An e-check, or electronic check, is a digital alternative to paper checks. E-checks go through the same authentication process as paper checks but are faster and generally more secure because the payment moves electronically. Local businesses where credit cards are not a popular payment method may find e-checks more convenient.
Unlike credit card transactions, e-check payments transfer funds directly from the customer’s bank to the merchant’s business bank account. This means no interchange fees to be paid to card networks nor markup costs to be paid to payment processors.
Banks charge merchants as little as 10 cents per transaction to accept e-checks and require only a simple email address to get started. Standard e-checks take at least 24 hours to clear but same-day e-checks are also available.
Key Takeaways:
- An e-check is a type of automated clearing house (ACH) payment called “ACH direct debit.”
- E-checks can only be used for accepting local payments.
- The electronic processing of e-checks makes it safer, cheaper, and faster to complete than paper checks.
- While generally convenient, not many US consumers pay with e-checks.
What Makes an E-check?
E-checks are the digital version of paper checks so they look exactly the same. An e-check indicates the customer’s bank details, the transaction amount, the recipient’s name, and the recipient’s bank details. The only difference is that e-checks are prepared electronically, through an online platform instead of on paper.
E-check vs EFTs vs Wire Transfers
Electronic fund transfer (EFT) is a catch-all phrase for all types of transactions funded by the issuer’s bank account—including wire transfers and e-checks. Wire transfers are similar to e-checks in the sense that both are bank-to-bank transactions. However, unlike e-checks, wire transfers do not go through the ACH network.
E-check vs ACH
“ACH payments” is a general term for all types of bank-to-bank transactions that are processed through the ACH network—including e-checks. The National Automated Clearing House Association (Nacha) is a US regulatory agency that oversees the payment processing, clearing, and settlement of all ACH payments.
E-check vs Credit Card Payments
E-check payments are directly funded by the customer’s bank account. Credit card payments, on the other hand, are funded by the customer’s line of credit approved by a banking institution that doesn’t necessarily have to be the same as the customer’s bank account.
How E-checks Work for Merchants
An e-check is an ACH direct debit payment managed by Nacha. ACH direct debits are pull transactions A pull transaction involves the merchant's bank communicating with the customer's bank to request for payment. often used to accept payments for recurring billings, subscriptions, automated mortgage payments, and membership fees.
The lifecycle of an E-check payment starts in two ways:
- Customer pays via merchant’s website: The customer fills out an e-check form on the merchant’s website, OR
- Merchant prepares an e-check on a virtual terminal: Customer provides the merchant with their bank information and the merchant fills out an e-check form on a virtual terminal.
Once prepared, the merchant sends the e-check to its banking service, which in turn, will request funding directly from the customer’s bank. Below is a summary of how e-check payment processing works.
It’s important to have your customer sign an authorization form before submitting a funding request through the ACH channel for the transaction.
Ways for Businesses to Accept E-check Payments
Unlike paper checks, merchants can accept e-checks remotely:
-
Connect Your Merchant Bank to Your Ecommerce Website
If you run a business that does not accept credit card payments, open a business bank account with a bank that offers integration with ecommerce platforms. This will allow you to add an e-check payment method option on the checkout page where your customers can input their bank details and, at the same time, authorize the payment.
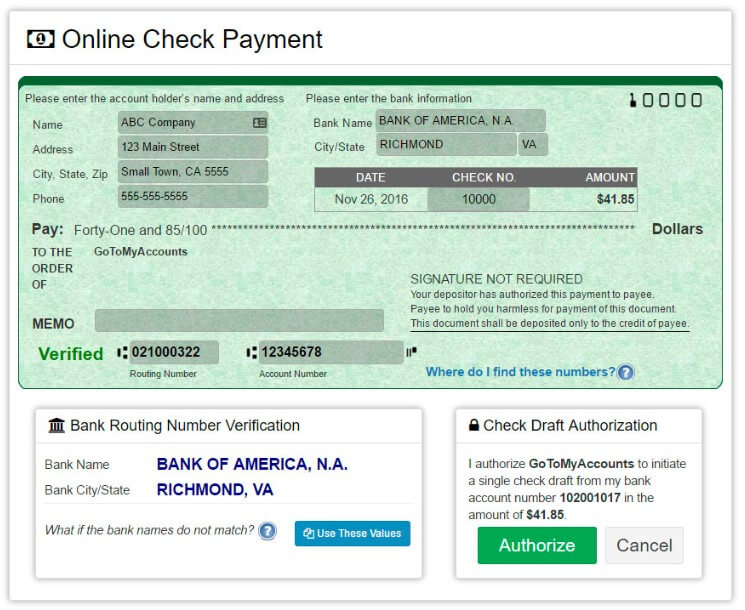
Merchants can add an e-check payment option on their website where customers can fill out e-check details and authorize the payment immediately. (Source: GoToMyAccounts)
-
Work With a Payment Processor That Integrates With Your Ecommerce Website
Payment processors can also work with the ACH network to process bank-to-bank transfers such as e-checks. Most payment processors already integrate with ecommerce platforms, and adding an e-check payment method option would only require a few adjustments to your checkout page settings.
