Inventory planning is the process of determining the optimal amount of stock to keep on hand in order to meet customer demand while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency. It is an essential aspect of proper inventory management, which helps you run a successful retail business.
An inventory plan involves forecasting demand, monitoring inventory levels, and making decisions about reordering points, how much to order, and where to order from. Let’s dive deeper into inventory planning, its benefits and challenges, and best practices you can implement for your business.
Benefits of Inventory Planning
Effective inventory planning can help businesses in a number of ways:
Improves Customer Satisfaction
Effective inventory planning boosts customer satisfaction by ensuring products are available when and where customers need them. Inventory planning makes sure products are not only available but that orders are fulfilled in a timely manner. It also ensures a consistent experience every time, which is important for both customer satisfaction and retention.
Related: How to Measure Customer Service Satisfaction + Examples
Reduces Carrying Costs
Carrying costs are essentially the money you spend holding onto inventory. The more inventory you have, the more you lose to carrying costs. Inventory planning reduces carrying costs by optimizing inventory levels to minimize excess stock. By accurately forecasting demand and maintaining optimal inventory levels, you can avoid overstocking and reduce the need for excess warehouse space, storage expenses, and inventory carrying costs.
Efficient inventory planning also minimizes inventory spoilage, reducing write-offs and disposal costs associated with obsolete or expired inventory.
Minimizes Stockouts
Stockouts are a costly problem—they not only mean missed sales, but they also make your business look bad and unreliable to potential customers. Inventory planning minimizes stockouts by strategically managing inventory levels and setting reorder points and safety stock levels. It helps you make sure you have enough stock on hand to meet customer demand even during peak periods.
Increases Profitability
Minimizing expenses and boosting sales are surefire ways to improve profitability. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, you can also minimize the need for emergency orders or rush shipments, which typically incur higher costs.
Plus, inventory planning enables you to make better purchasing decisions, negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, and optimize order quantities, resulting in cost savings and improved margins. Aligning inventory levels with demand and optimizing inventory management practices can help you improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and increase profitability.
Challenges of Inventory Planning
Inventory planning can be complex and challenging due to various factors. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach to inventory planning, including robust demand forecasting, efficient supply chain management, strategic inventory optimization, and effective risk mitigation strategies.
Here are some common challenges:
Variability & Uncertainty
Forecasting future demand accurately is difficult, especially for products with erratic or seasonal demand patterns. Uncertainty in demand forecasts can lead to overstocking or stockouts. Rapid changes in consumer preferences, market trends, or competitive dynamics can lead to demand volatility, making it challenging to predict and plan inventory levels accurately.
Seasonal fluctuations in demand also pose challenges for inventory planning, requiring you to adjust inventory levels and forecasts accordingly to avoid stockouts during peak periods and excess inventory during off-peak periods.
Supply Chain & Vendor Management
Lead times for procurement or manufacturing can vary due to factors such as supplier delays, transportation issues, or production delays. Managing lead time variability is crucial for ensuring timely replenishment of inventory.
Disruptions in the supply chain, such as natural disasters, geopolitical events, or supplier bankruptcies, can impact inventory availability and lead to stockouts or excess inventory.
Related reading:
Balancing Between Too Much & Not Enough
Holding inventory ties up capital and incurs costs such as storage, insurance, and obsolescence. But stockouts can result in lost sales, dissatisfied customers, and damage to reputation. Determining the appropriate level of safety stock to prevent stockouts without incurring excess inventory costs is a delicate balance.
Obsolete Inventory
Products may become obsolete due to changes in technology, consumer preferences, or market trends. Managing obsolete or expired inventory and minimizing write-offs requires proactive planning and inventory optimization strategies.
Technology Implementation, Management & Investment
Implementing and integrating inventory management systems, demand forecasting tools, and supply chain technologies can be complex and require significant investment in technology infrastructure and training—not to mention lengthy and complicated implementation and onboarding processes.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with regulatory requirements, such as safety standards, labeling requirements, or import/export regulations, can impact inventory planning and procurement processes, adding complexity and cost.
