Encryption is critical in unified communications (UC) to protect company data from being stolen or copied. Since UC solutions send information over the internet as data packets, they are vulnerable to eavesdropping techniques and local network breaches—putting your company communications system at risk. In this article, we explain why unified communications security is essential for businesses and the various ways to protect data through encryption.
Why UCaaS Encryption Is Critical for Businesses
Encryption is regarded as one of the essential components of a company’s cybersecurity strategy. It enhances data security, maintains company integrity, protects against breaches, and ensures regulatory compliance.
1. Enhances Data Security
Unified communication as a service (UCaaS) platforms have certain attributes that make them more difficult to secure than standard client-server apps. As a cloud-based tool, anyone can access it anywhere using any device. This makes it easy for people with bad intentions to obtain and intercept data moving between the UC provider’s server and the remote user’s device.
This is where encryption comes in—by keeping the web traffic safe and ensuring only the intended users have access to the data they share. Encryption works by converting plain text data into an unreadable format before transferring it to the cloud, thus protecting it from unauthorized users.
This algorithm makes any data sent through your UCaaS provider indecipherable without the encryption key. Ultimately, encryption offers an extra layer of data protection.
2. Maintains Company Integrity
As cybersecurity attacks rise, customers are naturally wary of sharing sensitive information with companies. However, when you proactively take steps to safeguard sensitive information, such as names and addresses, Social Security numbers, and credit card numbers, you effectively gain the trust of your key stakeholders. Your commitment to protecting customers’ data forms part of your credibility and helps you win more clients over time.
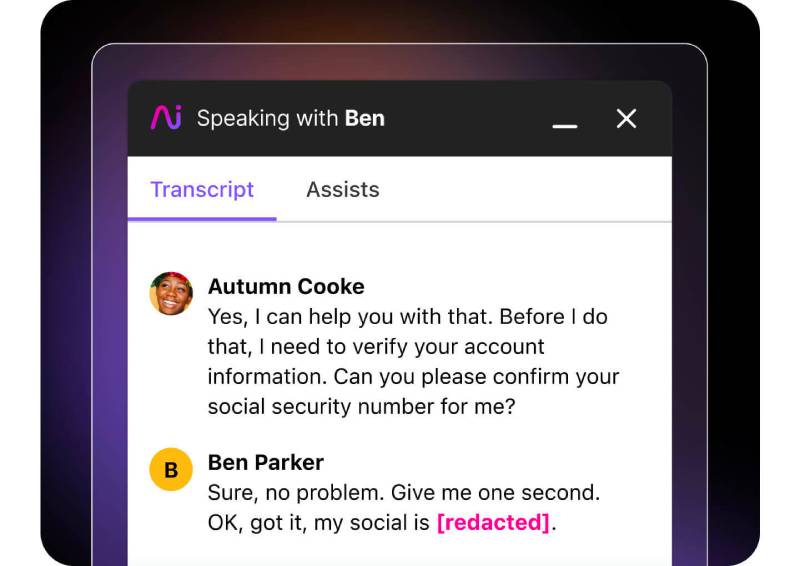
Dialpad AI automatically censors sensitive information in call transcripts. (Source: Dialpad)
Reliable voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) system Dialpad has an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered feature that automatically detects and obscures personal identifiable information (PII) in real-time call transcripts. PII includes credit card and Social Security numbers. Aside from improving data security, the automated redaction process saves time and, therefore, reduces operational costs, especially when managing large data volumes.
Use this platform to improve data security and maintain company integrity. To learn more about its AI features, read our comprehensive Dialpad review. Its monthly subscription starts at $23 per user.
3. Protects Against Breaches
Data breaches not only result in loss of customer trust but also serious financial and legal consequences. According to the latest IBM Security report, the average cost of a data breach reached an all-time high in 2023 of $4.45 million. The figure is a 2.3% increase from 2022 and a 15.3% jump from 2020. The breach-related costs come from detection and escalation, post-breach response, revenue losses from system downtime, and ransom demands.
