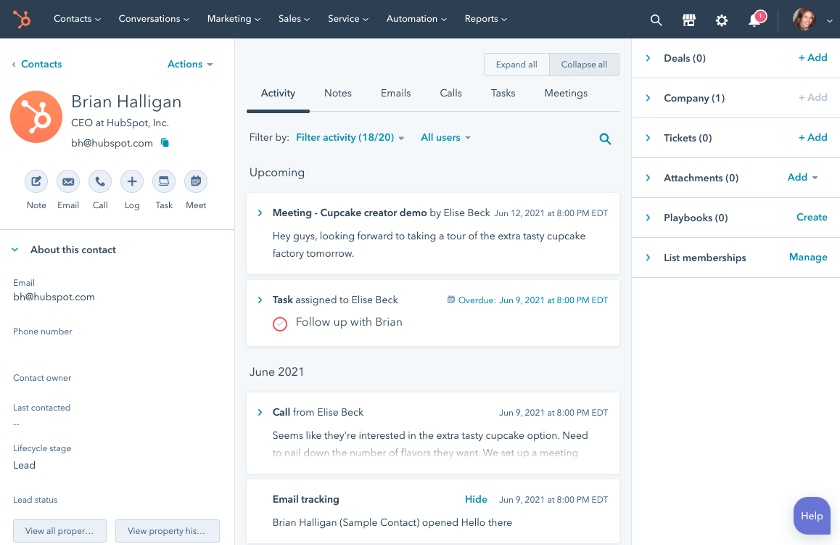
Though customer relationship management (CRM) software is commonly used for managing sales activity, it can also be a powerful tool for boosting customer satisfaction. Through case management and communication tools, CRMs are excellent solutions to engage and assist customers. In this article, we explore customer service CRM features, use cases, and the benefits of using a CRM for customer service activities.
Gain a comprehensive understanding of CRM systems in our e-book. In this guide, you’ll discover insights about the value of CRMs, the features they offer, different types of CRMs, and how to select the right product for your business. You’ll even learn how to create a CRM strategy and properly implement it into your operations.

The Expert’s Guide to Customer Relationship Management
Small Business Use Cases + Pro Tips
Here’s how to use a CRM for improved customer service in six steps:
1. Select a Customer Service CRM System
To use a CRM for customer service operations, pick a CRM solution with features designed to assist and satisfy those being provided the product or service. Many CRMs have some degree of customer support, case management, or communication modules as well as features for simplified payment processing. Here are some of our picks for the top customer service software:
Starting Price* | $25 per user, per month | Free to $45 per month (up to two users) | Free to $43 per month (up to five users) |
Best For | Managing customer service inquiries | Sending and collecting customer payment requests | Interacting with current customers on any channel |
Key Customer Service Features | Automated case routing plus knowledge articles and FAQ pages | Integrated credit card and ACH payment processing | Robust contact center with phone, email, social media, and live chat channels |
*Pricing based on annual billing. Monthly billing is also available at slightly higher prices.
In addition to standard purchasing factors such as budget and product usability, consider your customer service feature preferences and your industry when selecting a CRM. For instance, professional service and consulting businesses may prioritize having an easy way to let their customers pay compared to a business-to-business (B2B) software business that needs to manage a high volume of support requests.
Want to see more CRM options that could be well-suited for you? Here are our picks for the top CRMs for small businesses in 2022.
2. Add Users & Assign Their Roles
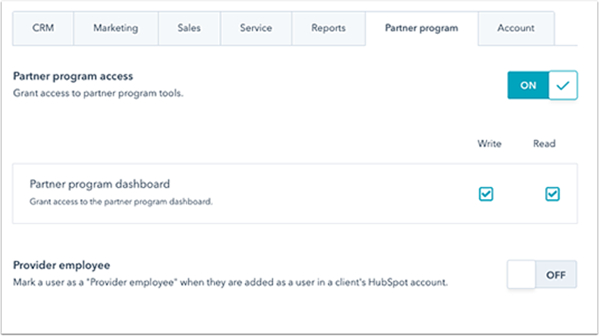
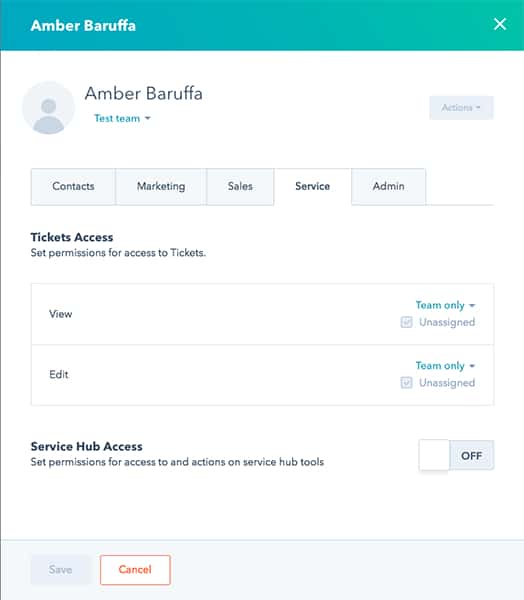
Once you’ve selected a CRM, start adding your customer service users and set their roles. For security purposes, CRM managers should follow the principle of least privilege and only give users enough modular and data access needed to perform their jobs. For instance, only customer support leaders—and not individual customer service agents—should have access to team reporting tools since managers are responsible for overseeing that operation.
