Landlords must request and evaluate each prospective tenant’s proof of income documents and determine if they are a qualified tenant who can pay rent on time. The most frequent and reliable sources of proof of income verification include pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements, and a letter of employment. However, supplemental forms like Social Security or profit and loss statements can also provide proof of earnings.
Read along as we review the 10 most helpful proof of income documents, what to do if tenants can’t prove their income, and tips for spotting fakes:
Document Type | Best For | |
|---|---|---|
1 | Pay Stubs | W-2 employees |
2 | Tax Returns | Self-employed business owners, freelancers, or contracted workers |
3 | Bank Statements | Reviewing transactions to corroborate with other documents |
4 | Letter of Employment | Use with pay stubs from W-2 employees |
5 | Offer Letter | Newly employed W-2 individuals |
6 | Certified Public Accountant (CPA) Letter | Self-employed individuals or freelancers |
7 | Social Security Benefits Statements | Proof of retirement or disability income |
8 | Court Order Agreement | Income payments from third parties |
9 | Profit & Loss (P&L) Statement | Self-employed business owners |
10 | Landlord Reference Letter | Applicants with previous rental history |
1. Pay Stubs
Best for: W-2 employees
Pay stubs are the most commonly used form to prove income for tenants. Also known as a check stub, pay stubs are a part of the paycheck that lists the details of an employee’s pay and deductions for taxes, health insurance, and Social Security. Currently, 41 states require employers to deliver pay stubs electronically or physically to each employee, so tenants can likely provide these documents.
To review the pay stub requirements in your state or the state your applicant is coming from, visit our article Free Pay Stub Generator (Plus Templates & State-by-State Laws).
How to Verify Income From a Pay Stub
Landlords should request the two most recent pay stubs from each potential tenant as part of the rental application and screening process. While each pay stub may look different, they all should have several important pieces of information that a landlord can use to evaluate the tenant:
- Applicant name and address
- Employer name and address
- Year-to-date (YTD) gross earnings
- Gross income for pay period
- Pay schedule/period
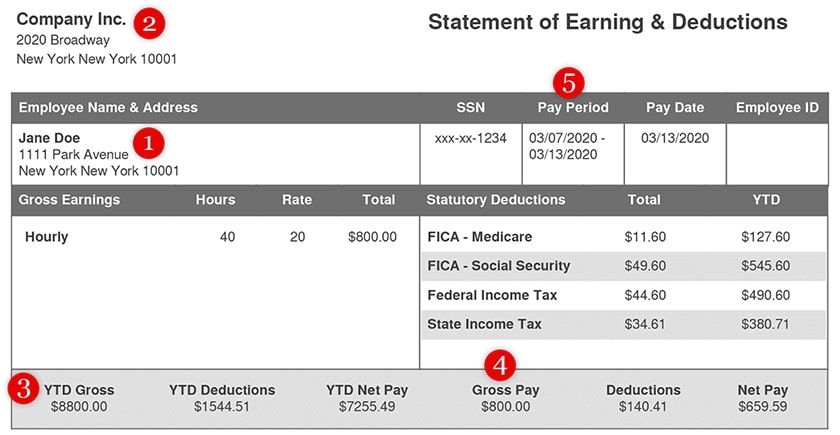
Example of pay stub (Source: Form Pros)
The tenant and employer’s name and address should be checked against the information they included on the application. Also, landlords can call and speak with the employer to confirm this information, particularly to verify that the tenant is currently employed at this location.
Landlords should consider the income per pay period and pay schedule to verify the income. Pay schedules, or pay periods, differ per company, which means the number of paychecks received per year will vary.
These are the most common pay periods, as well as how to spot them using the dates on a pay stub:
- Weekly: 52 paychecks per year; typically paid on each Friday of the month.
- Bi-weekly: 26 paychecks per year; typically paid on two set days per month, like the 1st and 15th or 15th and 30th.
- Twice per month: 24 paychecks per year; paid on uneven internals (unlike bi-weekly, which are very predictable throughout the month).
- Monthly: 12 paychecks per year; larger amount than other pay periods and gives a month as the pay period.