Meanwhile, data breach lawsuits may involve different types of damages, from identity theft and fraud-related costs to loss of income and emotional damages. The financial and legal repercussions of data breaches may lead to the business’ bankruptcy. By adopting unified communications security mechanisms, you significantly reduce the likelihood of costly, reputation-damaging breaches.
4. Ensures Regulatory Compliance
Specific laws and industry standards require businesses to implement data encryption. For healthcare companies, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires all Protected Health Information (PHI) transmitted electronically to be encrypted.
Meanwhile, organizations that handle cardholder data must comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), which mandates using strong cryptography to make primary account numbers (PANs) unreadable. Failure to abide by these regulations results in hefty penalties or imprisonment.
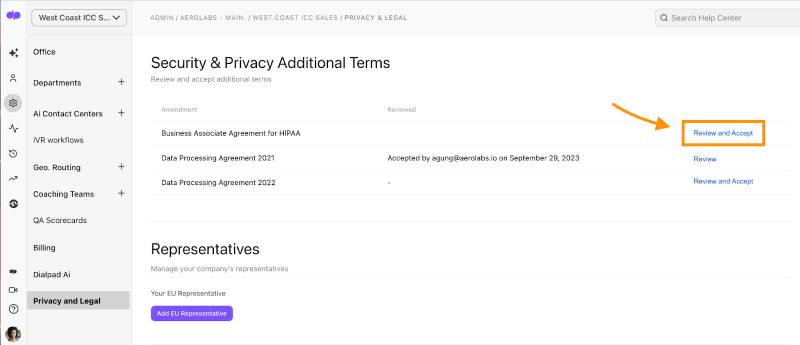
Dialpad lets companies sign a Business Associate Agreement for HIPAA. (Source: Dialpad)
Types of Security Methods for Encrypting UCaaS
With the emerging threats and vulnerabilities of unified communications solutions, it’s important to understand the associated security protocols when choosing a provider. Fundamentally, UCaaS security protocols must include encryption to protect data when at-rest and in-transit.
Click on each encryption method below to learn how providers encrypt your company data and maintain unified communications security.
UCaaS providers house data centers in multiple, globally disparate locations to keep their uptime percentages high. Georedundancy, the process of employing multiple servers worldwide, ensures that if one center is attacked or suffers a disaster, the others can instantly and seamlessly pick up the slack.
A UC provider uses data center encryption to protect at-rest data stored in these locations. This uses an encryption key to ensure data theft will result in scrambled information.
Here are two methods your provider may use to encrypt data as it is being stored:
- Full-disk: Full-disk encryption might use the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which encrypts fixed data stores. Keys using AES have options for texts that can be 128, 192, or 256 bits. The key or passphrase is entered directly when the system boots up.
- Database: This type of encryption is done on servers and may also use AES for encryption. Since these data centers are remote in most cases, remote passphrase or key entry is used by administrators when the databases start up.
Also known as E2EE, end-to-end encryption applies a layer of encryption only to the devices that are at play. As a result, sending data to a recipient is completely protected via scrambling from hackers attempting to listen in. The only party able to unscramble the transmitted data is the addressee.
E2EE technology also protects browser-based communications. If your customers or colleagues initiate a call from any Chromium 83-based browser that supports insertable streams, their communications will be secure.
One of the advantages of E2EE is that the sender or the recipient only decrypts it. The message cannot be altered while it’s in transit, and if someone attempts to access it at this stage, the message will be completely unreadable when it arrives. The downside is it doesn’t hide the fact that data was transferred and doesn’t protect information sent or received using a stolen device.