Alternatively, particular roles may need more access to certain tools than others. For example, someone responsible for writing knowledge articles for customers likely wouldn’t need access to the customer ticketing module to manage service requests and, therefore, should not be granted permission. CRMs like HubSpot let you edit user permissions such as read or write access for each software solution in their suite of marketing, sales, and service modules.
3. Create & Automate Your CRM Processes
Now that everyone is added to the system, develop your customer service processes and learn what you can automate with your CRM. Many subsets of customer service need some level of standardization, such as case and ticket management, payments and invoicing, client communications, and loyalty management. Some firms even include reputation management by generating surveys as part of their customer service operations.
When standardizing customer service, consider every step required to reach a final destination. For instance, when a customer needs help with something, the end goal is to resolve that specific case or ticket quickly with high-quality service. In between ticket submission and resolution is getting the case routed to the right rep, having the rep request additional information, and accessing knowledge resources to assist that particular case.
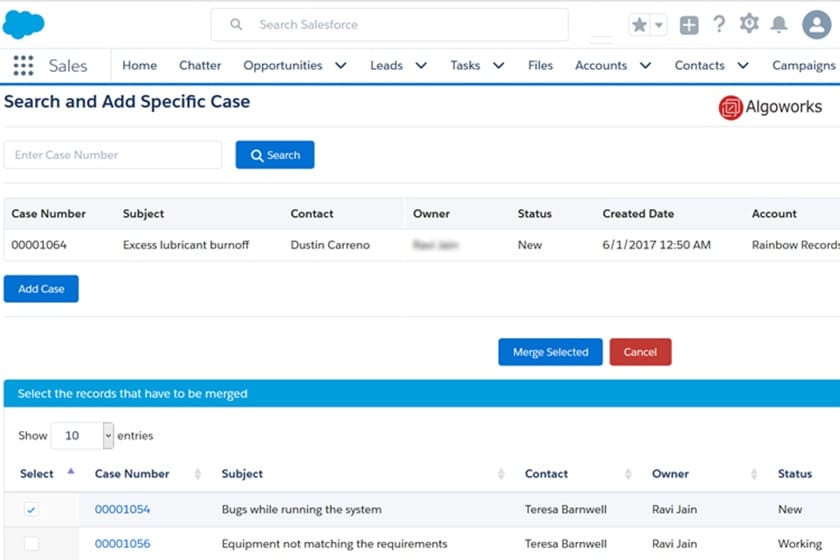
Once those stages are established, you can automate workflows in your CRM. With case management in Salesforce, for instance, teams can accept ticket requests through the CRM and automatically assign them to a rep based on case assignment rules such as customer size or case type. From there, the rep is automatically notified of the case to assist and can even have a survey automatically deployed to the customer after resolution.