To see how much a prospective tenant makes in a year, multiply the income per pay period by the number of paychecks per year. Then, divide that by 12 to get their gross monthly income. You can use the following equation:
(Income per Pay Period x Number of Paychecks per Year) / 12 Months = Gross Monthly Income
Based on the image above, multiply $800 per pay cycle by 26 checks to get a yearly income of $20,800. Divide this number by 12 to know their gross monthly income (in this example, it would be $1,733 monthly).
Example: ($800 per pay cycle x 26 checks per year) / 12 months = $1,733 per month
This number should be greater than or equal to the amount you’re charging for rent to determine if your tenant qualifies to afford your rental property.
If you haven’t decided upon the tenant income qualifier for your rental property, check out our article How to Screen Tenants for a Rental Property in 6 Steps and use the calculator under step three.
2. Tax Returns
Best for: Self-employed business owners, freelancers, and contracted workers
Tax returns, or 1040s, can be a supporting document for W-2 employees or a primary document for self-employed applicants. They benefit self-employed individuals because they do not receive pay stubs, so tax returns document their income instead.
Landlords should ask for the past two years’ tax returns to verify income and continued income. The applicant can get the copy they filed directly from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), their accountant, or download it online. Some applicants use tax preparation software and can access digital files to print, email, or upload a PDF version of their tax returns.
Did you know?
Freelancers and other contract workers or full-time employees who receive bonuses or have secondary contract jobs use an additional tax form called a 1099-MISC. This form accounts for miscellaneous supplemental income that can help to pay for a rental property.
How to Verify Income From Tax Returns
The tax return will confirm the numbers in pay stubs, shed further light on additional sources of income, and show debts like alimony, student loan debt, and other owned properties. Landlords use this additional information to determine the debt-to-income ratio of their tenants and adjusted income. For example, someone may earn $200,000 a year but has to pay $150,000 in alimony, which makes their actual income $50,000. This will be the difference in whether or not they can afford the apartment.
Important elements to look at when reviewing a tax return include:
- Applicant name and address
- Gross income
- Adjusted gross income
- Date of tax return
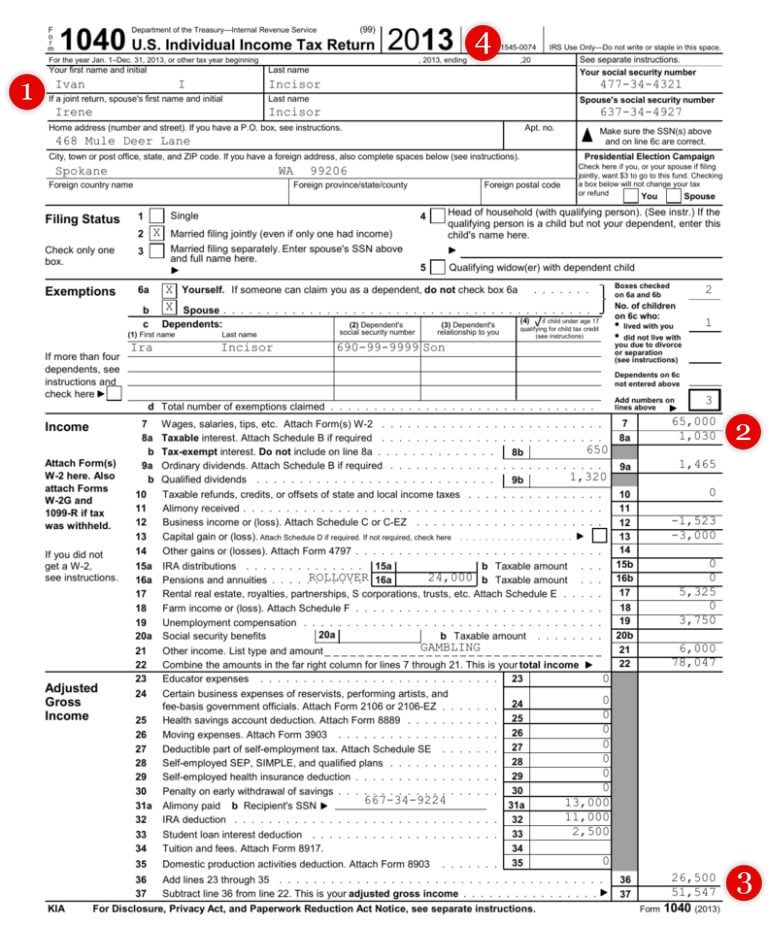
Example of income tax return form (Source: Studylib.net)
Landlords can look at the applicant’s name and address to verify that they match what’s listed on their rental application. They can then look at the wages and adjusted gross income to confirm that a prospective tenant can afford the rent. Take the gross income, divide by 12 months to get monthly income, and divide by 33% to determine one-third of their income to cover housing expenses. Also, if the adjusted gross income is significantly different than the gross income, landlords should use the same equation to calculate their income.
