Social entrepreneurship prioritizes social impact alongside profit. By addressing societal needs, this approach connects business success to doing social good.
What Is Social Entrepreneurship? Ultimate SMB Guide
This article is part of a larger series on Starting a Business.
Social entrepreneurship is a business approach focused on addressing social, cultural, or environmental issues. At the heart of social entrepreneurship are individuals who harness their entrepreneurial skills and resources to seek out lasting solutions to challenges often overlooked by conventional markets, working within a variety of organizational frameworks to achieve their goals.
Integrating social missions into business models offers a path to positive impact and consumer appeal. In this article, we cover how social entrepreneurship works, real-world examples, and steps to get started.
Social Entrepreneurship vs Traditional Business Models
Social entrepreneurship stands apart from traditional business models by prioritizing meaningful social impact as much as, or even more than, financial profit.
The key distinction of social entrepreneurship is how success is measured. Rather than focusing solely on financial returns, social enterprises evaluate their success based on the effectiveness and reach of their social impact. This approach does not disregard financial sustainability, but seeks a balance between economic goals and the mission to contribute positively to society.
Social Entrepreneurship: Key Areas of Interest
While many social entrepreneurs take part in multiple initiatives across various sectors throughout their careers, a social venture typically revolves around specific societal challenges. Some key areas that social entrepreneurs and their businesses might address include:
- Economic Development: Boosting job creation and financial opportunities in underprivileged communities through microfinance, business support, and employment platforms.
- Education: Enhancing access to quality education with innovative tools and programs, especially in underserved areas.
- Community Development: Strengthening communities through infrastructure development, social programs, and local engagement initiatives.
- Social Justice: Addressing inequalities and promoting rights and fairness in society.
- Gender Equality: Working to close the gender gap by promoting equal opportunities in education, employment, and leadership.
- Healthcare: Improving healthcare access and outcomes with affordable solutions, preventive care, and health education initiatives.
- Mental Health: Increasing awareness, access, and support for mental health services and initiatives.
- Agriculture: Supporting sustainable farming practices, improving food security, and increasing incomes for smallholder farmers.
- Environmental Sustainability: Focusing on conservation efforts, waste reduction, and promoting sustainable living practices.
- Renewable Energy: Developing and implementing affordable, clean energy solutions to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and combat climate change.
- Animal Welfare: Protecting and improving the lives of animals through rescue operations, habitat conservation, and advocating for ethical treatment practices.
There are roughly 11 million social enterprises across the world, according to the British Council’s 2022 report.
Types of Social Entrepreneurship Business Models
Social entrepreneurship can take the form of various business models to address social issues while ensuring long-term financial viability. These common models reflect the diverse goals of social entrepreneurs, from prioritizing profit to focusing solely on social impact.
The primary focus of these organizations is a social, cultural, or environmental mission. Any profits generated are not distributed to owners or shareholders, but are instead reinvested into their mission-focused projects. They may be eligible for tax-exempt status, reducing financial burdens and enhancing their ability to serve their mission.
Nonprofits often rely heavily on external funding sources such as donations, grants, and philanthropic contributions, as well as volunteer support to carry out their operations. They may engage in a variety of activities—including educational programs, health services, and environmental conservation efforts, aiming to bring about positive change without the motive of personal financial gain.
Hybrid models are an innovative approach to social entrepreneurship, blending the financial goals of for-profits with the social objectives of nonprofits. These businesses operate with a dual mission: to achieve financial sustainability and to make a significant social impact.
Hybrids have the flexibility to generate income through traditional business activities, services, or products, while also qualifying for grants and donations to support their social initiatives. This model allows them to diversify their funding sources and strategies, ensuring a more sustainable operation. A common form of hybrid organization is a social enterprise that may have a for-profit arm for revenue generation and a nonprofit arm for mission-focused activities.
Benefits of Social Entrepreneurship
Beyond making a positive impact, some of the main advantages of social entrepreneurship include:
| Customer Loyalty: Social enterprises attract ethical consumers and gain customer loyalty as many shoppers prefer supporting brands with a positive societal impact. | |
| Market Differentiation: Addressing societal issues helps social entrepreneurs stand out in competitive markets. | |
| Unique Funding Opportunities: Access to specialized funding sources like impact investments and grants can support projects that traditional financing might overlook. | |
| Attracting Talent: Passionate and talented individuals are drawn to social enterprises, bringing commitment and innovation that drive the business forward. | |
| Tax Advantages: Social enterprises may benefit from tax exemptions or incentives, allowing more resources to be channeled directly toward their social mission. | |
| Personal Fulfillment: Contributing to societal betterment offers social entrepreneurs personal satisfaction, often motivating them more than traditional business metrics. |
Challenges in Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurship is a unique field with its own set of challenges, including:
| Securing Funding: Finding investors aligned with both financial and social missions is challenging, limiting funding options for startup and growth. | |
| Balancing Goals: Maintaining a balance between social impact and financial sustainability requires careful management, planning, and responsiveness. | |
| Measuring Impact: Social impact is harder to quantify than financial performance, requiring detailed frameworks for assessment and communication. | |
| Regulatory Hurdles: Social enterprises face legal and regulatory complexities that differ from traditional businesses. | |
| Tax Complexity: Navigating tax codes and compliance is more challenging for social enterprises, often requiring expert guidance or consulting to optimize benefits and avoid pitfalls. | |
| Consumer Awareness: Building market understanding and trust in the social mission demands significant effort and transparent communication strategies. |
Including Social Entrepreneurship in Your Business
Whether you’re aiming to start a new social enterprise or just finding ways for your business to benefit the community, integrating social entrepreneurship involves these key steps:
Integrating Social Causes Into Your Business
For existing businesses wishing to incorporate social entrepreneurship as a partial focus, it begins with ethical practices that align with your values and resonate with today’s consumer concerns. Start by evaluating your supply chain for adherence to high social and environmental standards, and plan a phased transition to ethical sourcing.
Beyond that, you can commit a defined portion of profits to support social causes aligned with your business mission, reinforcing your societal contribution and building consumer trust through transparency.
Promoting sustainability is another area where businesses can make strides. You can work toward enhancing sustainability by pinpointing and improving areas like packaging, energy usage, and materials.
Involving employees through volunteer days, social impact initiatives, or incentives for supporting the company’s ethical mission not only enhances team spirit but also increases the business’s positive societal impact.
Starting a Social Entrepreneurship Journey
Starting a business within social entrepreneurship involves first identifying a cause that aligns with both personal values and business interests. Using resources like the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals can help pinpoint a relevant and impactful cause.
Next, choosing the right business model is essential. This includes determining how your offerings will address the chosen cause, with options ranging from nonprofit models focusing on social impact and funded by donations and grants, to for-profit models that balance earning with contributing, and hybrid models that blend the strengths of both for diverse funding and operational flexibility.