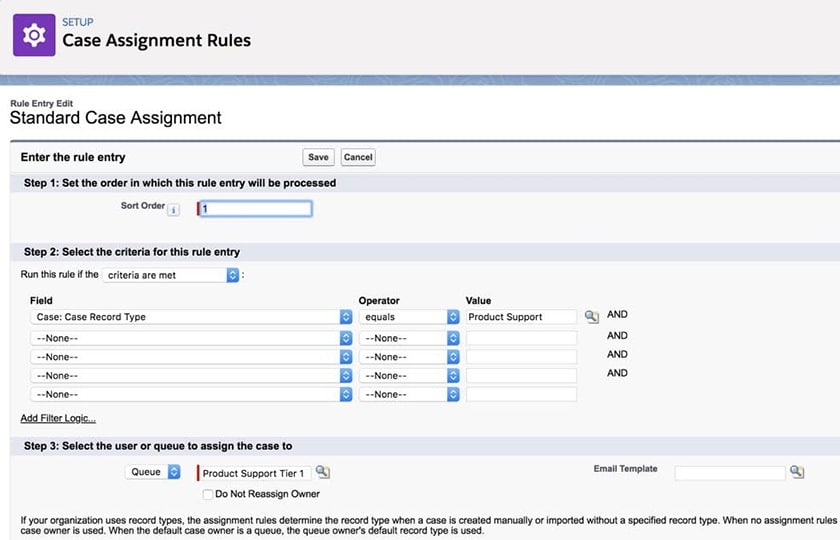
Salesforce case routing rules (Source: Salesforce)
4. Integrate Your Customer Service CRM With Third-party Tools
While there’s no shortage of CRMs with built-in customer service and support features, you may need to integrate outside tools to gain more system centralization and functionality. For example, most CRMs don’t have a built-in tool for handling customer payments. Businesses often need to integrate with an outside solution such as Stripe or Authorize.net to send invoices for payment.
Some teams might also be comfortable using certain communication tools like Mailchimp to maintain relationships with their customers through email and, therefore, must use integrations. The CRM tool you select might also not have any method for managing loyalty programs or incentivizing referrals. Products like HubSpot integrate with loyalty marketing tools like Swell to gain these types of capabilities.
5. Add & Manage Customer Data
The last step before you can start using your CRM for customer service is adding and utilizing actual customer data in the system. New customers will be generated from leads that result in a won deal. That said, users can edit current contact, lead, or deal records to move them to new statuses such as customer or account.
From there, customer service teams can view individual customer or account records to see their contact information, activity history, ticket requests, and associated tasks or notes. They can also filter out customer lists based on attributes like location, product type, and account size. Having all this data lets you more optimally assist customers with requests and give them an excellent experience because you have all the required information in one interface.
6. Run Customer Service Operations & Track Performance
As leads get converted into customers, users can undergo customer service activities such as case and account management. Assuming the automation is configured properly, reps will be assigned service tickets to effectively resolve customer issues as they come in. Additionally, because all the customer data is stored in one area, they’ll be able to provide personalized service with real-time information to boost customer satisfaction.
Certain CRMs, like Salesforce, also offer insights into how well your team performs at ticket management and customer support. As tickets get resolved, that data is processed and presented on dashboard reports that show the speed at which your customer support reps are resolving cases. Based on the metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs), managers can make adjustments to ensure the whole operation consistently runs smoothly.
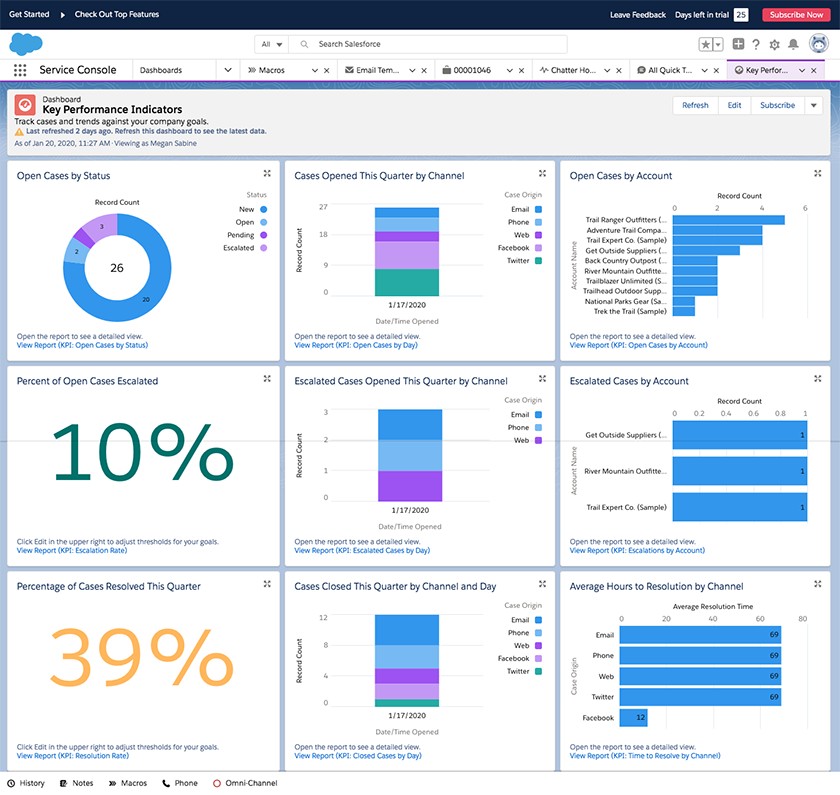
Salesforce case management performance dashboard (Source: Salesforce)
Use Cases for Customer Service CRMs
Most businesses invest in a CRM system to organize and communicate with leads, track opportunities in the pipeline, and collaborate on sales-related tasks. However, CRMs offer specific features that assist in handling customer service, client success, and account management operations to boost satisfaction and retain current business. Here are some of the most common CRM use cases and features for customer service:
- Nurturing and engagement: CRMs offer email marketing, short message service (SMS) texting, telephone, online chat, and social media communication tools that let businesses constantly interact with their customers and make upselling or cross-selling attempts.
