Wi-Fi calling is a voice technology that enables users to place and accept a voice call through a Wi-Fi network rather than the carrier’s cellular service. It’s commonly used to connect with contacts when you have little to no cellular signal. Most smartphones are equipped with this feature, but you must turn it on your mobile device’s phone settings to use it. In this article, you’ll learn more about what a Wi-Fi call is and how it benefits users.
Key Takeaways:
- Wi-Fi calling allows users to make a voice call through a Wi-Fi network.
- Wi-Fi calling benefits businesses because it’s less costly than cellular data and enables remote workers to stay connected to contacts in a location with a poor cellular signal.
- While it offers excellent benefits, using Wi-Fi calling may put company data at risk, especially when users connect to public, unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
- To activate Wi-Fi calling, users must toggle on the option on their device’s phone or connection settings.
How Wi-Fi Calling Works
Wi-Fi calling works by sending cellular data packets through a Wi-Fi connection, using voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) as opposed to the voice-over LTE network (VoLTE) protocol, which requires telecommunication providers’ mobile network.
Here’s a more detailed process of how Wi-Fi calling works:
- Step 1: A team member (e.g., agent) connects to the Wi-Fi and places a call on their mobile device with the Wi-Fi calling feature enabled.
- Step 2: The phone automatically detects the strongest network available after a phone number is dialed.
- Step 3: A request for a call is sent to the cellular service provider’s servers through the Wi-Fi network.
- Step 4: The provider’s servers connect the call to the answering party.
- Step 5: The answering party’s device receives the call through their cellular network.
- Step 6: The call is routed back to the caller through the Wi-Fi network, connecting the two parties.
The top cellular carriers support Wi-Fi calling, and the majority of iOS and Android devices offer built-in Wi-Fi calling capabilities. Given that the feature is built into the phone’s native dialer, you won’t need to open an app like Skype or Messenger to make and receive calls over Wi-Fi. The phone will automatically enable Wi-Fi calling if this feature is set as a default for placing calls. Similarly, it may be the backup solution when you have a spotty cellular reception.
Benefits of Wi-Fi Calling
Now that we understand the basics of Wi-Fi calling, let’s drill down into its advantages so you’ll know when it’s best to use the feature. These are the pros of Wi-Fi calling:
Most businesses already use Wi-Fi networks to sustain everyday operations. Since you’ll be using an existing network to place phone calls, you won’t have to worry about additional costs. If your employees work in the office most of the time, subscribing to cellular plans and providing dedicated business phones won’t be necessary. Workers will simply connect to your office’s Wi-Fi and may use their personal phones to communicate with team members and customers.
As mentioned, part of how Wi-Fi calling works is that modern smartphones offer this feature, allowing users to directly call contacts without launching an app on their phone. The zero-hassle setup and account registration make for an easier, faster way of connecting to colleagues and clients. On top of that, you don’t need to import or add phone numbers since the phone already has access to your phone book.
A smartphone’s battery drains fast when constantly searching for a cellular signal. With Wi-Fi calling enabled and the device connected to password-protected public Wi-Fi, you’ll save the phone’s battery life. This is especially beneficial for employees who frequently travel for business and cannot afford to run out of power when working remotely.
By using a wireless connection, you’ll be able to make calls even when you’re in an area with no cellular signal. In cases where the reception is unstable, Wi-Fi calling is automatically activated, supporting active calls. With this, you won’t have to endure choppy conversations and miss important details discussed.
Disadvantages of Wi-Fi Calling
While Wi-Fi calling is a cost-effective, convenient option for reaching contacts when you’re in a remote location, it comes with drawbacks. It’s important to be aware of these disadvantages to manage expectations and prepare for situations where Wi-Fi calling is less ideal to be used.
The quality of Wi-Fi calls depends on signal strength. In the office, you may have enough bandwidth to support multiple connected devices. However, in other public places, like airports or cafes where you’ll be sharing the connection with several others, fast internet isn’t guaranteed, affecting the quality of your phone calls.
To make a high-quality VoIP call, you must have a minimum bandwidth of 1 megabit per second (Mbps). Otherwise, you may experience VoIP problems like garbled sounds or dropped calls.
Confidential business information in calls may be compromised when you connect to free Wi-Fi in public places. Most of these networks are unencrypted, allowing bad actors to intercept data or use uninterrupted access to launch other types of costly, reputation-damaging cyberattacks.
To prevent this, avoid connecting to unsecured Wi-Fi networks. Choose a password-protected Wi-Fi, such as those available in airport lounges or cafes, and use a virtual private network (VPN). Be familiar with other VoIP security threats to adopt appropriate data protection measures.
When the Wi-Fi connection falters or you go to an area without Wi-Fi, your phone automatically switches to using data to support calls. This may result in fees for the internet service you didn’t plan on using. To avoid unplanned charges, revisit the Wi-Fi calling settings and tick off the option “Never use Cellular Network.” You may also turn on airplane mode while the Wi-Fi and Wi-Fi calling are enabled.