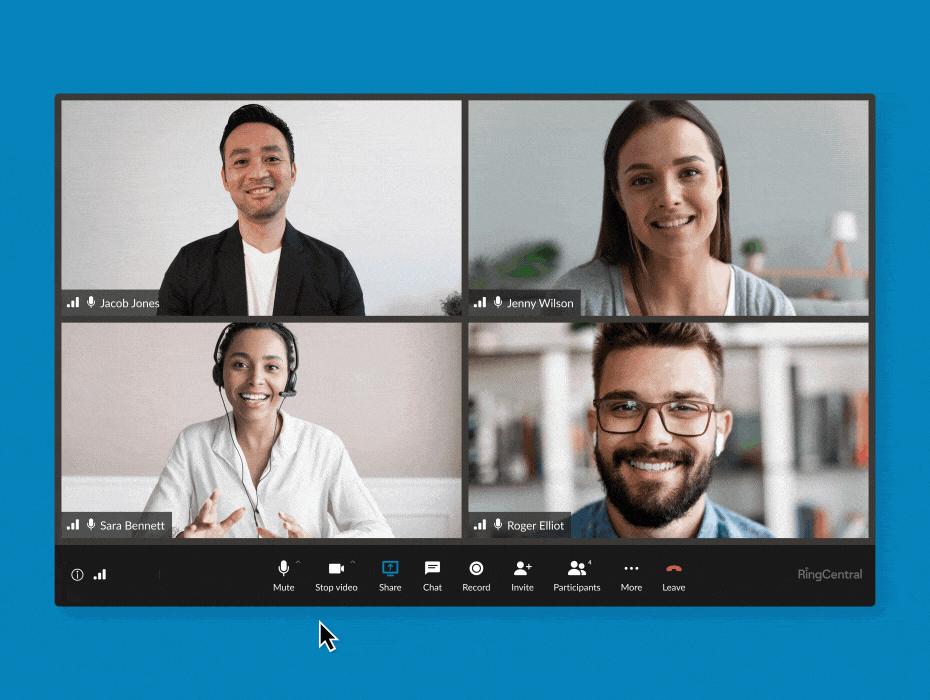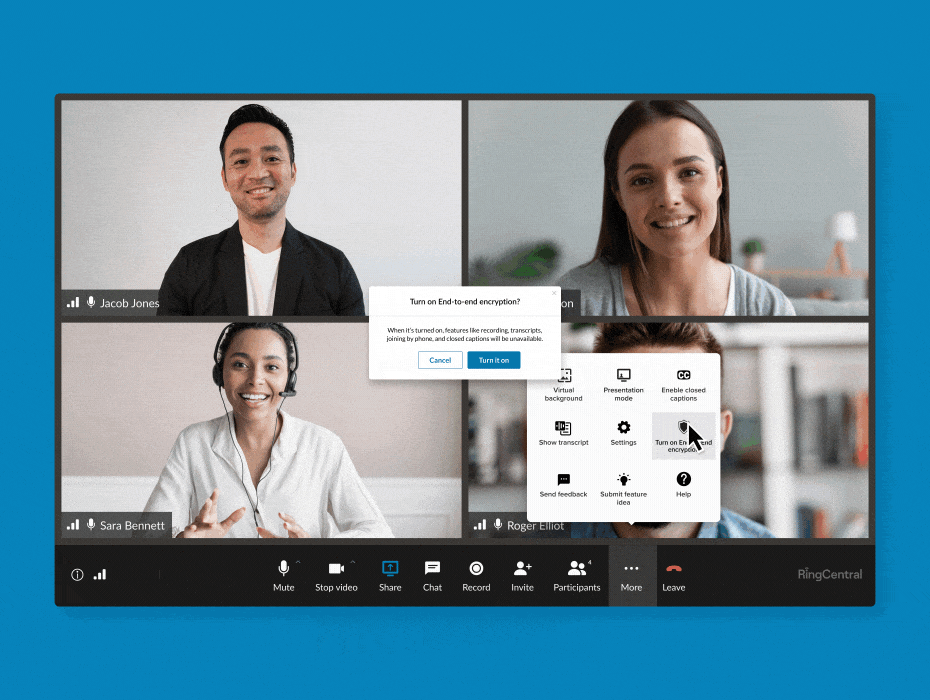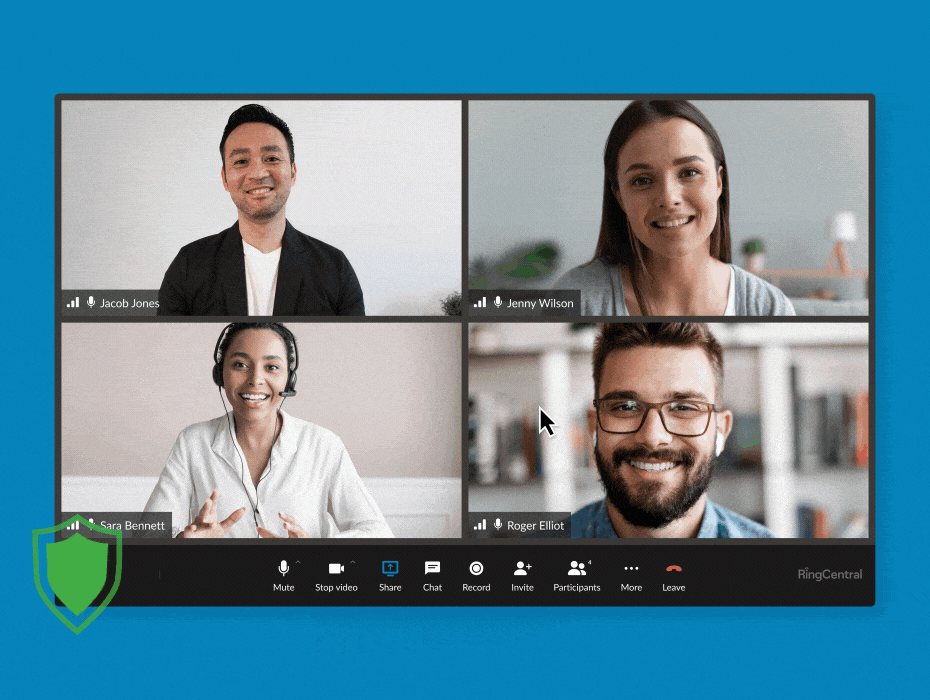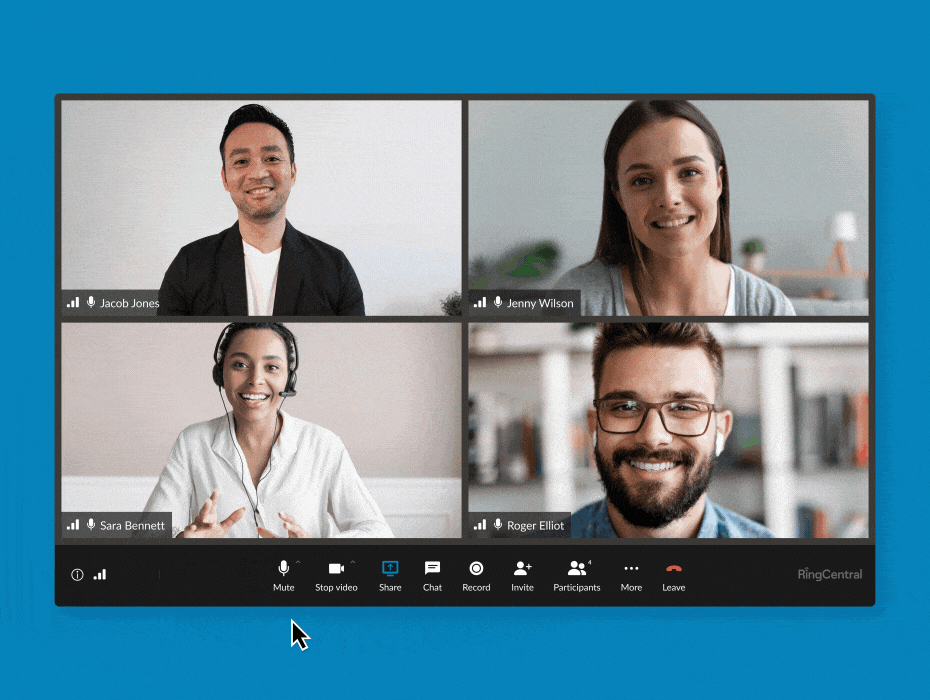
RingCentral supports end-to-end encryption for video meetings. (Source: RingCentral)
Business phone system RingCentral features E2EE in its video conferencing, allowing users to turn it on and off whenever needed. You have the flexibility to enable it when participants discuss sensitive information and then disable the feature when you’re done. All communications shared via audio, video, screen sharing, or chats are protected when E2EE is on.
