Landlords entering into lease agreements with tenants need to understand landlord-tenant laws. These laws lay down the groundwork for the landlord-tenant relationship and oversee crucial aspects of the process, such as lease terms, security deposits, and eviction procedures. We’ll break down these laws, state by state, providing a clear roadmap for landlords to ensure compliance and protect property investments.
Key Aspects of Landlord-Tenant Laws Landlords Need to Know
Understanding landlord-tenant laws is not only a matter of legal compliance, but it can significantly impact your investment decisions. As an investor, having a deep grasp of the intricacies of these regulations can mean the difference between a successful investment and one accompanied by legal and financial challenges.
For example, landlord-tenant rules and regulations governing security deposits and eviction procedures in your target market can directly affect your property’s profitability and tenant satisfaction. Here are some key aspects of tenant laws that landlords should consider when evaluating investment properties in specific states:
- Eviction procedures: Understanding the ease or complexity of the eviction process in a state is important to understand how quickly a landlord can regain possession of a property. This is pivotal in the event of a tenant’s breach of the lease agreement or non-payment of rent.
- Rent control: Rent control can limit your ability to increase rent, affecting potential rental income.
- Security deposit regulations: Different states have varying rules regarding the maximum amount for security deposits, the timeline for returning them, and allowable deductions.
- Lease terms: Some states may have specific lease requirements, such as mandatory provisions or notice periods for lease termination.
- Tenant screening: Be aware of any restrictions or regulations related to tenant screening practices, such as background checks and credit checks.
- Maintenance and repairs: State laws can dictate the landlord’s responsibilities for maintaining and repairing rental properties impacting your maintenance costs.
- Anti-discrimination laws: Familiarize yourself with fair housing laws and anti-discrimination regulations since violating these can lead to lengthy legal issues.
- Notice periods: Different states may require specific notice periods for various situations, such as notice to enter the property or notice of lease termination.
- Late fees: Understand the rules regarding late fees since some states impose limits on the amount that can be charged and when it can be applied.
Mobile account summary (Source: Baselane)
To collect security deposits and late fees, landlords can leverage platforms like Baselane to ensure they get paid on time and with minimal effort. With Baselane, landlords can automate rent collection to make it convenient for tenants to pay rent electronically. This reduces the risk of late or missed payments. By automating these crucial aspects of rental management, Baselane enhances financial stability and promotes a more efficient landlord-tenant relationship.
Landlord vs Tenant-friendly States
In addition to the key aspects, in the realm of landlord-tenant laws, states can be categorized as either landlord-friendly or tenant-friendly. Key factors such as the eviction process, regulations on rent increases, and rules for security deposits are used to determine which category a state falls in. These criteria provide valuable insights into the legal landscape that an investor might encounter when looking to invest in a particular state.
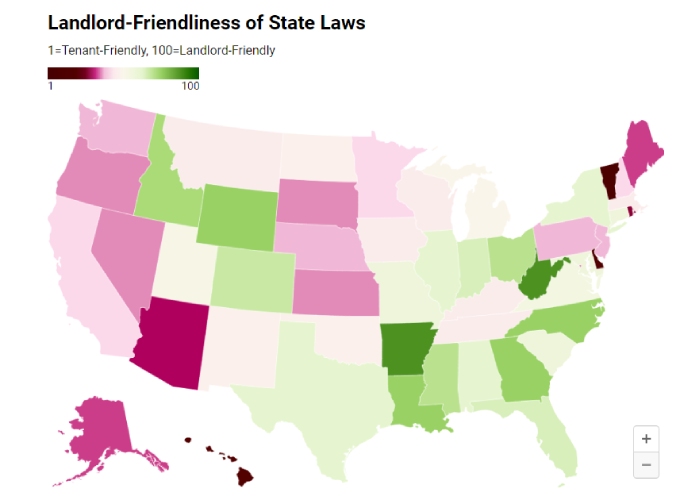
Landlord and tenant-friendly states (Source: SparkRental)
Most landlord-friendly states would have expedited and streamlined eviction processes, fewer restrictions on rent increases, and fewer regulations regarding security deposit limits and conditions for deductions. Whereas tenant-friendly leases generally offer extended notice periods to address unpaid rent before eviction can proceed.
Tenant-friendly states may also have rent control laws in place to reduce large rent increases. There will also be stricter regulations on security deposits, like the specific conditions that justify deducting fees from the deposit. It’s important to consider this when purchasing or deciding to rent your properties in a particular location.