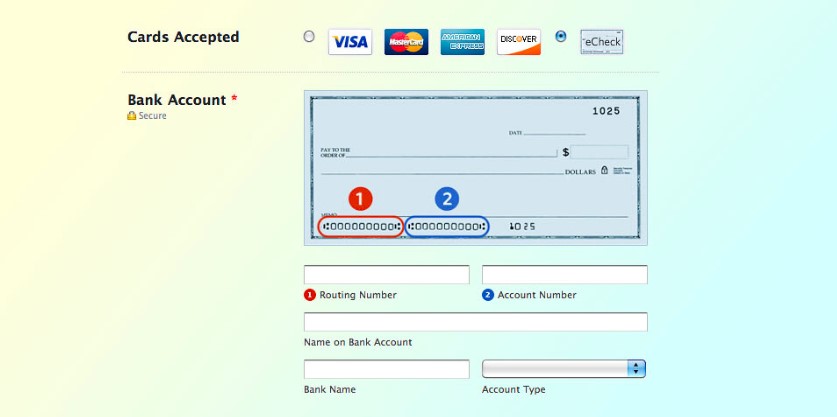
Payment processors that support e-check payments can easily add an e-check payment method option on your website’s checkout page. (Source: SolutionScout)
However, not all payment processors offer e-check payment services. If you are already working with one to accept credit cards, check whether this provider also supports e-check payments.
-
Sign Up for a Virtual Terminal Service
Virtual terminals are ideal for businesses that regularly accept payments over the phone from customers. This type of payment service can be provided by either a merchant’s banking service or payment processor. However, some providers may charge an additional fee to use their virtual terminal platform so it’s important to ask before signing up.
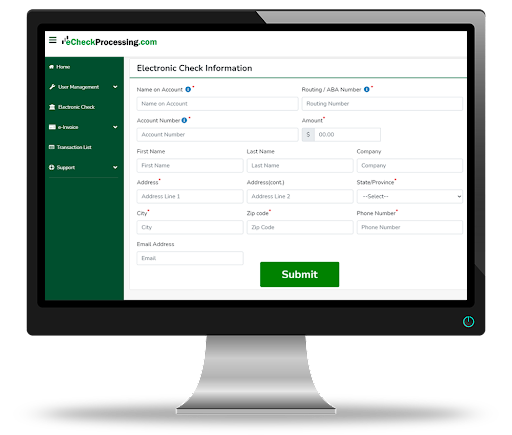
Virtual terminals allow merchants to accept e-check payments from customers over the phone. (Source: E-checkProcessing)
Costs of E-check Payment Processing
Regardless of whether you are working directly with your merchant bank or with a payment processor, processing e-checks will come with a small fee. The fee types resemble that of credit card payments but are significantly lower.
Below we summarize the fees for accepting e-check payments:
Fee Type | Description | Average Cost |
|---|---|---|
Transaction Fee | For standard low-risk transactions | $0.10–$1.50/ transaction |
From 1.99% + 25 cents/ transaction | ||
Application Fee | One-time fee for some providers conducting due diligence | Varies |
Setup Fee | Varies | |
Return Fees | $5–$20 | |
Monthly Minimum | Incidental fee for some providers that require minimum transaction value | $15–$25 |
Verification Fee | $0.15–$0.35 | |
Check Guarantee Fee | Incidental fee for high-risk merchants | 1.5% of total e-check revenue |
Hardware Rental Fee | For merchants that require a “check scanner” at their POS | Varies |
Termination/Early Termination Fee | For providers that require a long-term contract | Varies |
E-check Pros & Cons
Accepting e-checks has both advantages and disadvantages, so it’s up to the merchant to decide whether e-check payment processing is right for their business.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Cheaper transaction fees | Not as popular as credit card payments |
| More secure and faster than paper checks | Takes days to clear the funds |
| Alternative for high-risk businesses | Less convenient than card or digital wallet payments |
Processing e-check payments costs merchants significantly less than credit card transactions. There are no intermediaries such as card networks that impose non-negotiable interchange fees. However, there are incidental fees similar to credit card transactions such as verification and return fees (in case of chargebacks or insufficient funds).
And because e-checks are digital transactions, it is inherently more secure and faster to process than paper checks. E-checks are protected by similar technology used to protect credit cards such as encryption, authentication, digital signatures, duplicate detection, and digital certificates. That said, e-checks still take as long as 48 hours to process depending on your service provider.
E-checks are also a great alternative for high-risk businesses that have difficulty getting approved for a merchant account to accept credit card payments. That said, e-checks are not as popular as credit cards as a mode of payment, so merchants who are keen on having this payment method will have to educate their customers on its convenience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Learn more about some of the most common questions we get about e-checks below.
Yes, e-checks use similar encryption technology as credit card payments to protect transaction data during payment processing so unauthorized persons cannot easily steal or duplicate the information.
Not all businesses will find e-hecks a viable payment method. Typical businesses that accept e-checks are utility and service providers, nonprofits, B2Bs, and subscriptions. If you are having difficulty getting approved for a merchant account to accept credit card payments, then e-checks may also be a good option.
No, it is not. While both e-checks and debit cards pull funds from the customer’s bank to complete the payment, e-checks are not processed through the card network. This means the fees and the processing time are completely different.
In a way, yes. Both e-checks and paper checks are processed through the same ACH network; however, e-checks are digital, making them easier, faster, and cheaper to process than paper checks.
Bottom Line
Checks may not be the most modern mode of payment around and its use has been losing popularity over the years. However, the development of an electronic version of paper checks is allowing this old-school payment method to become more relevant as we move to a cashless society.
Merchants looking for an alternative to credit card payments (for whatever reason) should consider e-checks because they are affordable and very secure.
That said, e-check payments are not for everyone, so knowing what an e-check is and how it increases sales opportunities can help merchants decide if this payment method is worth the investment.