The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals website is a helpful resource for identifying global causes and actionable ways to address them.
Developing Engagement
Create a comprehensive plan to communicate your social enterprise’s mission and impact. Use a mix of channels—social media, email newsletters, your business website, etc.—to share compelling stories about your cause, the difference your business aims to make, and how stakeholders can get involved.
Your engagement efforts are crucial for capturing the attention of consumers, potential investors, employees, and applicants. But engagement isn’t just about sharing information; it’s about building a community around your mission.
Nonprofit organizations like the American Red Cross leverage social media to share success stories, awareness campaigns, and volunteer opportunities.
Navigating Networks & Funding
Joining networks is a great way to get started. Look for local or industry-specific social entrepreneurship networks, such as the Social Enterprise Alliance, Social Enterprise World Forum, or online forums like Next Billion. Engaging in their events or webinars allows you to learn from and connect with fellow entrepreneurs. These networks can provide valuable insights, share best practices, and offer resources.
Seek partnerships by collaborating with other businesses, nonprofits, and governmental organizations that can help guide your business journey and amplify your impact. Partnerships can also open up new markets and opportunities.
To access funding, look into grants available for social enterprises (like Small Business Innovation Research grants) and consider pitching to impact investors. Additionally, explore startup growth accelerators like Ashoka or Echoing Green that offer support to social entrepreneurs. Platforms like Kickstarter can also be used to launch products with a social mission.
Beyond this, pursuing certifications like B Corp can help validate and communicate your commitment to social responsibility. These certifications not only boost your credibility but also align you with a global community of businesses dedicated to making a positive impact.
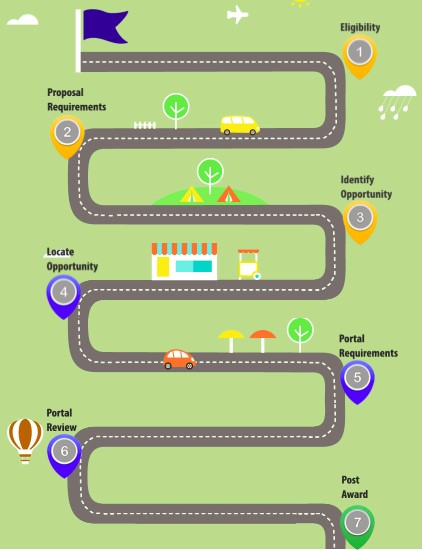
Small Business Innovation Research’s ‘roadmap’ explains the steps involved in the application process to receive a grant. (Source: United States Government)
Social Entrepreneurship Tips
When diving into social entrepreneurship, these tips can serve as guiding principles for creating meaningful change while starting a successful venture:
- Build Your Brand: Establish a strong brand identity through visual elements like logos, color schemes, and consistent messaging that reflects your social mission.
- Document Your Journey: Keep a record of your progress, challenges, and impact. This documentation can be highly valuable for storytelling in marketing or awareness campaigns, attracting investors, and refining your strategy.
- Stay Informed: Regularly read up on social entrepreneurship trends and case studies. Resources like the Stanford Social Innovation Review and the Harvard Business Review can provide useful insights.
- Measure Your Impact: Develop a framework for measuring your social impact from the start. This can include both quantitative and qualitative performance metrics tailored to your specific mission. Examples include school attendance rates in underserved communities, gallons of clean water provided, or percentage increase in local employment.
- Prioritize Transparency: Be open about your business practices, sourcing, and the allocation of profits toward your social mission. Transparency builds trust with your customers, employees, and partners, reinforcing your commitment to ethical practices.
- Engage Your Community: Actively involve your community in your mission. This can be through interactive events, social media engagement, or community projects.
8 Social Entrepreneurship Examples
Exploring the paths of successful social enterprises reveals how innovative models can drive both business success and significant social impact. These companies are great examples of the possibilities and diverse strategies of social entrepreneurship.
IKEA

