Voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) phone systems convert voice into digital signals, allowing you to make calls directly from mobile and compatible devices. They offer cost-effective communication solutions ideal for small businesses as they are scalable, feature-rich, and require little to no maintenance. In this guide, you will learn about the short history of VoIP phone systems, how they became today’s mainstream communications solution, and what to expect in the coming years.
History of VoIP: Telephone Technology Before VoIP (Around 1667 to 1970s)
VoIP is one of the most useful communications technologies developed in the last century. It is founded on other technological innovations, specifically the telephone and the internet. VoIP has distinct advantages over traditional phone systems with comprehensive integration, video and automated features, and multichannel reach. Here are some of the critical communications milestones that led to VoIP:
1667: Robert Hooke & the Audio Transfer Device
English philosopher Robert Hooke invented a primitive audio transfer device as early as 1667. He used a string telephone instrument to send sound waves over an extended wire via mechanical vibrations. However, the world would need to wait another 200 years for the next major step in the evolution of transmitted communications.
The 1880s: Samuel Thomas von Sommering & Alexander Graham Bell
In 1908, Samuel Thomas von Sommering developed the electrochemical telegraph. The signal was transduced electrochemically as bubbles from the electrochemical water decomposition. Further developments during this period included the design of the first electromagnetic telegraph, the communication of the first telegraph, and the completion of the transatlantic telegraph cable by 1866.
Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone and was awarded for telegraphing vocal and other sounds in 1876. By the 1880s, telephone exchanges were built in every major United States city.
1925: Bell Laboratories
One of the defining moments of telephony began in 1925 when AT&T and the Western Electric company joined forces and established the Bell Laboratory. Bell Laboratory sought to invent and design technologies that would expand communication services. By 1958, the first U.S. communication satellite was launched.
1966: Fumitada Itakura & Shuzo Saito
In 1966, Fumitada Itakura of Nagoya University and Shuzo Saito of the Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Company collaborated to propose linear predictive coding (LPC), a method to convert speech into digital signals. This speech-processing algorithm became the basis for VoIP and speech synthesizer chips.
1969 to 1974: ARPANET
The internet as we know it today began as a research project in 1969. The Advanced Research Project Agency (ARPA; called DARPA today), was a U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) agency focused on military technology. ARPA was working on remote computer access for improved communication between users. ARPANET was the first packet-switching network and early adopter of the IP network protocol communications suite.
Eight years later, in 1974, Culler-Harrison Incorporated’s office in Goleta, California, and MIT’s Lincoln Laboratory in Lexington, Massachusetts, made the first VoIP call over ARPANET (one of the earliest internet-capable phone networks).
The call went through, but the audio was clunky and full of static. At 2.4kbps, it wasn’t nearly as crystal-clear as the high-definition (HD) voice calls we have today. Still, this event marked a significant milestone in the development of VoIP communications. However, it would still take more than a decade before commercial VoIP solutions evolved to become a viable communications option.
Hosted Business VoIP Applications: 1990s
The early 1990s marked a period of rapid internet adoption for businesses. Various internet-based VoIP phone systems emerged on the market to solve business needs. Speak Freely was launched in 1991 as the first VoIP service and consumer-ready application. Soon after, VocalChat and VocalTec’s Internet Phone program entered the scene too.
Alon Cohen is the co-founder of VocalTec Inc. and the co-inventor of the Audio Transceiver, which enabled the creation of Voice Over Network products. VocalTec was the first to release an internet phone in 1995, and it was during this time that Intel, Microsoft, and Radvision initiated the standardization of VoIP communication activities.
VoIP was developed around 1995 originally to serve as a way to save money on long-distance and international telephone charges. VocalTec is considered by many to be the first VoIP company with its creation of the first internet phone for the masses.
Despite their cutting-edge technology, internet bandwidth wasn’t fast enough to support high-quality audio or fast load times. These factors made VoIP solutions slow and call quality barely acceptable, especially compared to today’s small business VoIP services. These programs failed to reach mainstream success, but they laid the essential groundwork for VoIP adoption when broadband internet changed the world in the early 21st century.