Landlord-Tenant Laws by State
Now that you know the key aspects that landlords should look out for and how friendly your state is toward landlords, take a look at the map below to review state-specific laws in your location. If you own a property in a different state from where you live, you have to follow the rules of the state where the property is. To find the landlord-tenant laws by state, just click on the map below.
Landlord-Tenant Laws by State
How States Set Their Landlord-Tenant Laws
States establish their landlord-tenant laws through a combination of historical context, local needs, legislative actions, and legal precedents. The Uniform Residential Landlord and Tenant Act (URLTA) was introduced in 1972 by the Uniform Law Commission. It offers a standardized framework that some states choose to adopt. It serves as a model for states seeking to harmonize their rental regulations while ensuring a degree of uniformity in various jurisdictions when there is an absence of federal oversight.
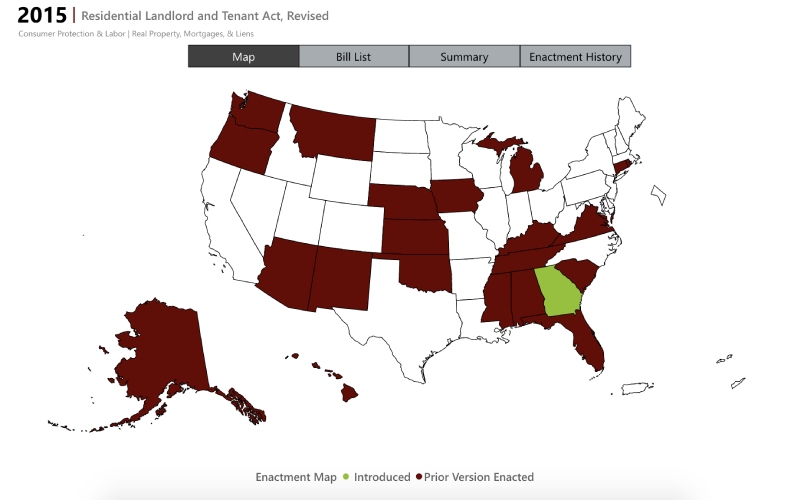
States Adopting URLTA (Source: Uniform Law Commission)
URLTA was specifically designed for residential rental agreements and does not apply to commercial, industrial, or agricultural rental arrangements. The act addresses security deposits, eviction procedures, and maintenance responsibilities, ensuring that landlords have a clear understanding of their obligations and rights. URLTA also provides clarity and consistency in lease terms, making it easier for landlords to create comprehensive and legally sound lease agreements.
General Responsibilities for Landlords & Tenants to Uphold Laws
Both the landlord and tenant have general responsibilities they must abide by in order to remain cordial in their living situation. At the heart of these obligations is the duty to maintain the rental property in a safe and habitable condition.
Landlord responsibilities are all geared toward providing a secure and comfortable living environment for their tenants. This encompasses everything from ensuring the structural integrity of the property to addressing maintenance issues promptly. Landlords must also provide essential services like water, heating, and electricity, as stipulated in the lease agreement—guaranteeing that a tenant’s basic needs are met.
The general tenant responsibilities are designed to safeguard the property and the landlord’s investment.
Tenants not only help preserve the property’s condition and value but also create a harmonious living environment that benefits all parties involved. These responsibilities will be clearly identified in the terms of the lease agreement and outline what tenants can and cannot do while occupying the rental property.
Other general responsibilities that are expected include:
Landlords | Tenants |
|---|---|
Security deposit: Each state has rules governing security deposit amounts and return policy and whether a landlord can make any deduction from that deposit. | Fulfilling payment responsibilities: When entering a rental agreement, tenants are responsible for on-time payment of rent and utilities. |
Disclosure of property owner: It’s a renter’s right to know the property owner’s details and contact information of who they should reach out to if a problem occurs. This also applies if a property owner sells their property to another owner. | Fixing damages: Any damage to the property that occurs beyond normal wear and tear should be the tenant’s responsibility to fix or pay for repair. |
Property turnover to tenant: Landlords must provide tenants with a vacant property on the move-in date stated on the lease. | Disturbance: Tenants are expected to not disturb their neighbors with excess noise so everyone can enjoy the premises. |
Property maintenance: Landlords must provide habitable living spaces to a tenant. That means landlords must make all repairs and maintenance, provide resources like garbage receptacles and waste management solutions, and keep common areas clean. | Allowing landlord entry: Landlords have the right to enter their property for inspection. Although they must inform you of the time and date of entry, you must let them in. |
Liability: If a landlord owes a tenant any money, like a security deposit, they continue to be responsible for it even if the property is sold. Funds must be returned or transferred to new ownership. | Vacating property at the end of lease term: When the lease term is over, you must vacate the premises on that date. Tenants should also leave the property in good condition. |
5 Ways to Avoid Breaking Landlord-Tenant Laws
Owning and managing property can be a challenging endeavor in itself. Landlords should be particularly mindful to avoid breaking landlord-tenant laws by state to minimize adding additional headaches to their investments. While some infractions can stem from challenging tenant interactions, others may occur due to a lack of awareness about specific regulations.