For more information on Avail or other top tenant screen services, read our article 6 Best Tenant Screening Services.
3. Bank Statements
Best for: Reviewing transactions and corroborating tax returns, pay stubs, and Social Security benefits
While bank statements primarily serve as secondary proof of earnings, they have several unique benefits for landlords to verify tenant income. This will show paycheck deposits, the tenant’s banking history, and cash reserves. In addition, it will indicate if the bank account is in their name and confirm their current address.
How to Verify Income From a Bank Statement
Landlords should ask the applicant for two to three of the most recent checking and savings statements to review. From there, they should check each statement for the following items:
- Applicant name and address
- Date of statement
- Beginning and ending statement balance
- Money in (deposits/credits) and money out (withdrawals/debits)
- Transaction history
- Bank name and address
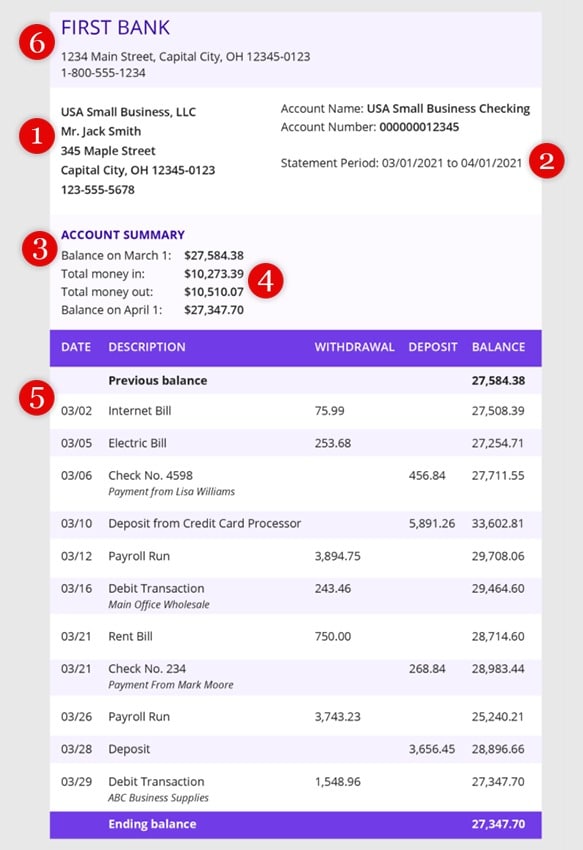
Bank statement sample (Source: Patriot)
Double-check the bank statement deposits against the amount indicated on the pay stubs to detect fraud and confirm monthly gross income. Review the applicant’s banking history to ensure there’s more money coming in than going out and that there are not a lot of frivolous purchases. Also, look for bounced checks, overdraft fees, and bill-paying history. Evaluate their savings account to see if there are enough reserves to pay for rent if the applicant loses their job or financial problems arise.
4. Letter of Employment
Best for: Use with pay stubs from W-2 employees
A letter of employment is used as secondary proof of an applicant’s gainful employment and income. It is also a way to determine a potential tenant’s employment length. Some landlords require tenants to be employed for a specific length of time in their current role to be qualified to rent their property. This shows consistency in income and commitment, which are beneficial traits of a highly qualified tenant.
How to Verify Income From an Employment Letter
An employment letter often takes more effort to obtain than pay stubs or bank statements because it needs to be requested by the applicant from the applicant’s employer. The actual letter should be on company letterhead and contain the following elements:
- Applicant name
- Date of letter
- Beginning date of employment
- Applicant position at the company
- Gross yearly salary (and guaranteed bonuses, if applicable)
- Employer name, address, contact information, and signature

Letter of employment example (Source: TemplateLAB)
Unfortunately, employment letters can be easily forged in a Word or Google document. On the other hand, they contain information that is used to confirm the employment details of the potential tenant. Check the employer’s name, address, and gross yearly income against pay stubs and the information written on the rental application. Call the company to confirm the details and research through LinkedIn to ensure the document is truthful employment and an income qualifier for the tenant.