Jeff Pulver, an American internet entrepreneur, must be mentioned when talking about VoIP news and developments. He invested in various startups and co-founded Vonage and Vivox. His early work with his company, Free World Dialup, played a large role in the Federal Communication Commission’s decision to classify VoIP as an internet application and not a telephony service.
VoIP Expansion: Early 2000s
With the upgrades in communications, landline systems became increasingly popular and connected businesses, consumers, friends, and families. Phones became the primary means of communication, but calls outside of local areas incurred high per-minute costs. Landlines were stationed at home, in public spaces, or in the office, making these available for shared use. Call quality still lagged; there were call drops and party lines where two or more subscribers shared a telephone line or circuit.
Broadband internet became readily available and affordable in most populated areas of the developed world by the early 2000s. This, combined with the invention of the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) codec, which made it easier for software to send audio as data over the web, set the stage for VoIP’s emergence.
VoIP providers charged a single flat monthly rate for their services, which was more enticing than paying for separate internet packages and landlines. Vonage launched in 2001 and became a huge success for consumers and businesses. Skype soon joined the scene in 2003 to demonstrate a new level of internet-based voice communications potential.
Did you know?
Marian Croak is the engineer known for pioneering the VoIP technology of converting data into digital signals for easy transmittal over the internet. She is credited for being one of the essential inventors of VoIP, establishing the fundamentals for the communication systems we know today.
Croak has received more than 200 patents and several awards and was inducted into the Women in Technology International Hall of Fame in 2013. In addition to her accomplishments in VoIP technology, while working with AT&T, she patented the technology that allows people to donate money using text messaging.
Present Day
VoIP communication systems continue to innovate and offer new and advanced VoIP phone features. Most VoIP providers offer functionality like video calling, messaging, file sharing, automated attendants, and call recordings. Others provide more advanced tools like customer relationship management integrations, interactive voice response (IVR) tools, real-time analytics, and hot desking.
Based on our latest critical VoIP statistics report for small businesses, 61% of companies are switching to VoIP setup, and there is a continuous 20% rise in productivity with VoIP. Reduction of telecommunication costs, specifically setup and long-distance calling, are key benefits enjoyed by small teams with limited budgets.
The Future
While VoIP has reached great heights, VoIP technology continues to improve. The next stage is enhanced functionality through disruptive integration with 5G and artificial intelligence. With 5G-enabled smartphones operating on 5G networks, VoIP services expect better packet prioritization, analytics, and automation, as well as improved reliability.
The flexibility of VoIP through omnichannel service delivery will allow organizations to break down the silos and deliver a more client-centric strategy for higher customer satisfaction. Next-generation VoIP intelligence turns data from different interaction points into seamless customer conversations.
Research and information estimate that the VoIP services market will reach $194.5 billion by 2024. VoIP’s growth is primarily driven by low installation and maintenance costs, minimal staff support, better reliability, and robust features.
Parallel to the development of VoIP, communications platform as a service (CPaaS) is gaining traction as developers can better integrate communication, automation, and customer service features into existing business applications and software.
Learn more about CPaaS and how it helps deploy multiple channels for customer and internal outreach by checking out our CPaaS market trends for an overview of the CPaaS market.
VoIP is always moving. For an accurate understanding of where the industry is going, check out our VoIP news and trends piece.
