In real estate, leasing agents play a pivotal role in facilitating property transactions by connecting property owners with potential tenants. As with buyer and seller agents, proper training and knowledge are essential to the industry’s growing demand for their services. You must understand the responsibilities of a leasing agent, work with a landlord or property management company, build your clientele, and manage rental listings. While this is a lot to learn, our experts will start you on the right path by teaching you how to become a leasing agent.
Step 1: Learn What a Leasing Agent Is & Its Responsibilities
Leasing agents are realtors, real estate agents, or brokers who serve as liaisons between property owners and prospective tenants. Their primary roles involve marketing and promoting available rental properties, conducting property showings, screening and qualifying tenants, and negotiating lease agreements. Leasing agents are crucial to ensuring smooth and legally compliant transactions between property owners and renters while offering guidance and assistance throughout the leasing process.
Successful real estate leasing agents possess a unique blend of traits and skills. To learn how to be a leasing agent, you must excel in communication, negotiation, and organization to interact effectively with clients, secure favorable lease terms, and manage their workload efficiently. Customer service, adaptability, and empathy are essential for addressing tenant and client needs. Market knowledge, marketing proficiency, legal expertise, and sales skills round out their skill set, enabling them to thrive in the dynamic real estate leasing field.

Being a leasing agent can be a rewarding career.
Depending on the type of rental property, leasing agents may work onsite. For example, apartment complexes and multi-complex subdivisions, business offices, and industrial complexes often have agents who work in the main office, catering to the units and tenants within the company.
Some key responsibilities and tasks of leasing agents include:
- Marketing and advertising: Leasing agents promote rental properties through various channels to attract potential tenants.
- Property showings: Conduct tours of available properties to showcase their features and amenities to prospective renters.
- Tenant screening: Assess applicant qualifications and backgrounds to ensure they meet leasing criteria.
- Rental agreements: Prepare and negotiate leases and month-to-month rental contracts, specifying terms and conditions.
- Lease management: Oversee lease renewals and terminations, handling related documentation.
- Tenant communication: Address tenant inquiries, concerns, and maintenance requests.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain comprehensive property records, including lease agreements and tenant information.
Step 2: Consider Your Financial Goals & Salary Potential
Leasing agents typically get paid 50% to 100% of the equivalent of one month’s rent on the units where they secure a tenant. However, if they work for a property management company in a building or set of buildings, they may be paid an employee salary instead. They may also charge additional fees, such as tenant screening and lease renewals. Sometimes, the tenant pays the commission as part of their move-in costs, if they hire an agent to help them secure suitable housing, or the landlord and tenant split the fees.

It’s essential to consider income and expenses.
One financial benefit of being a leasing real estate agent vs a selling agent is that you can close many deals more quickly than it takes to list, market, and sell a house. While finding, screening, and securing good tenants can take time, there are no lender approvals, title searches, appraisals, or closings to deal with. Depending on the property type and rental prices, commissions can be lower than an agent would make from a sale, but this is not always true. Again, it depends on the property’s location and type.
How Much Can a Leasing Agent Earn?
