Businesses are increasingly opting for cashless transactions as they seek to streamline operations, increase efficiency, enhance security, and cater to consumer preferences. The transition from traditional cash-based transactions to digital payment methods has accelerated, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic when contactless payments had become a preferred way to pay.
Key Takeaways:
- The shift toward cashless transactions is driven by businesses’ desire to streamline operations, enhance security, and meet evolving consumer preferences.
- While cashless transactions offer numerous benefits, businesses must navigate challenges such as technological requirements, security concerns, and regulatory compliance.
- Cashless businesses face regulatory scrutiny, particularly regarding issues of financial inclusion and equitable access to goods and services.
- The most popular cashless payment methods in the US in 2022 are credit and debit cards, followed by ACH payments.
The Rise of Cashless Transactions
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift from cash to card payments, as consumers and businesses alike sought to minimize physical contact and adhere to social distancing measures. Concerns about the potential transmission of the virus via cash transactions prompted many individuals to embrace digital payment methods as a safer alternative. As a result, businesses witnessed a surge in card payments and online transactions, leading to a significant reduction in cash usage.
Prior to the pandemic, an increasing number of businesses, particularly in urban areas, were adopting cashless payment policies. According to a report by The Federal Reserve, cash use has declined from 2021 (20%) to 2022 (18%), while card use has increased from 57% to 60%.
Aside from the growing preference among customers for cashless payment methods, many establishments recognize the benefits of cashless transactions such as improved efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer experiences. However, the prevalence of cashless businesses sparked debate and controversy, with critics raising concerns about financial exclusion and discrimination against individuals who rely on cash for their transactions.
In response to the perceived drawbacks of cashless businesses and concerns about equitable access to goods and services, several states have enacted legislation to ban or regulate cashless payment policies. States such as New York, Philadelphia, San Francisco, and the district of Washington, D.C. have implemented laws requiring businesses to accept cash as a form of payment. These measures are designed to ensure that all consumers, including those who may be unbanked or underbanked, have the option to pay with cash.
Benefits of Going Cashless
Going cashless offers numerous advantages for businesses, contributing to increased efficiency, enhanced security, and improved financial management. Below are some of the key benefits associated with adopting cashless payment methods:
- Faster Transactions: Physical currency handling and manual cash counting are eliminated with cashless payments, making transactions faster overall. This efficiency minimizes transaction times, reduces wait periods at checkout, and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Lower Costs: Cashless transactions can help businesses reduce operational costs associated with cash handling and management. When there is no physical currency, businesses can avoid expenses related to cash counting, storage, and transportation.
- Lower Exposure to Crime: Cashless businesses are less vulnerable to theft and robbery compared to establishments that primarily deal with cash. Many small businesses like food trucks, gas stations, bazaar stalls, and small convenience stores, are more prone to petty theft, and keeping a lot of cash on their premises increases their crime-related risks.
- Reduced Transaction Mistakes: Errors or mistakes when handling cash transactions are not uncommon in small businesses. Some of these common mistakes are incorrect cash counts, misplaced or lost cash, and lack of reconciliation. Digital payment systems offer built-in features such as automated transaction tracking and reconciliation, reducing the likelihood of errors or discrepancies in financial records. This helps businesses maintain accurate accounting and financial reporting practices.
- Tendency to Increase People’s Spending: Businesses that aim to upsell or increase their customer’s spending will benefit from the cashless effect. This effect is the tendency to spend more or be willing to pay more when paying with a card or other digital forms of payment. The convenience and ease of digital transactions can lead to impulse purchases and higher average transaction values, ultimately boosting sales for businesses.
- Streamlined Recordkeeping: Cashless transactions enable businesses to easily maintain detailed and accurate records of all financial transactions. Electronic receipts and transaction logs facilitate seamless recordkeeping, simplifying accounting processes and providing valuable insights into business performance.
Challenges & Considerations
Transitioning to a cashless business model presents various challenges and considerations for small businesses. While there are compelling reasons to adopt cashless payment methods, businesses must navigate potential obstacles and address key considerations to ensure a successful transition. Below are some challenges and considerations associated with going cashless:
Technological Requirements
Going cashless entails significant investments in technology infrastructure, including point-of-sale (POS) systems, payment terminals, and digital payment processing software. Small businesses may face difficulty in selecting and implementing the right technology solutions that meet their needs while ensuring compatibility and security.
Related:
Initial & Ongoing Costs
The upfront costs of adopting cashless payment systems, such as hardware and software purchases, installation, and training, can strain the financial resources of small businesses. Additionally, ongoing expenses related to transaction fees, equipment maintenance, and software updates may impact profitability and cash flow in the long run.
Related:
Security Concerns
Digital payment systems introduce new security considerations and vulnerabilities that businesses must address to protect sensitive customer data and mitigate the risk of fraud and cyberattacks. Small businesses must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, tokenization, and regular security audits, to safeguard against potential threats and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Related:
Customer Education & Adoption
Educating customers about the benefits and procedures of cashless transactions is essential to encourage adoption and minimize resistance to change. Small businesses may encounter challenges in promoting cashless payment options effectively and addressing customer concerns about security, privacy, and convenience.