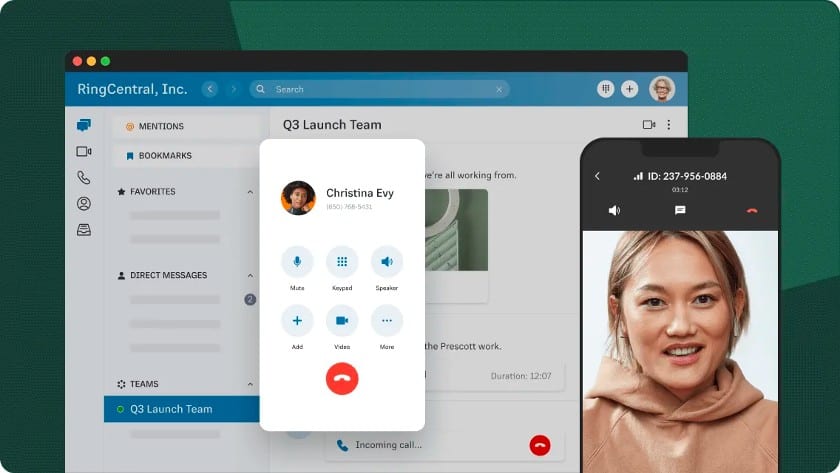
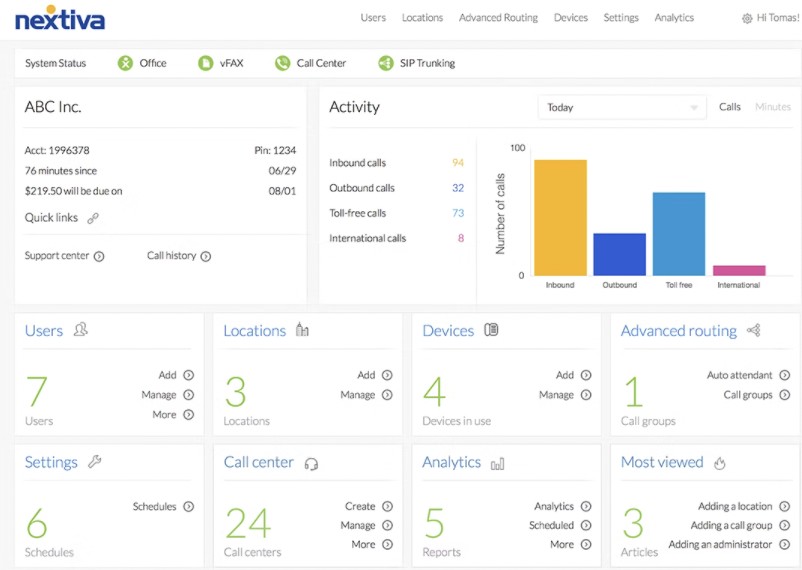
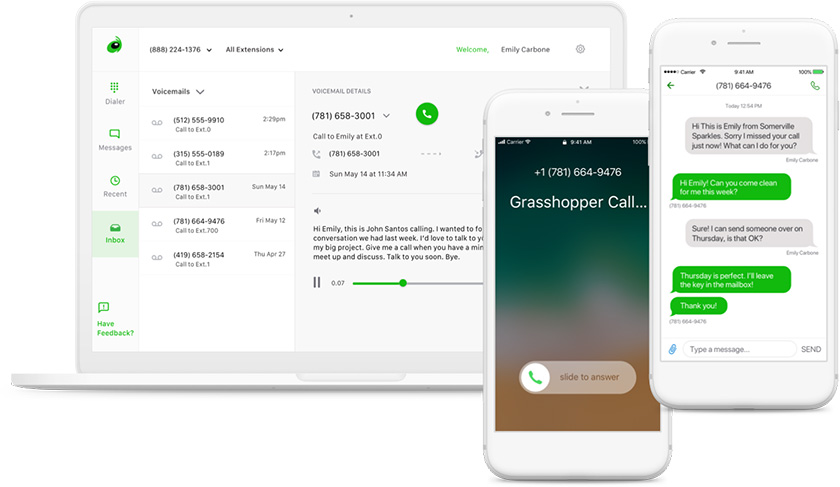
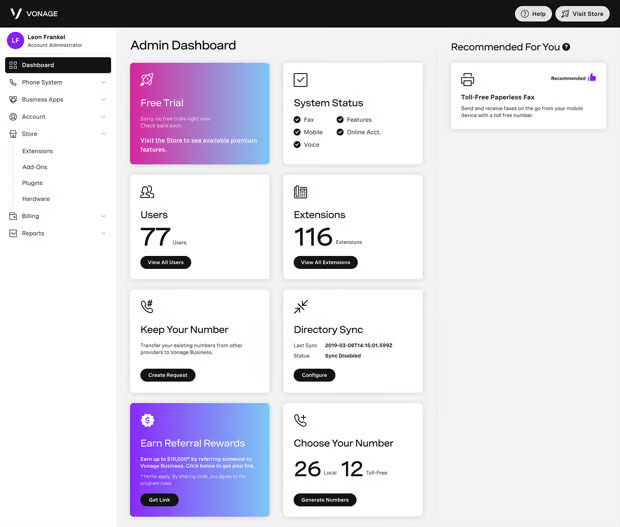
VoIP Providers
The history of VoIP technology continues to evolve, making it more affordable and feature-rich than primitive landline services. Businesses now have several options in terms of VoIP service providers, where entire offices will be able to use VoIP smartphone apps to conduct business communications on the go.