Landlords can proactively prevent potential breaches of landlord-tenant laws by following these tips:
- Thoroughly understand local laws: Begin by acquainting yourself with the specific tenant rules and regulations in your state and municipality. Regulations can vary significantly, so a solid understanding of the local legal landscape is the foundation for compliance.
- Craft comprehensive lease agreements: Create lease agreements that align with the prevailing laws and regulations. Ensure these documents include all necessary clauses, such as rent payment terms, maintenance responsibilities, and notice periods for entry or lease termination.
- Regularly update your knowledge: Landlord-tenant laws can evolve. Stay informed about any changes or updates in the legal framework that governs your rental property. This ongoing education can help you adapt to new requirements and avoid inadvertent violations.
- Fair and consistent practices: Implement fair and consistent practices across all your rental properties. Treat all tenants equally, adhere to lease terms, and avoid any discriminatory practices. This fosters a reputation for fairness and compliance.
- Seek legal counsel when necessary: If you encounter complex legal issues or disputes with tenants, don’t hesitate to consult with legal professionals who specialize in landlord-tenant law. Their expertise can guide you through intricate legal matters, helping you make informed decisions while remaining in compliance with the law.
What to Do if a Tenant Violates the Laws
If a tenant violates the laws or breaches the terms of their lease agreement, landlords should take specific steps to address the situation while adhering to legal procedures. First and foremost, communication is key. Landlords should engage in open and constructive dialogue with the tenant to discuss the issue and seek a resolution. In many cases, misunderstandings or disputes can be resolved through effective communication.
If communication proves ineffective, landlords should review their lease agreement and understand the rights and remedies it provides. Depending on the nature and severity of the violation, landlords may need to issue written warnings or notices to the tenant, clearly outlining the problem and the necessary corrective actions. These notices should comply with state and local laws, specifying reasonable deadlines for compliance.

Example lease agreement (Source: eForms)
In more serious cases, such as non-payment of rent or severe lease violations, landlords may need to initiate legal proceedings. This typically involves filing for eviction through the appropriate legal channels—adhering to state-specific eviction laws and timelines. It’s crucial for landlords to consult with legal professionals who specialize in landlord-tenant law to ensure that they follow all legal requirements during the eviction process.
Did you know? Landlords can offer difficult tenants “cash for keys” instead of going through eviction proceedings. This involves offering a sum of money in exchange for tenants to vacate the property. Take a look at this option in the article Cash for Keys: Removing Tenants (+ Download Agreement).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In a rental agreement, landlords typically have responsibilities that include property maintenance and offering essential services. This means they must ensure the property is safe and habitable while promptly addressing repairs when needed. On the other hand, tenants are usually responsible for paying rent on time, maintaining the property in a clean and undamaged condition beyond normal wear and tear, and adhering to the lease terms. It’s essential to include the specific obligations of each party in the lease agreement.
No. Landlord-tenant laws are not the same in every state. They can vary significantly from one state to another. Each state has its own set of regulations governing rental properties and the rights and responsibilities of landlords and tenants. Some states are considered renter-friendly states because they have laws are designed to prioritize and protect the rights and interests of tenants. These variations can include rules related to security deposits, eviction procedures, and rent control.
In most cases, landlords can terminate a lease or initiate eviction proceedings for reasons specified in the lease agreement or allowed by local laws. Common reasons include non-payment of rent, lease violations, or the end of a lease term. However, landlords should be aware that specific legal procedures and grounds are required for eviction. In many jurisdictions, landlords cannot evict tenants without a valid cause or must provide proper notice and follow due process.
Bottom Line
As landlord-tenant laws can vary significantly from state to state, it is essential for both property owners to stay informed about the specific regulations in their locality. Regularly reviewing these laws and seeking guidance from legal professionals or individuals well-versed in state-specific regulations is helpful to stay out of a potentially lengthy legal battle. Taking these proactive steps will help minimize potential issues with future tenants.