How to Create an Inventory Plan
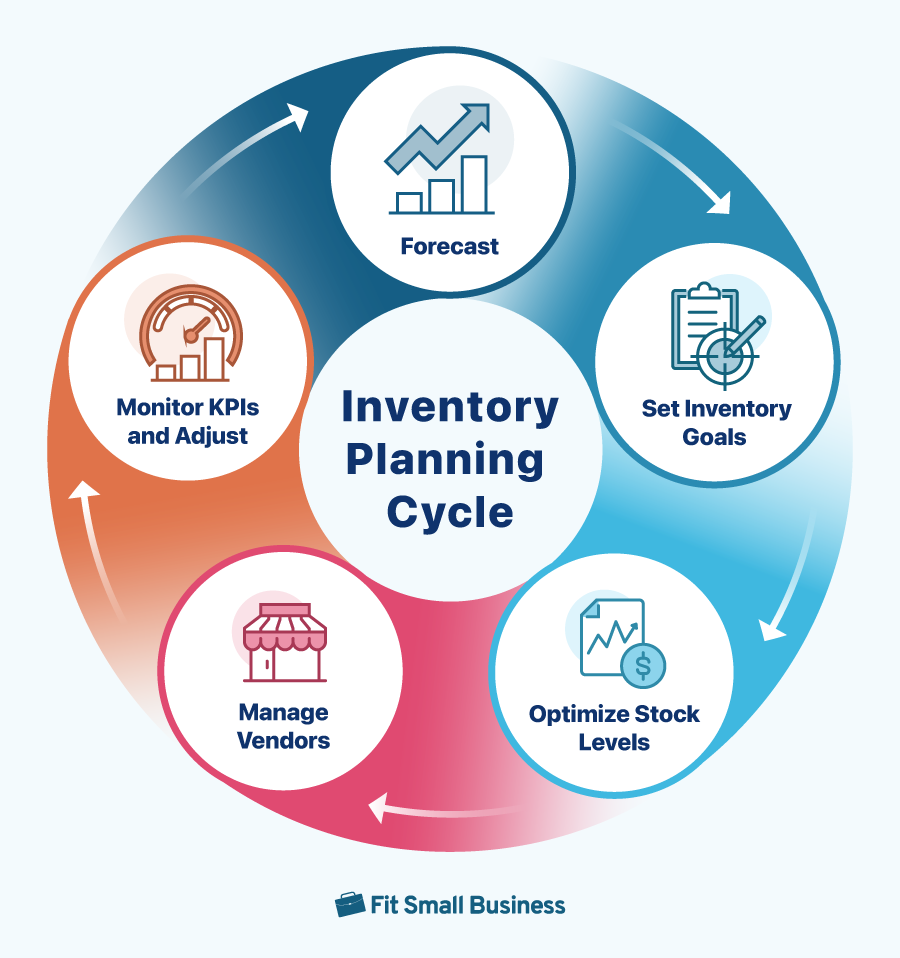
Inventory planning requires a combination of data analysis, forecasting techniques, and strategic decision-making. Let’s look at how to put this into action:
Step 1: Gather & Analyze Data to Accurately Forecast
Collect historical sales data, demand forecasts, lead times, supplier information, and other relevant data that will inform your inventory planning process.
Use statistical techniques and demand forecasting methods to analyze historical sales data and identify patterns, trends, and seasonality in customer demand. You can predict future demand for products or services based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors.