Here are four highly rated VoIP service providers, ideal for small businesses, that scale with the size of your company:
Not what you’re looking for? In addition to these options, if you’re a small business or solopreneur looking for cost-effective VoIP solutions, read this guide on our recommended top six cheap VoIP services. These low-cost options offer various services, from texting to video conferencing and team chat.
VoIP’s Impact on Business
The era of the landline phone, which lasted more than a century, is quickly coming to an end. VoIP’s impact on the business world is becoming increasingly obvious and its sheer volume of features is making it the only real choice for modern business. With VoIP, international calling is cheaper, which is especially valuable in a business world where the inconvenience of geographical distances is shrinking.
With VoIP, you can take business calls on your mobile phone without needing to give out your personal details to your customers. Additionally, your agents can do the same and bring the world of the professional contact center to their private residences or on the road. This brings us to one of the most important aspects of modern VoIP communications: its compatibility with hybrid work.
VoIP makes it easier to communicate with both colleagues and customers from any environment—as long as it has an internet connection. Its compatibility with unified communications technology makes it easy to convert a business call to a video conference. As business becomes more mobile-oriented, it’s clear that VoIP technology will help make users more agile in daily communication.
Frequently Asked Questions
The short answer to this is yes. There are VoIP software and applications available that will enable you to make and receive calls for free. However, businesses typically need more advanced features, such as automated call distribution, chatbots, or live call answering services. On average, VoIP phone systems cost about $20 to $200 per agent, monthly, depending on the features and service fees.
No single person is responsible for VoIP. The history of VoIP is filled with discoveries and inventions by different people over time. Robert Hooke, Alexander Graham Bell, Fumitada Itakura, Shuzo Saito, and others all play a significant role in the emergence and history of VoIP.
VoIP offers many advantages, including competitive pricing, low-cost installation, overhead expenses, and portability. Businesses using VoIP enjoy features such as chat, auto-attendants, and call analytics that help improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
VoIP is relatively new but anchored on the technological advancements of the internet and the telephone. For those wondering when VoIP was invented, it rose to fame in the mid-1990s as a cost-effective option for international and long-distance calling.
Regarding VoIP vs Wi-Fi calling, both use the internet but are not the same. VoIP refers to the use of packet-switched internet telephony to make voice calls instead of a regular analog telephone line. Wi-Fi calling refers to the ability to make calls over a Wi-Fi connection built into your device.
Bottom Line
This VoIP history highlights that this relatively new technology has been rapidly expanding over the past few years. It has a rich history, with the telephone and the internet acting as major founding blocks that led to VoIP as we know it today. As the internet continues to advance and become more affordable, we will likely see VoIP technology solidifying itself at the forefront of business communications.
Are you looking to get started with a strong VoIP provider? Consider RingCentral; it’s one of the most feature- and integration-rich providers in the industry. Sign up for its 14-day free trial today.