In the event that the provider’s cloud servers are attacked by bad actors, you’ll have the peace of mind that data remains confidential. RingCentral’s E2EE is available on desktop and mobile apps and browsers. Refer to our RingCentral review for more information about the business phone system. If you’re ready to adopt the platform in your operations, subscribe to its base-level plan for only $30 per user, monthly.
Most providers’ UCaaS security measures include secure real-time transport protocol (SRTP) and transport layer security (TLS), which protect data transmission. SRTP is a transport protocol that securely sends data packets using cryptographic ciphers. The primary method for encryption with SRTP is AES, reducing the chances of targeted attacks using direct denial of service (DDoS).
SRTP is flexible enough to add new encryption algorithms when needed. Some providers like Dialpad use their additional keys to ensure even greater security during UCaaS processes like conference calls and online meetings.
TLS protects some of the finer-tuned details of your call, like phone numbers. It encrypts detailed information like usernames to restrict access from external parties. TLS’ main methodology uses a public key infrastructure (PKI) hierarchy that is only made available to the administrator.
Usernames and passwords used in UCaaS transmissions are completely indecipherable once sent by outside forces. After the TLS handshake is completed, when a connection is established, encryption begins. While the public key is accessible to most, the secondary private key’s mathematical relationship to the public key has complex algorithms so that the message will be nearly impossible to decipher.
Best Practices for UCaaS Security
Given the cybersecurity risks involved in moving communications to the cloud, it’s important to find a unified communications solution with robust privacy and encryption features. Consider the providers’ security infrastructure and practices before choosing a solution. At the very least, they must have georedundancy, penetration testing, and incident response. Additionally, check the global compliance standards they adhere to, paying attention to your industry regulations.
Aside from choosing a secure UCaaS solution, be aware that human errors may also result in data leaks and breaches. For this reason, you must follow these best practices for unified communications security:
Enforce a Strong Password Policy
This reduces the likelihood of successful hacking of team members’ accounts. Use a combination of random words or phrases, numbers, upper and lower cases, and symbols when creating a password. To make password management easier and safer, get a corporate password manager app that keeps all passwords in one secure location.
Limit Company Data Access
Unrestricted user access increases the risk of exposing confidential data, especially when team members are unaware that they’re dealing with sensitive information. Moreover, when an account is compromised, unrestricted access allows bad actors to further infiltrate the system. To reduce these risks and secure unified communications, provide access to select data only that team members need to perform their responsibilities.
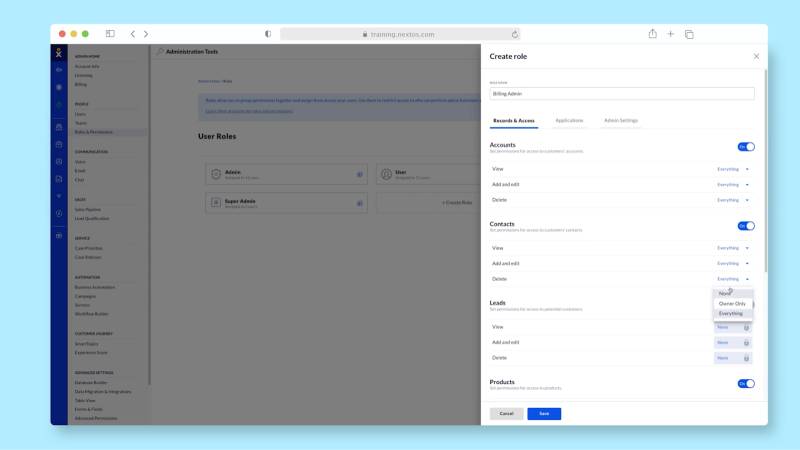
Nextiva allows you to create custom roles to manage data access. (Source: Nextiva)
Unified communications solution Nextiva lets team leaders configure permission settings based on the user role. It features different user permission settings categories, including Applications and Admin. The Applications settings control access to analytics and surveys, while Admin is for account and billing information, customer data, and voice and chat settings.