Various forecasting techniques, such as moving averages, exponential smoothing, or time series analysis, can be used to predict future demand and plan inventory levels accordingly. These methods rely on historical data and statistical models to forecast demand patterns and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
Learn more: Demand Forecasting: Models & Why It’s Important
Conduct an ABC Analysis
An ABC analysis categorizes inventory into three groups based on their value and importance:
- A: High-value items with low frequency
- B: Moderate-value items with moderate frequency
- C: Low-value items with high frequency
This method helps prioritize inventory management efforts and resources based on the relative importance of items. Focus inventory management efforts on high-value items (A category) while streamlining processes for lower-value items (C category).
Step 2: Set Inventory Goals & Service Levels
Determine your inventory management objectives, such as minimizing stockouts, reducing excess inventory, improving cash flow, and maximizing customer satisfaction.
Define the desired service level or fill rate that you aim to achieve, indicating the percentage of customer demand that you want to satisfy from available inventory.
Safety stock is the amount of inventory you need to keep on hand to reduce the risk of stockouts. Maintaining a buffer of extra inventory protects against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply chain disruptions.
Calculate the appropriate level of safety stock needed to protect against variability in demand and lead times, taking into account factors such as demand variability and supplier reliability.
Now you’ll want to figure out the inventory level at which a new order should be placed—you want to both avoid stockouts and overstocking. This is when you calculate the inventory level at which a new order should be placed to replenish stock before it falls below a certain threshold, known as the safety stock level.
Calculate reorder points for each product based on demand forecasts, lead times, and desired service levels, indicating when to place new orders to replenish inventory. You can automate this process with lots of inventory management platforms.
Your EOQ is essentially the ideal quantity of inventory your business should have. EOQ is a mathematical formula used to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, including ordering costs and holding costs. It balances the costs of ordering and carrying inventory to achieve the most cost-effective inventory replenishment strategy.
Maintaining a strategic EOQ minimizes total inventory costs, including holding costs and ordering costs. Determine the optimal order quantity for each product, considering factors such as order costs, holding costs, and demand variability.
Here’s the formula for calculating EOQ:
For example, you want to determine EOQ for a plain white T-shirt that your boutique sells. Let’s say you sell 500 shirts per year and it costs you $5 to hold one shirt in your inventory and $20 to place an order. Plugging it into the formula:
EOQ = √ (2 *(500 * $20) / $5)
Thus, the optimal quantity per order for your T-shirts is 63.
Step 3: Optimize Stock Levels
Review current inventory levels and adjust reorder points, safety stock levels, and EOQs as needed to optimize inventory levels and align with inventory management goals. Balance the need to have enough inventory to meet customer demand with the desire to minimize excess stock and associated costs.
Step 4: Manage Vendors
Evaluate suppliers based on factors such as reliability, lead times, pricing, and quality, and establish strong relationships with preferred vendors to ensure timely delivery and competitive pricing. Considering the time it takes for orders to be fulfilled and adjusting inventory levels accordingly ensure timely delivery to customers.
Vendor-managed inventory is a collaborative inventory management approach where suppliers are responsible for monitoring and replenishing inventory levels at customer locations based on agreed-upon targets and performance metrics. It helps reduce stockouts and inventory holding costs by improving supply chain visibility and coordination.
Step 5: Monitor KPIs & Adjust
Track and analyze key inventory management metrics such as fill rate, inventory turnover, stockout rate, and days’ sales of inventory (DSI). Use KPIs to identify performance trends, areas for improvement, and opportunities for optimization.
Continuously monitor inventory performance, track key metrics such as stock levels, fill rates, and inventory turnover, and make adjustments to the inventory plan as needed based on changes in demand, market conditions, or supply chain disruptions. Inventory turnover, for example, tells you how quickly inventory is being sold or used. You can adjust purchasing decisions accordingly to optimize cash flow and minimize carrying costs.
Related: Retail Metrics: How to Drive Sales in Your Small Business
Inventory Planning Methods
There are a few different approaches and methods you can use when it comes to retail inventory planning. Here are some popular ones:
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory: JIT inventory planning aims to minimize inventory holding costs by receiving goods from suppliers exactly when they are needed for production or sale. This method reduces excess inventory and storage costs but requires close coordination with suppliers and carries a risk of stockouts if supply chain disruptions occur.
