Interactive voice response (IVR) is a voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) technology that helps callers access information or technical experts to resolve concerns. It’s best for businesses and contact centers that experience high call volumes and are looking to reduce wait time while improving quality service. In this article, we answer, “what is IVR?” and explore how it can optimize communications stacks for better performance and customer service.
Definition of IVR
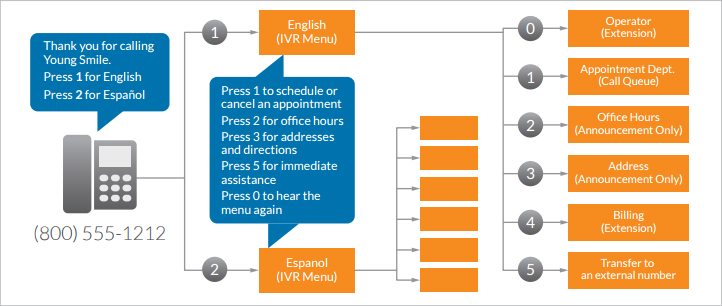
What is interactive voice response, or IVR? It is an automated phone system technology that enables incoming callers to exchange information through a series of phone menu options. Voice response systems use the caller’s responses to route calls to the correct extension. This technology helps small businesses’ customer service strategy by helping callers access experts or information to solve their concerns.
Callers listen to prerecorded greetings, selecting actions from phone menu options that route them to appropriate extensions. IVRs are generally used in call and contact centers to manage high call volumes and improve customer service. This technology enables businesses to handle all incoming calls professionally—even when agents are unavailable. Self-service options allow callers to navigate through simple tasks like payment independently.
How Does IVR Work?
As an automated telephone information system, IVRs interact with customers through prerecorded messages or text-to-speech (TTS) technology with a dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) interface. Callers respond using voice or by pressing keypad numbers. If the system cannot address the concern or the issue does not fall within the parameters of the preset menus, callers are routed to agents for further assistance.
Now we’ll answer the question, “What is an IVR system and its stages?” The system moves through four stages:
- Customer call: The process begins with a person calling your customer support line.
- IVR greeting: The system deflects inbound calls by greeting the caller with a prerecorded message and providing menu options.
- Caller selection: The customer chooses the applicable option related to their purpose of calling.
- IVR response: The system offers further submenus or routes the caller to the appropriate extension or information.
How IVR systems work
IVRs are usually the first point of contact between callers and a business’ call or contact centers. They’re structured to have top-level menus and submenus, as necessary. With each series of questions, the system deduces the purpose of the call and directs callers to the appropriate extension or communication channel.
IVR systems allow users to choose using their phone’s touch-tone keypad, but more modern systems accept spoken input. As IVR software evolves, speech recognition enables the system to understand and respond to caller queries in real time.
Benefits of IVR Solutions
Before designing an IVR system, you must clearly understand what is IVR and how it improves customer service. Customers have an increasingly high standard of customer service. According to HubSpot’s 2022 State of Service Report, 90% of customers say an immediate response is essential when they have a customer service question. In addition to better service, IVRs lower costs, increase credibility, and enhance individual and team performance.
IVR systems reduce operating costs by automating tasks and answering basic questions. An IVR is more cost-effective than hiring a traditional in-house receptionist. It also makes call routing more efficient, allowing your team to focus on more complex, higher-value tasks like customer service and analytics. IVR is also included in most cloud contact center packages, making it more affordable than traditional, on-premise solutions.
Get the data you need to properly monitor and manage your team’s performance and IVR effectiveness. IVRs provide relevant data and results based on call center monitoring metrics, depending on your provider. Track calls and satisfaction rates through analytics to understand your system’s strengths and weaknesses.
IVRs help businesses project a professional image and boost credibility by giving you an enterprise-level call answering solution without breaking the bank. Impress customers by using a business phone system that presents a welcoming, consistent, and on-brand greeting. This gives the impression that you’re an organized, sizable business dealing with high-volume calls daily.
When IVRs are designed correctly, they are tools that provide relevant information and facilitate independent issue resolution. Create self-service opportunities that allow your customers to search and find information and complete basic functions without speaking to live operators. This helps reduce call volumes and increase first-contact resolution rates, improving customer service.
By offering the right lead questions and submenu options, accurately route callers to the right agent and minimize circuitous transfers and extended wait times. IVRs capture important details, such as challenges and customer profiles, before agent interaction. This ready information gives agents a better understanding of the problem to provide effective and personalized customer support.
A high volume of inbound calls exhausts and frustrates agents unnecessarily, especially when dealing with simple and repetitive inquiries. IVR automates the resolution of basic functions and frequently asked questions (FAQs), decreasing the low-value calls agents handle daily. You can opt to prioritize VIP callers or customize the system for skills-based routing, allowing agents to focus on solving more complex issues related to their expertise.