Did you know?
Many employees earn sizable guaranteed bonuses that make up most of their salaries. If so, the employer should include their bonus amount in the employment letter. You can have it as part of the salary if it is guaranteed yearly. If the bonus is discretionary or performance-based, which means it’s not guaranteed, it may not be something you want to include as part of their tenant income qualifier.
5. Offer Letter
Best for: Newly employed W-2 individuals
If an applicant just accepted or is just beginning a new job, they may not have an employment letter to provide as part of the rental application. Instead of the employment letter, they can submit an offer letter to prove they will be gainfully employed. To remain valid, a landlord should only accept offer letters if the applicant has been hired within the past 30 days.
How to Verify Income From an Offer Letter
The applicant will need to request the offer letter from their new employer, or they may have a copy of the letter if the hire was within the last 30 days. The offer letter should be on company letterhead and contain similar information as the letter of employment:
- Applicant name
- Employment start date
- Applicant position at the company
- Gross yearly salary (and guaranteed bonuses, if applicable)
- Employer name, address, contact information, and signature

Example offer letter sample (Source: Formstack)
Similar to the letter of employment, landlords can verify this information with the employer by calling to confirm the details. They also can research the applicant and company on LinkedIn. Keep in mind that if the applicant is newly starting this position, they may not have posted it on LinkedIn yet out of courtesy to the previous employer.
6. Profit & Loss Statement
Best for: Self-employed business owners
A self-employed applicant should provide the landlord with a profit and loss (P&L) statement to show their business’ income and expenses. This secondary supporting document should be used in conjunction with tax returns, bank statements, and a CPA (certified public accountant) letter. A tenant can ask their accountant or bookkeeper for their P&L statement or pull it from their records if they do their own accounting with a product like QuickBooks.
How to Verify Income From a P&L Statement
This document will show the landlord whether the owner is taking a draw from their accounts and how much or if they’re paid as a W2 employee on the payroll. Aside from these, it shows the applicant’s expenses, whether the applicant has positive or negative cash flow, as well as the history of the business. This data is vital for landlords as this will verify if the applicant is qualified and if the applicant’s business net income and the revenue generated are enough to pay rent.
The items that a landlord should be on the lookout for are:
- Company name
- Time period of the statement
- The total profit or loss during the period stated
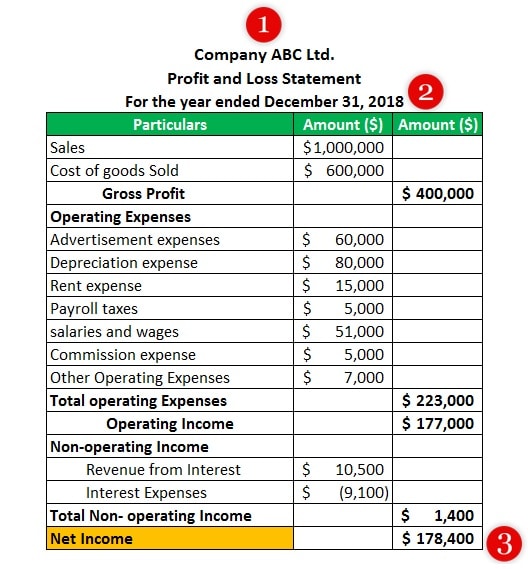
Example of profit and loss statement (Source: WallStreetMojo)
Check with the Secretary of State’s corporate filings division to verify the ownership of the business and if the business is active and in good standing. Research the business online through Google and LinkedIn to review the company’s history. If the corporate filing shows a resident agent different from the tenant-applicant, call the resident agent to verify the applicant is the business owner.
7. Certified Public Accountant (CPA) Letter
Best for: Self-employed individuals or freelancers
A CPA letter is, in essence, a letter of employment for self-employed people. While they could write their own employment letter, it would be less believable to landlords because the facts and figures are written by the self-employed applicants themselves who own the business and want to live in the rental property.