- Just-in-Case (JIC) Inventory: Unlike JIT, the JIC approach involves keeping a buffer of extra inventory, known as safety stock, to protect against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply chain disruptions. It helps mitigate the risk of stockouts but increases holding costs.
- Open-to-Buy (OTB) Planning: OTB planning is an approach you can use to create buying budgets for specific periods of time. It accounts for expected beginning-of-month and end-of-month inventory, planned sales, and planned markdowns. Basically, an OTB budget tells you how much you can spend on inventory at some future date, whether it be the holiday season or the month of May.
- Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): MOQ is a method where businesses set a minimum quantity of inventory that must be ordered from suppliers to achieve economies of scale and minimize ordering costs. It helps optimize ordering frequency and reduce per-unit costs but may lead to excess inventory if demand is lower than expected.
Best Practices for Inventory Planning
Implementing best practices for inventory planning can help businesses optimize their inventory levels, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. Here are some key best practices for effective inventory planning:
Automate What You Can
Invest in inventory management software, demand forecasting tools, and supply chain technologies to streamline processes, improve visibility, and enhance decision-making. Leverage inventory automation to reduce manual tasks and errors in inventory planning and replenishment.
Here are some ideas of what to automate in inventory planning:
- Low stock alerts
- Reordering and replenishment
- Demand forecasting
- Supplier communication
- Data integration
- Analytics reporting
Implement Inventory Control Policies
Establish inventory control policies and procedures, such as inventory counting methods, replenishment processes, and inventory tracking systems, to ensure accurate and efficient inventory management.
You might consider a periodic review system, where inventory levels are reviewed at regular intervals, such as weekly or monthly, and orders are placed to replenish stock based on inventory levels at the time of review. It simplifies inventory management but may lead to stockouts or excess inventory if demand varies significantly between review periods.
Establish inventory control policies and procedures for order placement, replenishment, cycle counting, and inventory adjustments. Standardize processes to improve accuracy, efficiency, and consistency in inventory management.
Leverage Integrations
Integrations are key to running a well-rounded, data-driven business. Look for business tools that can work together to create a single command center for everything in your business, rather than a disjointed set of tools that don’t talk to each other. Find a point-of-sale (POS) system that integrates with your inventory management software, and prioritize accounting platforms that do the same.
Collaborate With Suppliers
Build strong relationships with suppliers and collaborate closely to improve supply chain visibility, reliability, and responsiveness. Implement vendor-managed inventory (VMI) or collaborative forecasting and planning initiatives to align supply with demand more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
These are some of the most common questions around inventory planning.
Inventory planning is the process of determining the optimal amount of stock to keep on hand to meet customer demand while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency. It involves forecasting demand, monitoring inventory levels, and making decisions about reordering points, how much to order, and where to order from.
There are several approaches you can take to inventory planning, including:
- Just-in-time (JIT) inventory
- Just-in-case (JIC) inventory
- ABC analysis
- Open-to-buy (OTB) planning
- Minimum order quantity (MOQ)
- Economic order quantity (EOQ)
An inventory planner, also known as an inventory analyst or inventory manager, makes sure a company maintains optimal levels of inventory to meet customer demand while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency. This involves demand forecasting, inventory analysis and control, supplier management, and more.
Inventory planning involves demand forecasting, inventory optimization and control, supplier management, securing safety stock, order planning and replenishment, inventory analysis and performance monitoring, and technology automation and integration.
Bottom Line
Strategically managing inventory levels helps you boost customer satisfaction and profitability while reducing costs. But navigating the complexities of inventory planning requires a comprehensive approach, leveraging data analysis, forecasting techniques, and strategic decision-making.
Successful inventory planning not only optimizes inventory levels but also fosters agility and responsiveness, positioning your business for sustained growth and success.