Customer relationship management (CRM) data is information that can help make a business’ decisions and other operational activities more accurate, objective, relevant, and timely. CRM data can include gathered information of a personal, contextual, or measurable nature, such as contacts, leads, customers, accounts, cases, deals, opportunities, activity, performance, and more.
CRM data helps you build a CRM database—a powerful contact management machine. This article explores the four types of CRM data to collect and how you can use them to gain insights for lead and sales opportunities.
Pro tip: Navigating the CRM marketplace can be overwhelming, with general-use and industry-specific options all offering unique features, pricing models, and user experiences. Check out our ultimate guide on how to choose a CRM for insights into understanding your CRM goals and requirements, and then selecting the right product for your business.
Types of CRM Data
Sales, marketing, and customer service teams categorize data based on specific parameters such as its intended purpose, accuracy, uniqueness, relevancy, level of importance, and data sources. This way, they can generate the right data types to attain specific goals, like generating qualified leads and moving them to the bottom of the sales funnel. Below are the four types of data found in customer relationship management systems.
1. Identity Data
Identity data is unique to a particular customer or lead. You can identify this data in a specific record within your CRM system or other business database. CRM data examples under this category include the following:
- Person’s name
- Birthdate
- Address
- Phone number
- Email address
- Company name
- Account number
Aside from identifying records, this CRM data type facilitates communication with prospects and customers. For instance, you will need to create a call list with identity-based information before cold calling. Having identity data helps hasten the prospecting period for the best results.
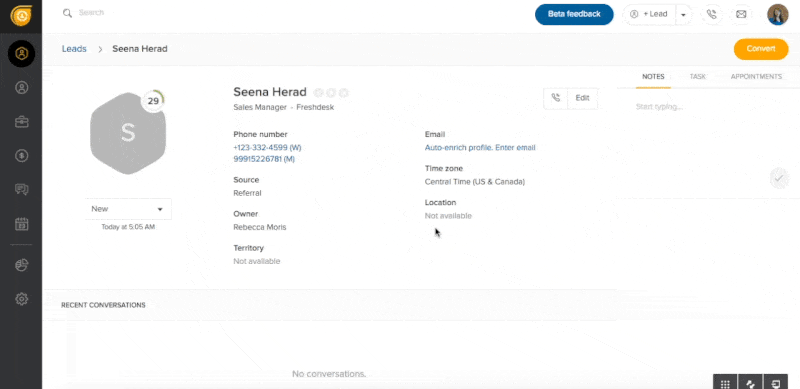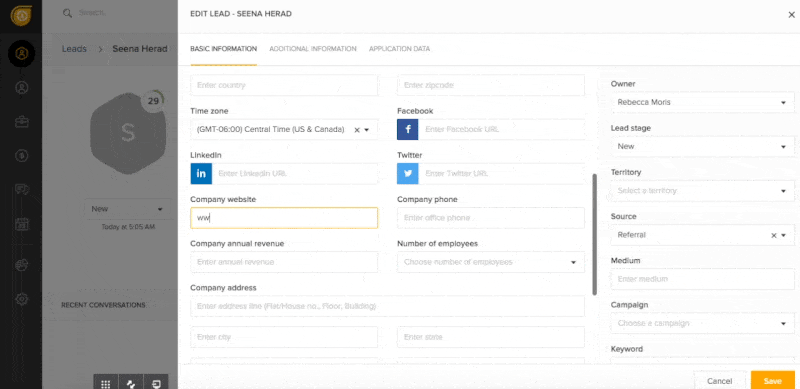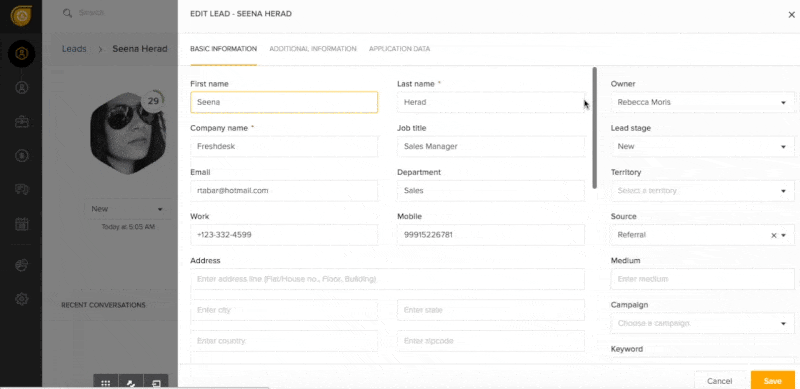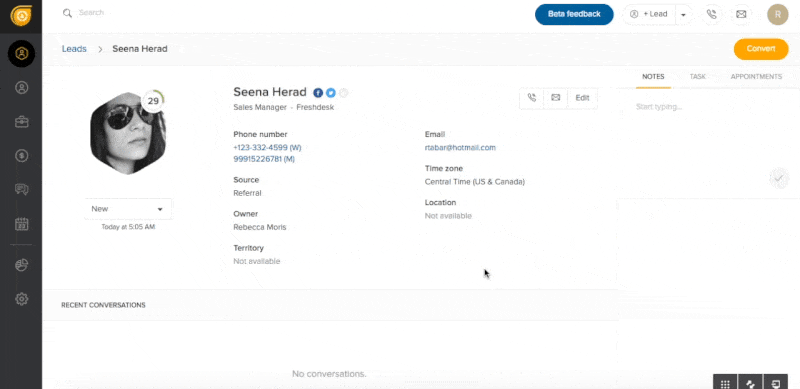
Pro tip: Sales teams can use CRM tools like Freshsales to add, customize, and store identity data in a one-page profile or list format view. Users can easily update, search, filter, and view lead and customer records based on personal identifiable information (PII). Freshsales also automatically enriches the identity data of contacts, leads, and accounts.