Accessibility & Inclusivity
While cashless transactions offer convenience and efficiency for many customers, businesses must ensure that they remain accessible and inclusive for all population segments, including those who may not have access to bank accounts or digital payment methods. Despite the increase in cashless transactions, around 93% of consumers plan to continue to use cash as a mode of payment. In some states, going fully cashless is illegal as it will discriminate against the homeless, elderly, immigrants, and low-income earners.
Regulatory Compliance
There are many regulatory considerations for cashless transactions and small businesses will need to navigate this complex landscape. Some regulations to consider involve consumer protection laws, Payment Card Industry standards, and data privacy regulations. Ensuring compliance with applicable regulations and standards requires ongoing monitoring, adherence to best practices, and investment in compliance-related resources and training.
Related:
Cashless Payment Trends & Outlook
There is a significant shift towards cashless transactions around the world. Here are some statistics that underscore this shift and offer insights into the growing prevalence of cashless payments:
- In a 2022 Pew Research Center survey, 41% of Americans said none of their purchases were paid with cash, an increase from 29% in 2018.
- According to a 2022 report, around 89% or nine in 10 Americans are using digital payments, and around 62% have used two or more forms of digital payments.
- The use of cash payments decreased from 2016 to 2022. Around 46% of consumers who used cash in 2022 are 55 years or older.
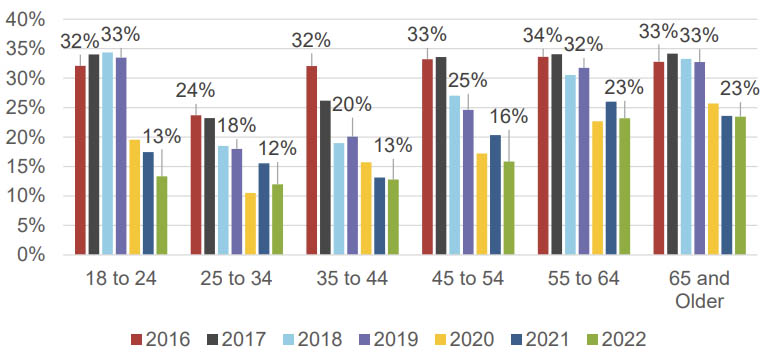
Shares of cash use by age group (Source: Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco)
- Households with less than $25,000 annual income make up 36% of cash payments in 2022.
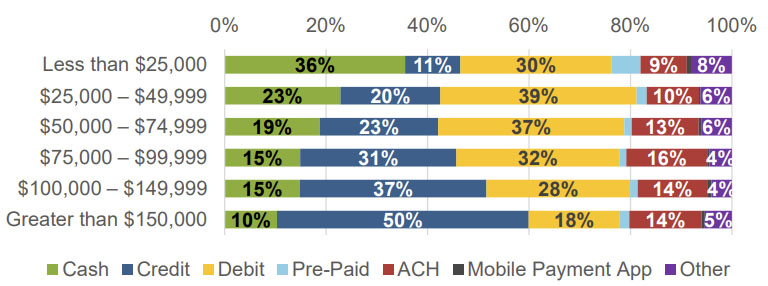
Share of payment instrument use by household income (Source: Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco)
- As of February 2023, 26 states have introduced proposals to ban cashless establishments.
- The Asia-Pacific region has the most number of cashless transactions. It is estimated to have 515 billion transactions in 2022, with Europe coming in second with 290 billion transactions, and North America in third with 218 billion transactions.
- The number of cashless transactions worldwide is projected to be around 2.2 trillion transactions by 2027, an increase of 126% from 1,016 billion transactions estimated in 2022.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Click through the sections below to read answers to common questions about cashless transactions:
A cashless business is an establishment that conducts its transactions entirely through digital payment methods, such as credit cards, debit cards, mobile wallets, or online transfers, without accepting cash as a form of payment.
Many businesses are going cashless because of the growing preference of consumers for cashless payment methods. Also, a cashless business approach eliminates the need for physical currency handling and offers benefits such as increased efficiency, enhanced security, and streamlined recordkeeping.
The problem with cashless businesses is that it excludes certain demographics, particularly those who rely on cash for transactions, such as the unbanked or underbanked population. According to people who are against cashless businesses, refusing cash payments is a form of discrimination against individuals who do not have access to digital payment methods, potentially exacerbating financial inequality. Additionally, cashless policies can raise concerns about privacy, security, and customer choice, prompting regulatory scrutiny and public debate.
Whether to make your business cashless depends on various factors, including your target market, industry norms, and operational considerations. Although transitioning to a cashless model can offer benefits, it’s essential to consider potential drawbacks. Evaluate your business’s unique needs, customer preferences, and regulatory landscape to determine if going cashless aligns with your business goals and values.
Bottom Line
The shift toward cashless transactions offers numerous benefits for businesses, including increased efficiency and enhanced security. However, it’s crucial to carefully consider the potential drawbacks, such as excluding certain customer demographics and navigating regulatory challenges. Ultimately, the decision to go cashless should align with your business goals, customer needs, and regulatory requirements.