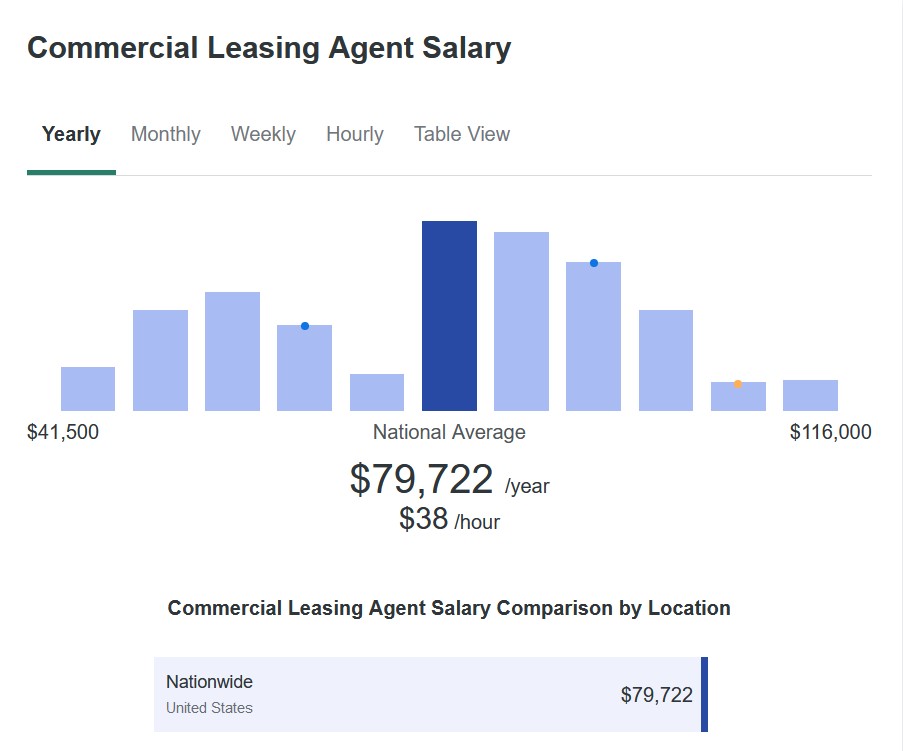
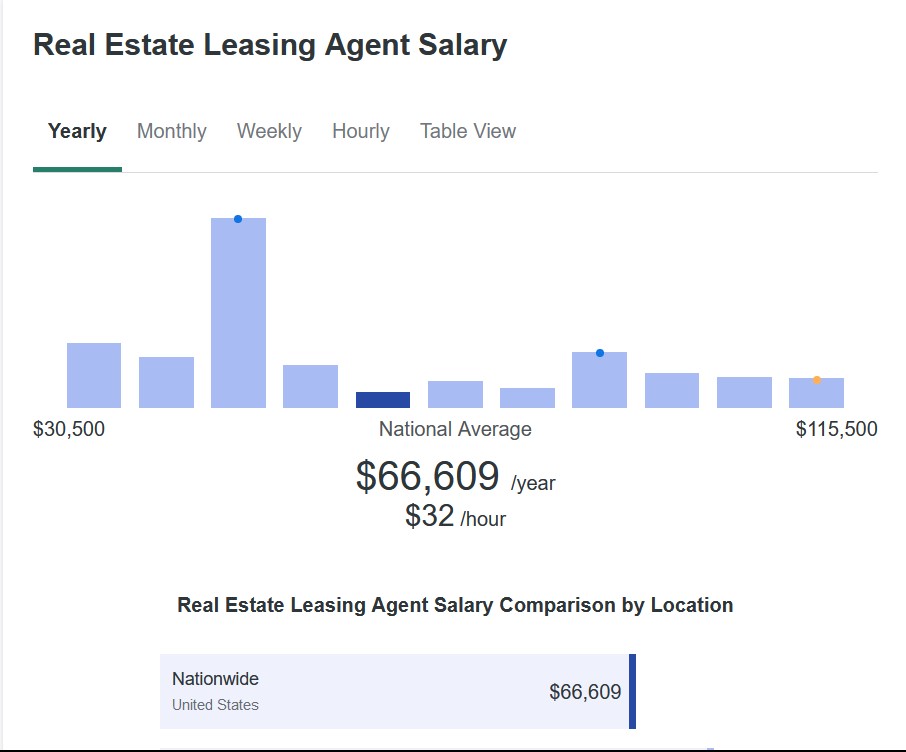
According to ZipRecruiter, a commercial leasing agent’s salary can range from $41,500 to $116,000, with a national average salary of $79,722, whereas a residential leasing agent earns between $30,500 and $115,500, averaging $66,609. What you will earn varies by location, experience, and rent values.
