact it hopes to have on the community.
Key Sections
- Executive summary: Like traditional business plans, a nonprofit business plan should include a summary at the beginning that lists the key points of the business plan.
- Mission statement: This is the foundation of the whole nonprofit organization. This should describe the specific social, environmental, or community issues your organization will address.
- Needs analysis: This is similar to the market research section of a traditional business plan. Research and include detailed information about the community your nonprofit will serve, other organizations that work on similar issues, and any specific gaps your organization will fill.
- Programs and services: This section describes all the programs and services the nonprofit will offer and mentions how they align with the nonprofit’s mission. For each program or service you outline, include the population the program serves and how you will measure its success.
- Fundraising strategy: How will your nonprofit generate the financial resources needed to support its mission? Include details about fundraising campaigns, grant applications, corporate partnerships, and other donor strategies.
- Organizational structure and management: List the nonprofit’s key team members. This may include the leadership team and staff, as well as a full list of the board of directors. If you rely on volunteers, include information about how you recruit, train, and manage them.
- Operations and administrative plan: Describe all the processes that keep your organization running from day to day. This might include administrative tasks, tasks associated with legal and regulatory requirements in the industry you serve, and fundraising. Mention internal communication and reporting procedures, as well.
- Marketing and outreach strategy: Describe how you will promote your programs and raise awareness of your cause. Include strategies for reaching donors, volunteers, and the beneficiaries of your services. This might include printed materials, social media campaigns, community events, and media outreach.
- Impact measurement: Outline the methods and metrics you will use to measure the impact of your nonprofit’s efforts. Include how you will evaluate the success of individual programs and services as well as how you will track progress toward long-term goals.
- Financial plan: Nonprofit organizations have an obligation to demonstrate fiscal responsibility. This section should include your projected operating budget, along with any income statements, cash flow projections, and contingency plans for financial difficulties.
Best For
Nonprofit organizations of all sizes—from grassroots community groups to large, charitable foundations—benefit from the structure and planning that composing a nonprofit business plan provides. A nonprofit business plan helps organizations that rely on donors, grants, or corporate partnerships attract funding. Newly formed nonprofits can use a nonprofit business plan to establish credibility and articulate their vision.
Business Plan Writing Services
If you need a business plan, but don’t want to write it yourself, you have two major options; use business plan writing software or pay a professional to create your plan. Several companies provide business plan writing services with experts who do market research and create custom-designed plans. Many of these companies also offer other writing services such as a pitch deck, feasibility study, or franchise-specific plans.
How to Choose a Biz Plan Writing Service
When choosing a business plan writing service, you first want to review the background of the writers. Some companies provide writers with MBAs (Master of Business Administration).
You also want to review samples of the business plans created. The company likely provided their best-designed business plans in their portfolio, so make sure to ask how much a particular well-designed business plan will cost; it may be out of your budget.
Cost of a Business Plan Writing Service
A basic business plan writing service will typically charge you a minimum of $2,000. If your plan requires extensive research, custom graphics, and enhanced overall design, that cost can go up to over $10,000.
Contact Your Local SBDC for a Review
If you have your business plan and are looking for someone to review it for feedback, your local SBDC (Small Business Development Center) may be able to help. The SBDC provides no-cost consulting and is funded in part by the SBA (Small Business Administration). There are over 1,000 SBDC locations across the US, most of them housed in or near state colleges and universities. Visit the SBDC website to find your local SBDC.
One of the SBDC’s core services is to provide detailed reviews of business plans. Depending on the expertise of your local SBDC Consultants, you may get lucky and have a business plan expert at your local center. Inquire if he or she can review your biz plan and provide feedback.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
These are the most common questions I hear about business plan types.
There are dozens of business plan types that you might use to create a roadmap for various business strategies. Most small businesses benefit from a traditional or a one-page business plan. Existing businesses can benefit from targeted business plans like an expansion plan, contingency plan, or feasibility plan.
Every business plan starts with an executive summary that highlights the key takeaways from the entire business plan. You’ll also typically need to include the following sections:
- Opening organizational and legal pages
- Company summary
- Products and services
- Market and industry analysis
- Marketing strategy and implementation summary
- Management and organization summary
- Financial data and analysis
- Appendix
Bottom Line
Various business plan types can help you plan your business strategy, attract business partners, or qualify for small business loans and grants. Your next steps after writing your business plan depends on your business type and the business plan type.
