Although many voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) phone systems offer uptime guarantees and robust phone management features, they’re not foolproof solutions. Since they heavily rely on internet connection, call quality can easily be affected by network troubles. Some of the common VoIP issues businesses encounter include jitter, choppy audio in calls, dropped calls, and failure to accept and place calls.
These problems negatively affect customer satisfaction. It’s important to address them immediately, especially because 76% of consumers stop engaging with a business after a single bad experience, according to the Invoca Buyer Experience Benchmark 2022 report. In this article, we’ll explore common VoIP dilemmas and ways to fix them.
1. Jitter or Data Packet Loss
Causes: Poor internet connection and network congestion
If parts of the call go missing or garbled, you’re experiencing a jitter. To understand how this problem happens, you must understand what VoIP is and how VoIP calls work. Data packets travel simultaneously over the network to a specific internet protocol (IP) address. Once they arrive, the jitter buffers organize the data packets, collecting and storing audio data and then sending them to the recipient, ensuring that words are audible.
A jitter happens when there’s a delay between the transmission and reception of data packets over the network. This typically results from unstable internet connection and network congestion. Ideally, jitter should not exceed 25 milliseconds (ms). Otherwise, the call quality suffers.
How to Fix It
To address jitter or data packet loss, try the following VoIP troubleshooting action steps:
- Upgrade your internet connection: Your current internet plan may not have sufficient bandwidth to support all the connected devices. If this is the case, troubleshooting jitter involves asking your service provider to upgrade your connectivity plan. VoIP systems typically require at least 100 kbps upload and download bandwidth per line.
- Reduce local network traffic: As mentioned, network congestion causes jitter. By reducing the traffic volume or the amount of data being transmitted across the network, you’re less likely to experience jitter. Use a network monitoring tool to locate packet streams that move VoIP data along and measure quality of service (QoS).
- Use wired hardware: Devices that use Wi-Fi are more likely to experience jitter, as they are more vulnerable to interference from other wireless devices. That said, consider installing wired connection points in your office to enable team members to easily connect when experiencing jitter. This is especially beneficial for meeting rooms, where most users engage in audio and video conferencing, which require stable internet.
Popular VoIP phone system RingCentral offers QoS reports outlining near real-time information about the overall health of your phone system. It displays various filters that represent call quality data. For example, the internet service provider (ISP) filter shows the number of good-quality calls that went through each specific ISP. The QoS report helps you spot VoIP issues more easily and address them quickly before they become a costly nuisance.
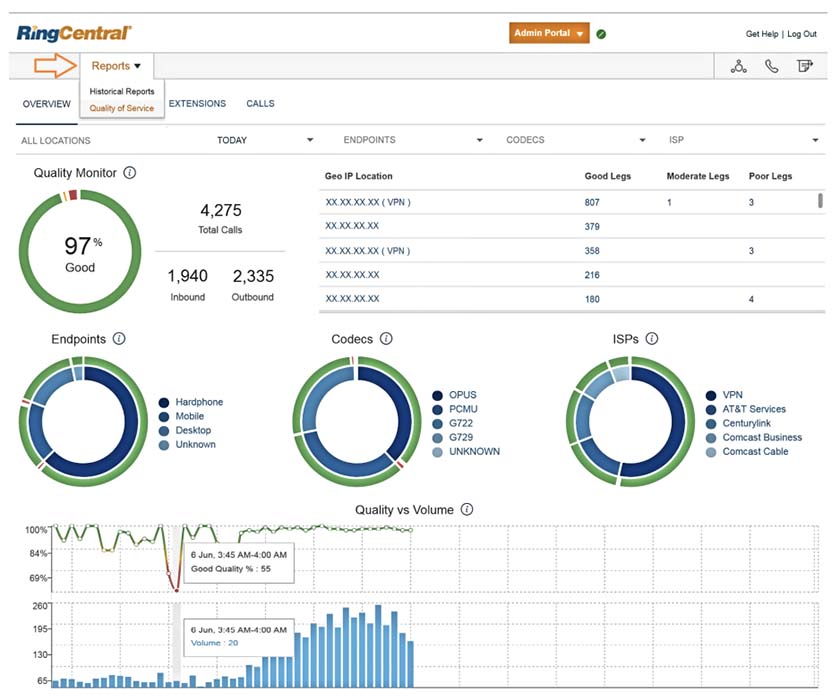
RingCentral’s QoS reports offer meaningful insights about call quality. (Source: RingCentral)
In our RingCentral review, we recommended the platform to businesses looking for a complete phone solution, since it offers robust call management capabilities. These include call queues, multi-level auto-attendant, and call monitoring. Its subscription starts at $30 per user, monthly.