How to Verify Income From a CPA Letter
Landlords must request that business owners get a letter from their accountant as proof of their income and past income. The letter should include:
- Accountant’s name, address, contact information, and signature
- Applicant name and company name
- Date of letter
- Date business started
- Stake in company
- Income for the past two to three years
- Projected or year-to-date income for the current year

CPA letter example (Source: Templateroller)
To verify the income, landlords should double-check the applicant’s tax return documents and P&L statements against what is written in this letter. It’s best to contact the accountant to understand the numbers and confirm any details if there are any inconsistencies.
8. Social Security Benefits Statement
Best for: Proof of retirement or disability income
A Social Security statement generally verifies income by retirees or disabled tenants receiving Social Security disability benefits. It’s best when used as a supporting document along with the applicant’s tax returns or bank statements. Because Social Security or disability income may be lower, it’s essential to look at the bank statements to verify the applicant’s cash position.
How to Verify Income From a Social Security Benefits Statement
Applicants can request their benefits statement directly from the Social Security Administration, and it should include the following items:
- Applicant name and address
- Date of request
- Income payment amount
- Payment schedule

Example of Social Security benefit statement (Source: Studylib)
The landlord can call the Social Security office number on the letter and ask to verify that the applicant receives the benefits mentioned in the statement. Due to confidentiality laws, the office may only confirm this once the applicant permits it.
9. Court-ordered Agreement
Best for: Income payments from third-party sources like alimony or lawsuits
A court-ordered agreement is a signed legal document between an arbitrator and a third party that the court has ordered to pay. The most common types of court-ordered agreements include spousal alimony, child support, and a payout from a trust or lawsuit. Court-ordered agreements are not as common, but still can be a verifiable source of income for potential tenants.
How to Verify Income From a Court-ordered Agreement
Applicants may already have a copy of their court-ordered agreement in their files. If they don’t, they can get it from their attorney or the court clerk’s office where the ruling occurred. Unless they’ve been sealed, these documents are part of the public record, meaning you can look them up via the county clerk’s office. Confirm the following details:
- Shows the document is a court-ordered agreement
- Income amount and frequency

Example of court-ordered child support agreement
Landlords must verify if the payments are monthly or paid in one lump sum. If it’s a lump sum, request additional bank statements to ensure there’s still enough money to supplement or pay rent consistently. If the agreement is structured as a monthly stipend, make sure it’s the income multiple you’re willing to accept.
10. Landlord Reference Letter
Best for: Applicants with previous rental history
A reference from a previous landlord should be supplementary documentation, giving insight into the applicant’s character and financial standing concerning previous rental properties. Like the employment letter, the landlord reference letter must be requested from the applicant’s previous landlord, which may take more time and effort. In addition, some landlords may refuse to write them at all.
How to Verify Income From a Landlord Reference Letter
When reviewing the landlord reference letter, landlords should look for the following information:
- Applicant and previous address
- Previous landlord’s name and contact information
- Amount of rent paid per month
- Length of tenancy
- On-time rental payments

Landlord reference letter example (Source: SampleTemplates)
See how much the applicant paid at their previous residence and if they made their rent payments on time. Compare that to the amount of rent you will be charging and their current income to decide whether they can afford to pay the rent you require. You can also call the previous landlord to confirm the stated information. Also, some landlords will only stick to the facts and not include a character reference or personal details on the tenant to avoid violating Fair Housing laws.
What to Do if Tenants Cannot Prove Income
There are times when applicants cannot prove their income or may be unable to afford the property (for example, a newly graduated college student looking for their first apartment, or an individual recollecting their finances after bankruptcy). This scenario has two options: to reject the tenant or ask them to get a co-signer or guarantor.
If you’ve decided that you do not want to accept the applicant as a tenant, it is essential to handle declining the applicant properly. It’s a good idea to create a rejection letter, also known as an adverse action letter, with a checklist of potential legal reasons an applicant is denied.
To learn more about what needs to be included in your rejection letter, visit our article How to Screen Tenants for a Rental Property in 6 Steps (+ Screening Questions & Income Calculator).