How to Turn on Wi-Fi Calling in Phones
To become more familiar with Wi-Fi calling and its benefits, set it up on your mobile device. Follow the simple steps below for enabling it on smartphones:
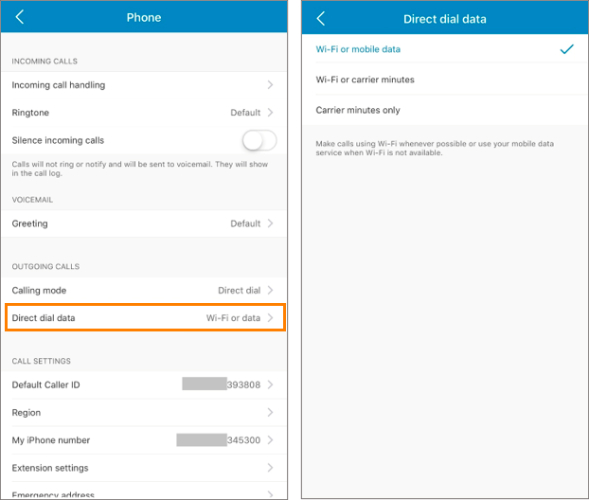
The first option for activating Wi-Fi calling on iOS is to go to Settings and select “Phone.” Tap “Wi-Fi Calling” and toggle the “Wi-Fi Calling on This iPhone” option. Here’s the other option:
- Go to Settings, scroll through the options, and select “Cellular.”
- Tap “Wi-Fi Calling.”
- Toggle on the “Wi-Fi Calling on This iPhone” option.

Activate Wi-Fi calling on iOS’ cellular settings. (Source: T-Mobile)
An interesting feature to note when exploring Wi-Fi calling on iPhone is the option to activate this tool on other iOS devices like MacBook and iPad. When you toggle on the option “Add Wi-Fi Calling For Other Devices,” the devices signed into the iCloud account are able to place calls when your mobile is not nearby.
Follow these steps to set up Wi-Fi calling on Android phones:
- Launch the phone app.
- Tap the triple dot icon at the right-hand side of the screen next to the search icon and select “Settings.”
- Find the “Wi-Fi Calling” option and toggle it on.
Meanwhile, for Samsung phones, these are the simple steps:
- Go to Settings and tap “Connections.”
- Toggle on “Wi-Fi Calling.”
- Choose the “Wi-Fi preferred” option.
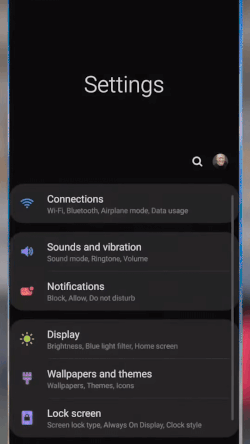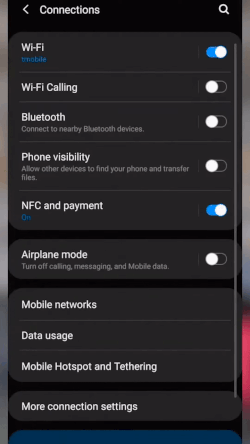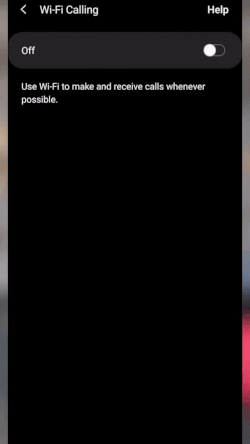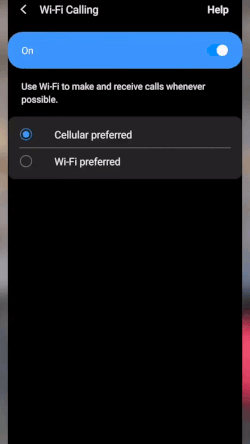
Enable Wi-Fi calling on Android’s connections settings. (Source: T-Mobile)
Top Phone Systems With Wi-Fi Calling
Now that you have learned Wi-Fi calling’s definition, its pros and cons, and the steps for setup, we’ll explore the different virtual phone systems that feature Wi-Fi calling. While you technically don’t need a softphone app to enable Wi-Fi calling since it’s built into your phone, you might need a VoIP service if your carrier doesn’t support this technology.
Moreover, if you plan to use this feature on your desktop, you must download the provider’s softphone app to place and accept calls. These are some of the top business phone systems worth considering:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes. Wi-Fi calling comes at no additional cost since you only need a Wi-Fi connection to use it. However, you may be charged fees if you place international calls. The exact cost will depend on your phone service provider.
Yes. When the Wi-Fi signal is weak or you go to a dead zone, your device will use the carrier’s cellular network and switch to VoLTE to sustain the call.
The status bar shows the name of the carrier followed by “Wi-Fi” when you’re using Wi-Fi calling. Meanwhile, it will display the name of the carrier followed by “using cellular data” when you’re on cellular.
Bottom Line
Wi-Fi calling saves companies more on communication costs as it eliminates the need for on-site employees to get separate cellular plans and business phones. For on-the-go workers, Wi-Fi calling through public networks enables staying connected to colleagues and customers even in a location with poor cell reception.
Now that you know the basics and benefits of Wi-Fi calling, configure your phone settings and activate this feature using the simple steps mentioned in this article. Consider VoIP providers offering Wi-Fi calling and other useful call management features to streamline business communications efficiently.