- Case management: Some CRM systems have modules for efficiently handling customer inquiries and service requests in terms of ticket routing, automated case assignment, notifications to reps, knowledge service guides, and case resolution.
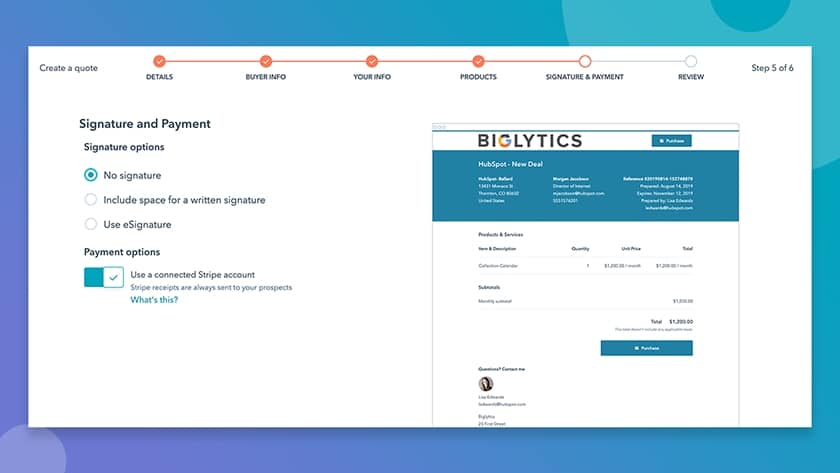
- Order and payment processing: CRMs let users easily create and send quotes and purchase orders to customers directly from the system. Some products even process credit cards, debit cards, or ACH payments through built-in tools or integrations.
- Loyalty program management: Industry-specific CRMs for restaurants, retail stores, and ecommerce businesses often have features for tracking and administering customer loyalty programs.
- Customer support performance analysis: In addition to case management features, CRMs often have performance dashboards to evaluate the speed and production of customer support operations and customer satisfaction ratings.
Benefits of Using a CRM for Customer Service (+ Stats)
Not sure if a CRM is an effective solution for improving customer service? Check out these benefits plus stats that prove the effect CRM products have on satisfaction, retention, and case resolution:
- CRMs directly improve customer retention and satisfaction. Both of those customer service aspects are “significantly impacted” by 47% of businesses that use a CRM.
- CRMs provide a better customer experience (CX) through multichannel communication and customer interaction tracking. 75% of customers spend more with a business that offers an excellent customer experience, with communication options cited as an important factor in CX.
- A CRM offers users a solid system of data management and customer intelligence. In fact, 72% of businesses state that using a CRM gives them access to better customer data.
- CRMs help increase profitability from current customers. Businesses that invest in a CRM see typical profit gains from customer retention between 25% and 85%.
- CRMs store information important to customers, such as their previous activity and engagement history. In fact, 68% of customers believe that a critical factor for solid customer service is knowing their service history.
- CRMs help improve the revenue generated from current customers. As much as a 39% increase in revenue from upselling and cross-selling campaigns is cited as a result of using a CRM.
Sources:
Bottom Line
Though CRM platforms are used for managing sales opportunities, many offer case management and client communication features that make them ideal for overseeing customer service activities. To use a CRM to improve customer service, teams need to select the right product for them, find what they can automate and integrate, and take advantage of the reporting tools to improve their support operations.