On the other hand, if you feel that the prospective tenant has a promising background but does not have enough income to meet rent requirements, you can ask them to seek a co-signer or guarantor. It could be a family member, friend, co-worker, or anyone the applicant knows who is willing to be liable on the lease if the applicant cannot or will not pay the rent. The guarantor should complete an application and submit their documents for the landlord to review to ensure they are qualified to co-sign the lease.
If the applicant does not have anyone, they can ask to be a guarantor. Some companies will guarantee the property with you. The Guarantors is an insurance company that provides financial solutions, minimizing risk for landlords and providing opportunities for tenants. Landlords must sign up and choose the right level of protection for their property. Then potential tenants can apply through The Guarantors to get financial assistance to rent a home.

The Guarantors property manager homepage
Tips for Spotting Fake Proofs of Income
Now that you know what proof of income is, how landlords verify income, what financial information a landlord can ask for, and what counts as proof of income, it’s also essential to know how to spot fraudulent documents. Knowing what to look for can help you vet your prospect’s proof of income, thus saving you time, money, and possible litigation. Here are some tips for how to spot fake income documents:
- Listen to your gut: If the applicant’s income doesn’t add up or you feel something isn’t right, go with your intuition. If you have trouble verifying their claims, you should reject them as a tenant. If there are issues initially, they often become magnified later on and may cost you evictions and legal fees.
- Require tenants to sign Form 4506: If you want to verify the information on a profit and loss statement or validate a potential tenant’s income, you can request a transcript from the IRS with a signed Form 4506. The transcript will show the tenant’s federal tax documents. The transcript is the official income received and recorded by the IRS and is stamped as official, so it can’t be forged.
- Use a checks and balances system: The purpose of collecting several documents to prove an applicant’s finances is to apply a checks and balances system. Review pay stub financials against tax returns and bank statements. Check the letter of employment against the pay stubs. Use the CPA letter in comparison to tax returns and P&L statements. Reviewing all the documents next to each other will show if there are any fakes or inconsistencies.
- Do research online: With most individuals and businesses on the internet, landlords can easily do research online through Google, government websites, and LinkedIn to verify information provided by the applicant. Use the internet to your advantage, but remember not everything on the internet is truthful.
- Pay attention to inconsistencies: When doing your checks and balances with the paperwork, note the specific numbers you find. If the salary on a letter of employment reads $60,000 and the pay stubs say the salary is $55,000, you should immediately be alert for a fake document.
- Notice if paperwork has official markings: Documents from employers should all be on letterhead or include the company’s logo for which the prospective tenant works. Tax returns, court-ordered agreements, and Social Security statements should have government markings. A red flag should be raised if you do not see these titles and logos on official paperwork.
Stay aware of these tips and other prominent tenant scams by reading our article 20 Types of Tenant Scams Every Landlord Needs to Know.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
If the applicant is self-employed, you may use any of the following forms for proof of income:
- 1099-MISC tax form: This form shows any payments received from other organizations. For independent contractors with several sources of income, these can be used as income documentation.
- 1040 tax form: The previous year’s 1040 tax form can be used as evidence of income if the applicant has a licensed accountant prepare their taxes or file them online.
- P&L statements: This shows the applicant’s profit and loss for their business, whether the applicant has positive or negative cash flow and the history of the business.
- Business manifest: A copy of the applicant’s business license and a business manifest that details how much they pay for themselves is also acceptable as proof of income documents.
Yes, if an applicant isn’t actively working but receives unemployment payments, workers’ compensation, or disability insurance, this can be used as proof of income documents. Applicants should ask their employer, the state’s unemployment office, or their insurance provider for the necessary paperwork.
If an applicant is a newly employed applicant, they can use the offer letter as proof of income. They must request the offer letter from their new employer, or they may present a copy if the hire was within the last 30 days. Ensure that the offer letter is on company letterhead and contains similar information as the letter of employment, like name, employment start date, position at the company, gross yearly salary, as well as employer name, address, contact information, and signature.
Bottom Line
Landlords must request specific documentation as part of their rental application process to verify the income of each potential tenant. Without income verification documents, landlords can put themselves into a tough situation, resulting in a loss of profit, time, money, or eviction. Review each document with a fine-toothed comb, and don’t hesitate to ask for supplemental documents to protect your real estate investment and profits.