Freshsales’ contact auto-enrich feature eliminates manual data entry. (Source: Freshsales)
2. Descriptive Data
As its name implies, descriptive data refers to a contact, lead, customer, or opportunity with contextual information, characteristics, or traits. Sales teams can use descriptive data to search or filter multiple records at once since the details are highly relevant to multiple leads or customers. Common examples of customer relationship data in a descriptive item include:
- Marital status
- Educational level
- Job title(s)
- Industry
- Geographic location (territory, region, or ZIP code)
- Organizational size
- Lead or deal stage
- Organizational affiliations or memberships
Descriptive data provides insights into specific records to help sales, customer service, or marketing teams better engage with leads. For instance, knowing identity data like someone’s name during sales activities helps you start a conversation with a lead, but knowing their title, industry, and company size helps you find and tailor a solution to their unique needs.
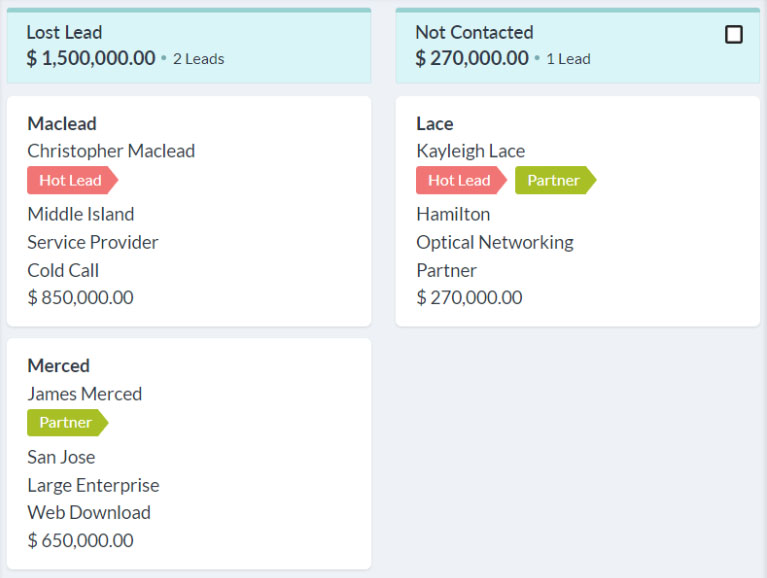
Pro tip: CRM platforms can store and organize descriptive data within a profile or through CRM tagging and labeling features. Users can add data like job titles or add labels describing a record’s traits, which helps tailor contact conversations appropriately. In Zoho CRM, you can color code tags to differentiate CRM records based on their importance at the time of their creation, which can be automated using workflow rules.
Zoho CRM’s Kanban view of lead data with colored tags (Source: Zoho CRM)
3. Qualitative Data
Qualitative CRM data include motivations, behaviors, or feelings by a lead or customer that cannot be measured numerically. This data type is subjective, gathered via surveying, activity tracking, and in-depth discussions. Here are some real-world examples of qualitative data:
- Activity information such as a lead contacting you about pricing
- A potential customer expressing satisfaction on the product demo
- A lead expressing confusion about a product’s tiered pricing and add-on features
- A customer being “very satisfied” with their recent purchase from your business
- An online survey with an explanation of rejecting an offer
- “Better usability” indicated as a desired product attribute by a customer
- “Looking to improve operational efficiency” listed as a reason for a lead’s interest in your product or service
The main difference between descriptive and qualitative data is the scope from which the information is sourced. Descriptive data describes what the record “is” while qualitative data describes what the record “thinks,” “does,” or “feels” toward a brand, product, or service. Examples include the affordability, durability, reliability, satisfaction level, and other qualities of a product or service.
Pro tip: CRMs like Pipedrive let you add qualitative data to profile records as notes or activity. Reps can add and view information on prior activity to better understand what a specific lead or customer feels and needs. Additionally, a CRM like HubSpot can mass deploy customer satisfaction feedback surveys to offer solutions or make sales and operational adjustments.