2. Latency
Causes: Insufficient internet bandwidth and slow networking equipment
VoIP latency is closely related to jitter. While jitter refers to the delay in transmitting data packets, latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel from one endpoint to another. If the latency values are high, the participants will talk over one another and experience a choppy conversation. Similar to jitter, latency issues result from insufficient internet bandwidth. It may also be due to slow networking equipment.
The acceptable latency for VoIP calls is 150ms. When you exceed this figure, the call quality is reduced. However, if you want to facilitate optimal-quality calls, keep latency values below 20ms.
Note that the majority of customers call businesses for information and purchase decisions, so poor-quality phone calls can directly affect the bottom line. According to the Invoca Buyer Experience Benchmark 2022 report, 42% of customers call to ask for more product details, while 30% do it to complete the sale.
How to Fix It
To address latency issues, implement the following changes:
- Upgrade your internet bandwidth: Similar to fixing jitter, one solution for latency problems is to ask your ISP to increase the bandwidth to accommodate more VoIP calls and maintain excellent call quality. Consider providers offering up to 5,000Mbps if you regularly receive large volumes of calls.
- Replace outdated networking devices: Invest in VoIP routers to ensure that VoIP calls are given priority even if the network experiences high volumes of traffic.
- Reconfigure rerouting settings: If data packets make several stops to reach their destination, delays are bound to happen. Let your information technology (IT) team reconsider and adjust the routing settings.
3. Phone Echoing
Causes: Faulty hardware, acoustic feedback, and interference
Phone echoing, one of the common VoIP issues, occurs when you hear your voice or any sound from your end being repeated during a live call. It causes frustration among call participants as it makes conversing more difficult. Although phone echoing is one of those VoIP problems attributed to a slow internet connection, like jitter, it could also be due to acoustic feedback.
When you’re in speakerphone mode, the microphone receives a sound from the speaker and sends the sound back into the call. Similarly, when there are wireless devices close to your phone, this creates interference that results in phone echoing. Another reason for phone echoing is malfunctioning Ethernet or handset cords. Damaged cables are likewise a culprit.
How to Fix It
To rectify and prevent phone echoing, use these VoIP troubleshooting strategies:
- Lower the speaker phone mode volume: This reduces the likelihood of acoustic feedback. Or, if possible, turn off the speakerphone mode.
- Don’t put VoIP phones near electronic devices: Keep desktop computers, monitors, or power strips three to four feet away from VoIP phones to avoid electromagnetic interference.
- Update equipment: Ensure that your hardware isn’t damaged. Inspect cables regularly and make sure that the plastic jacks on Ethernet cables aren’t chipped or broken off.
If you’re looking for high-quality VoIP phones, Ooma is an excellent choice of provider, as it offers a wide range of IP and conference phones. It has its own first-party hardware and supports various brands, such as Yealink and Grandstream. Its analog telephone adapter (ATA) Telo allows you to use traditional landline phones to place and accept phone calls via the internet. Take advantage of Ooma’s buy-one-take-one deals to save more on hardware costs.

Ooma offers its own first-party hardware. (Source: Ooma)
For featuring robust call management capabilities and an easy-to-use interface, Ooma earned a high score in our Ooma review. Handle phone calls more efficiently by maximizing the provider’s features: virtual receptionist, ring groups, call forwarding, call park, and three-digit extensions. Ooma Office’s entry-level subscription plan is priced at $19.95 per user, monthly.
4. Poor Audio Quality
Causes: Poor internet connection and incorrect audio settings
Audio problems include delayed voice, static sounds, and one-way audio, wherein you hear the person at the other end of the line, but they don’t hear you. Some users who encounter this VoIP issue assume the internet phone is not working. But often, the real cause is a poor internet connection. Sometimes, the audio settings are not configured properly, for instance, when the correct microphone is not selected, or the volume is set to low.
How to Fix It
To resolve poor audio quality, use these tips:
- Improve internet connection: Run a VoIP speed test to determine how much bandwidth you need to accommodate the volume of phone calls. The poor audio quality may indicate that the bandwidth isn’t enough.
- Revisit audio settings: Check if the proper microphone is selected and the volume is turned up. This also applies to joining video meetings. Make it a habit to check your audio settings.