Round-the-clock availability is a key element to high-quality customer service, but not all companies, especially small businesses, have the resources to offer live, 24/7 client support. IVR reduces client frustration by offering access to FAQs and product information after business hours and during holidays. When no live agents are available, calls can be routed to mobile phones, different offices, or even voicemail for callbacks.
Noteworthy IVR General Features
IVRs present callers with options and route the calls based on their responses. It helps agents and call centers triage customer needs by prioritizing calls based on the urgency of concerns or priority status. In addition to these functionalities, other key IVR features worth mentioning are:
- Self-service: IVRs enable businesses to facilitate simple queries without human intervention. Allow customers to resolve their concerns independently, such as PIN code change, active accounts, or placing orders.
- Call routing: Different routing strategies are based on predefined criteria to ensure your callers get where they need to be. Choose from skills-based routing, time-based routing, and round-robin routing—different approaches based on your team’s skills, schedule, or availability.
- Third-party integrations: Expand the capabilities of your phone system by integrating your IVR with customer relationship management (CRM) systems. This gives your agents essential caller information and historical insights for better client servicing.
- Call recording and transcription: Equip your supervisors with the information they need to evaluate agent performance and address review cases for best practices. Call documentation helps managers and analytical tools identify patterns and practices that improve overall performance.
How Businesses Use IVR Tools
If you’re wondering what is an IVR system’s role is in business operations, traditionally, IVRs were mainly used in call centers. However, technology has evolved to provide information on promos and updates. The technology is now being used to automate simple processes and give callers self-service options. Here are examples of how IVRs are used in business:
Companies use IVR to encourage callers to provide feedback or answer short surveys. Set up your system to ask callers to answer a survey before the call ends. This makes IVRs an excellent tool for measuring customer satisfaction and experiences.
Include payment reporting in your self-service IVR options and automate updating payments. For example, payments made outside a business’ website may require manual reporting. Use a voice response system that allows customers to enter the payment date, reference number, and amount paid. The information is automatically linked to your database for recording and processing.
IVR systems add a layer of security and authentication because businesses can request callers to confirm sensitive information before engaging with an agent. Some systems incorporate voice recognition technology to identify and verify a caller.
Enable your customers to fill out sales forms using their keypad, and the computer sends the completed form to your sales team. This IVR functionality helps your team close leads that reach your call center. The option to complete the sale immediately via IVR technology minimizes the possibility of a lead changing their mind as they check out from your website.
In addition to the use cases cited above, other examples of the practical application of IVR include:
- Balance inquiry
- Access and updating of account information
- Setting PINs or changing passwords
- Information lookup (product price, dimensions, and availability)
IVR solutions are used across a variety of industries that include banking, healthcare, finance, and education. For example, IVRs update parents on their child’s performance. In banking and finance, IVRs verify the caller’s identity and provide account information like loan application statuses and account balances. Lastly, IVRs are used in healthcare for patient satisfaction surveys, results and patient monitoring, and appointment scheduling.
If you want more information about IVRs and how to design your system, check out our list of the best IVR design practices and tips to incorporate into your phone system.
Top VoIP Providers With IVR Solutions
If you need an IVR system for your business, consider the features you need and your budget when choosing an IVR provider. The best vendors of IVR technology enable intelligent and efficient call routing, offer professional voice recording, and offer extensive integrations. Take the time to review the features included in each plan. The three providers listed below are great platforms for small businesses to consider:
Click on the tabs to find out more about VoIP providers offering advanced IVR services:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the limitations of IVR platforms?
Some people prefer to talk to live agents over machines. Some may find the interaction difficult, while others may find it slow or too tedious. What does IVR mean for those who don’t like computer-based customer service? This can lead to call abandonment and customer frustration. However, this is countered by having a well-designed response system. Check out our phone tree templates and customize them to suit your business needs.
What is the difference between auto-attendants & IVR systems?
Both systems route calls to queue or voicemail and offer callers menu options. However, IVRs offer more tailored interaction and advanced input configurations than auto-attendants. We discussed the IVR definition and found it highly interactive, handling more complex tasks like payments and surveys. Auto-attendants are business phone system features that answer and direct inbound calls based on a caller’s responses to the automated greeting or menu system.
How many options should an IVR have?
According to research on what is IVR and recommended best practices, there should be no more than five options on the main IVR menu, followed by a maximum of three submenus. Keep in mind that the listing of options should be in order of importance.
Bottom Line
IVRs improve the customer’s journey through an efficient and personalized calling experience. Answering the question “What is an IVR system?” helps you understand that well-designed IVRs result in fewer transfers, increased first contact resolution, and better agency performance. VoIP service providers with IVR solutions, like RingCentral, Nextiva, and 8×8, offer effective solutions that help businesses with call management, customers’ access to information, and prompt issue resolution.