4. Quantitative Data
Quantitative data determines a record’s behaviors or feelings objectively and numerically. This data type represents how a record behaves, thinks, or feels. Here are some examples of quantitative data:
- Number of times a customer or lead clicks an email message
- Number of times the lead called the toll-free number to ask questions
- Number of times the prospect requested a callback
- Number of unopened emails
- Products or items in the shopping cart
- Potential revenue size of a current deal
- Total service tickets filed by a customer
Because quantitative data is entirely numeric, it’s primarily used for analytics and CRM reporting. Teams can take this measurable CRM data to identify bottlenecks in their sales process, the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, progress on complex sales goals, and how individual reps are performing.
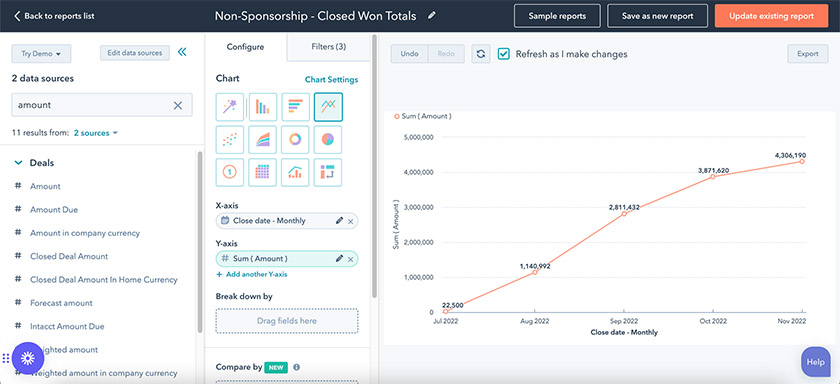
Pro tip: CRM software like HubSpot allows you to add quantitative data into individual records. The system aggregates numeric values to provide insights through reporting for revenue projections, average deal size, and total deals won. Sales reps can use the artificial intelligence (AI) sales assistant to learn deal management tips based on currently stored CRM sales data.
Why Collect CRM Data?
CRM data helps sales teams stay organized and optimize selling. Moreover, managers can bolster and track sales and marketing efforts by leveraging marketing automation, analytics, and reporting features. The main reasons to collect and utilize CRM data include:
Teams can collect and store CRM data to access relevant information and complete lead generation, marketing, and sales activities. Sales reps can search, filter, and track contact details based on the above-discussed CRM sales data types. A robust CRM database with enough storage for your business requirements makes this possible, ultimately improving efficiency, productivity, and collaboration among teams.
Storing contextual information in a CRM, such as the lead’s industry, job title, thoughts, behaviors, and feelings toward your business, allows you to make personalized conversations and marketing content for them. This helps build better relationships with leads and customers while getting optimal conversion rates on sales and marketing campaigns.
Lead segmentation is the process of dividing leads into smaller categories based on their characteristics and activities. Storing data within a CRM makes it easier to filter out lead and customer contact lists based on descriptive, qualitative, and quantitative information. This type of segmentation lets you easily design and deploy targeted marketing and cold calling campaigns to desired audiences.
Collecting behavioral information, performance data, and customer feedback lets teams understand and improve their products and services. These include product or service attributes, customer support operations, and the way they build and maintain relationships with their contacts.
For CRM systems with analytics and reporting tools, quantitative CRM data helps show measurable performance metrics and present key performance indicators (KPIs). On a higher level, it will also provide intelligence on what parts of your sales, marketing, and customer support operations are doing well, which need improvements, and what you can do to enhance those functions.
Frequently Asked Questions
CRM data, like identity, descriptive, quantitative, and qualitative data, is usually collected using customer relationship management (CRM) software. A CRM system extracts data from multiple sources, including your company website, online store, social media, and email survey forms. Reps can also enter data, like a customer’s speech verbatim during a phone call, manually into the CRM in the form of notes. Most advanced CRMs have AI capabilities to auto-log notes.
Sales teams use CRM data to generate leads, track sales performance, communicate with customers, and collaborate with teammates. Having reliable and accurate data and CRM streamlines contact, deal, and sales pipeline management. On the other hand, marketing teams use CRM data to strategize new marketing campaigns. Customer support teams use CRM data to determine the best resolution for a ticket and improve customer satisfaction to boost referrals.
Artificial intelligence (AI) automates data gathering in CRM software through its advanced algorithms. This technology pulls data from all your digital channels like your website, social media, emails, phone calls, and even short messaging service (SMS). It can also retrieve and analyze prospect or customer information to generate more accurate and relevant CRM data.
Bottom Line
Sales teams collect and manage identity, descriptive, qualitative, and quantitative CRM data to gain valuable insights for lead and sales opportunities. You can also leverage various CRM data types to better understand your prospects, customers, and operational processes. Effective CRM sales data collection improves productivity, solution offerings, and, ultimately, prospect and customer relationships to win more deals.