- Reduce background noise: If possible, answer calls in quiet places. If you’re in a busy environment, use a noise-canceling headset to ensure the other person on the line will hear you clearly.
5. Dropped Calls
Causes: Data packet loss, call duration limit, and signal loss
Dropped calls refer to calls being disconnected from the network. Sometimes, it’s due to data packet loss, where the network processes the voice data too slowly. Other times, it’s because of the call duration limit, in which your VoIP service provider puts a cap on each calling session to avoid exorbitant charges. Similarly, signal loss may cause dropped calls. When you lose an internet connection or the device is simply not getting enough signal, the calls automatically disconnect.
Dropped calls are among the top phone connection issues that easily affect the company image in a negative way. Some customers may think that the service representative intentionally hung up, while others are frustrated at sharing information over and over when they contact the business again after being disconnected. According to Invoca Buyer Experience Benchmark Report 2021, 54% of consumers said they needed to repeat their reason for calling multiple agents.
How to Fix It
When troubleshooting VoIP issues like dropped calls, apply the following actions:
- Increase bandwidth speed: Evaluate your communication needs and decide if it’s time to improve your internet’s bandwidth strength. Configure QoS in the router settings so that VoIP calls are prioritized.
- Extend call duration limit: Ask your VoIP service provider to increase the limit or remove it altogether. Check the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) timeouts on your router as well and adjust accordingly.
- Move the router to a more strategic location: Try to keep your router away from large objects or thick walls. With this, VoIP phones will have a better signal.
Reliable VoIP provider Google Voice limits phone calls to three hours, a generous call duration limit for businesses that accommodate non-technical customer service requests. It also helps that the solution offers a service level agreement (SLA) of 99.9% uptime guarantee, available in all subscription plans.
Google Voice allows three-hour call duration limits.
(Source: Google Voice)
As mentioned in our Google Voice review, this VoIP solution is ideal for solopreneurs who need a free business phone number. Aside from one local phone number, its free version includes unlimited calling and texting within the United States and voicemail. If you plan to upgrade to the paid subscription package, the entry-level plan costs $10 per user, per month.
Visit Google Voice via Google Workspace
6. Inability to Place or Accept Calls
Cause: Enabled Session Initiation Protocol Application Layer Gateway (SIP ALG)
VoIP not working to make outbound and receive inbound calls is a common problem among businesses. This typically occurs when the SIP ALG is enabled. This tool, found in many networked routers, rewrites VoIP packets to get them through firewalls. This modification process, however, directs packets to the wrong IP address, resulting in failed outbound and inbound calls.
How to Fix It
Fortunately, troubleshooting this VoIP problem is as easy as disabling the SIP ALG in the router’s menu. Reboot your router after turning SIP ALG off. In some corporate firewalls, you may need to set up port forwarding. Log into your router and go to the port forwarding settings. Enter the port numbers and your device’s IP address. Select a forwarding protocol and save the changes. After applying these steps, do a test call.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A person or an organization can infiltrate a business phone system through different means:
- Social engineering scams: Persuading employees to provide confidential information
- Eavesdropping: Listening in on business calls without the person knowing
- Malware: Injecting malware into apps, websites, or browsers and employees unknowingly downloading the malicious software
Being vulnerable to hackers is one of the disadvantages of VoIP, with bad actors disrupting normal business operations and extorting money. To reduce the risk of falling victim to VoIP hacking, companies must enforce strong security measures, such as using virtual private networks (VPNs) for remote access, implementing two-factor authentication, updating VoIP firmware, and conducting regular audits.
The items below are some of the things that often contribute to VoIP problems. Thus, when VoIP’s not working, be sure to check these:
- Cable connections: All cables must be plugged properly and securely. Inspect them every now and then to ensure that there are no damaged cables.
- Hardware equipment: Your VoIP phones must be up to date and registered with your VoIP provider.
- Internet connection: The internet bandwidth must support the volume of calls in your call center. Upgrade your plan if necessary.
Yes, it’s possible to make and accept VoIP calls on an iPhone or Android device. The voice data, converted into digital signals, is delivered to the receiver through your phone’s data plan using 3G, 4G, or LTE.
Bottom Line
VoIP problems negatively affect call quality, agent productivity, and ultimately, customer satisfaction. Thus, it’s important to address them immediately before your business suffers lost profits and a tainted reputation. As you familiarize yourself with VoIP problems and solutions, look for service providers offering excellent customer service to ensure you get the timely assistance you need whenever you encounter issues.