Our Nextiva review outlines other capabilities that help secure business communications. Start using this business phone solution for only $30.95 per user, per month.
Let Remote Workers Use Virtualized Private Network (VPN)
Many on-the-go employees use public Wi-Fi to stay connected when traveling. Unfortunately, hackers take advantage of these unsecured networks to steal personal information and login credentials from unsuspecting individuals. With VPN, all the data sent between the device and the router are encrypted, making access to data difficult.
Revisit Call Logs Regularly
This helps you determine your team’s normal usage and take corrective actions when you detect excessive use. A large volume of activities may point to entities gaining unauthorized access to your system. Some VoIP security threats involve bad actors making high volumes of calls to premium international numbers, thus increasing your communication costs.
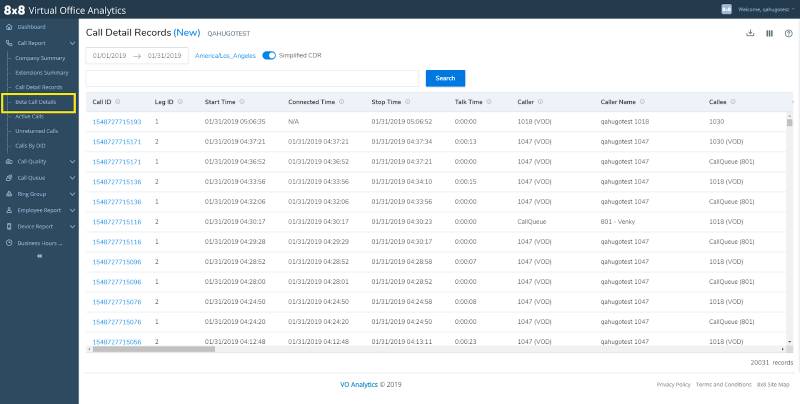
8×8 provides a comprehensive report on call detail records. (Source: 8×8)
Business phone solution 8×8 lets users easily check call logs with its call detail records. The report offers the most important information about previous calls: start time, connected time, stop time, and talk time. Similarly, it outlines the caller’s name and callee. With this comprehensive report and by checking billing statements, you’ll be able to easily spot anomalies in call center activities. Check out our extensive 8×8 review to learn more about its features.
If you’re keen on using this platform for business communications, the provider offers five subscription plans with custom pricing. Contact 8×8 to learn the exact rates.
Install Firewalls
Firewalls improve cybersecurity by preventing malicious traffic from infiltrating your network. Moreover, it keeps malware from accessing the network or devices through the internet. This preserves the security and integrity of your system, customer data, and stakeholder communications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Unified communications face various security threats, including Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, packet sniffing, and call tampering. DDoS involves overwhelming a targeted server with traffic to disrupt normal operations, while packet sniffing allows bad actors to intercept sensitive data transmitted through a network. Call tampering is when hackers add noise packets to an ongoing call, making it hard for participants to understand each other.
A communications security system is a set of methodologies prohibiting unauthorized entities from accessing telecommunications data. It involves various disciplines, including cryptographic security, which involves encrypting data to make it unreadable to outside parties, and transmission security, which prevents unsanctioned access to data being physically transferred to avoid service interruptions.
The primary function of unified communications is to integrate different communication channels into one platform. These channels include phone, short messaging service (SMS), instant messaging, and video conferencing.
Bottom Line
Any business that uses a cloud solution like UCaaS should have a proper encryption strategy to fight cyberattacks. Pick the right UCaaS provider for your business to help you reap the security benefits of unified communications. In the same way, empower your workforce with ample training on data security to prevent data breaches resulting from unawareness. With the right tools and knowledge, you’ll be able to safeguard company data and preserve customer trust.