(Source: IKEA)
Since 2012, IKEA has partnered with social entrepreneurs globally, focusing on creating jobs and tackling environmental challenges. This collaboration includes working with organizations like the Jordan River Foundation to develop unique products that support sustainable livelihoods for artisans, including refugees.
TOMS

(Source: TOMS)
TOMS introduced the one-for-one giving model, donating shoes for each purchase, inspired by children’s needs. This unique approach set TOMS apart in a crowded market, highlighting its social commitment. The company later expanded its focus to address additional community needs like mental health, access to opportunity, and ending gun violence.
Warby Parker

(Source: Warby Parker)
Similar to TOMS, Warby Parker was founded with a clear social mission to ensure that a pair of glasses would be donated for each pair bought. This model addressed the issue of impaired vision affecting people’s ability to learn and work, particularly in low-income communities. Over time, Warby Parker honed its strategy by collaborating with nonprofit partners to directly deliver glasses to those in greatest need, increasing the impact of its donations.
Ben & Jerry’s

(Source: Harvard Business Review)
Since 1985, Ben & Jerry’s has led in social entrepreneurship by donating 7.5% of pretax profits to social causes, focusing on justice and environmental conservation. It also works to reduce emissions, notably through the use of solar power at its Vermont factory, and is recognized as a B Corp for its commitment to social and environmental issues. The brand effectively uses social media to combine product promotion with social activism, engaging a broad audience with its mission.
Merit

(Source: Merit Goodness)
Merit combines high-quality clothing with a mission to support education, dedicating 20% of its profits to a program that aids Detroit-area students in preparing for college. Beyond financial support, Merit enriches students’ experience with mentorship, tools, and guidance, and engages 10th graders in capstone projects where they design and produce their own product collections.
The Ocean Cleanup

(Source: The Ocean Cleanup)
The Ocean Cleanup, founded by Boyan Slat at the age of 18, is a nonprofit aiming to reduce ocean plastic by 90% by 2040. Starting with a focus on the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, they’ve deployed innovative systems to capture and remove plastic waste, including river-cleaning initiatives. These efforts mark significant progress in combating ocean plastic pollution.
Benetech

(Source: Benetech)
Benetech is a nonprofit that uses technology to improve education for underserved groups, such as those with learning differences. Their Bookshare initiative offers customizable e-books, while Service Net facilitates data sharing among social service organizations. With these efforts, Benetech has empowered over 1.5 million individuals worldwide.
Goodwill

(Source: Goodwill Industries International)
Well-known thrift retailer Goodwill Industries International empowers individuals through employment opportunities, offering job training and placement services. Its network spans the US, Canada, and 13 other countries, adapting to local needs. As a hybrid organization, Goodwill bridges business and social change, creating impactful community solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some questions we frequently encounter about social entrepreneurship.
Bottom Line
Social entrepreneurship empowers businesses to drive profit while making a positive impact on society. By identifying a mission, using the right business model or strategy, and engaging the community, businesses can create a more sustainable and equitable future while generating financial sustainability and consumer appeal.