To determine how much money you can make as a leasing agent, you must do some market research to discover the average rents for your location and property type. From there, you’ll need to decide how many vacancies you need to lease and in what time frame to determine your gross income. You can also look for a salaried position. Either way, there will be additional expenses to deduct:
- Marketing and advertising costs
- Traveling and vehicle expenses
- Overhead expenses like office and technology
- Professional dues and fees
- Multiple listing service (MLS) costs
- Insurance
- Continuing education
Step 3: Get Licenses & Property Certifications
In many U.S. states, leasing agents may need a real estate license due to their involvement in real estate transactions like property showings, working for owners, and lease negotiations. However, licensing requirements vary by state. Some states allow unlicensed employees to manage rental properties for owners. Prospective leasing agents should thoroughly research their state’s regulations to determine whether licensing is needed, considering their specific job responsibilities, long-term goals, and roles.
If licensing is required in your state, learn how to become a leasing agent by following these steps:
- Meet your state’s licensing requirements
- Complete prelicensing coursework
- Get fingerprints and a background check
- Pass the real estate exam
- Affiliate with a brokerage
- Obtain errors and omissions insurance
- Submit your license application
Continuing education may also be necessary for license renewal. Specific prerequisites and hours can differ significantly, so aspiring leasing agents should research their state’s real estate licensing regulations. To further aid your professional growth and development, look for continuing education classes related to leasing real estate and working with investors and property managers. Courses in negotiating and sales are also useful, as are legal disclosures.
The Colibri Real Estate course dashboard (Source: Colibri Real Estate)
To begin your education on how to be a leasing agent, get your prelicensing education with a real estate education platform such as Colibri Real Estate. Colibri offers comprehensive prelicensing course packages tailored to each state. These packages include exam preparation, instructor assistance, and a vast library of professional development resources. Furthermore, Colibri supports your career journey with courses ranging from continuing education and broker licensing to post-licensing and luxury real estate certification.
Visit Colibri Real Estate – Use Promo Code: FSB30 for 30% off
There is no specific leasing license, but you can get a leasing agent certification through the National Apartment Association. The Certified Apartment Leasing Professional (CALP) designation provides coursework and hands-on learning, and is recognized as a top certifying agency for obtaining an apartment leasing agent certification.
Step 4: Work With a Landlord or Property Management Firm
The decision to work as a leasing agent for an individual landlord or a property management company boils down to your long-term goals. For example, if you want to have full control over managing the property, working for an independent landlord is a good option. If you want a salaried position with a few specific duties, a property management company may be the better choice, although this is not always true. Each option has advantages and disadvantages, so let’s examine the importance of choosing the right work environment and other factors to consider in firm selection.
Pros & Cons of Working for an Individual Landlord
By choosing an individual landlord over a property management company, it could cost more time to find clients, and you may require broker affiliation. However, you could encounter less competition and receive rental referrals from your real estate sales agent colleagues. Additionally, if you sell real estate in addition to leasing, you can have two income streams with more frequent but smaller commissions from rentals and larger income from sales spread out over more months.
Here are some additional pros and cons of working for an independent landlord:
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| List and sell real estate in addition to your leasing agent responsibilities | Since it is not a specific real estate niche, prospective landlord and tenant clients may be more difficult to find |
| More control over setting your fees | Depending on your state, you may be required to have brokerage affiliation |
| Less in-office competition for rental listings | If you perform duties beyond leasing, you may need to meet the requirements of becoming a property manager |
| Sales agents may send you a lot of rental referrals | You’re dependent on the landlord as your source of income |
Pros & Cons of Working for a Property Management Company
Working as a leasing agent for a property management company has some definite advantages, like making it easier to get clients, fewer expenses, and the potential for a steady paycheck. However, it can provide less autonomy, client selection, and income potential. It could be a viable option if you’re looking for how to get a leasing agent job without a real estate license. Therefore, you must weigh both the options of working for a brokerage and a property management firm, interview a few firms, and align your decision with your long-term goals.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| More likely to have a steady stream of landlord and tenant clients | Limited to leasing activities |
| The company may cover many of your overhead and marketing expenses | Earning potential could be limited to a salary or wages |
| If you’re an employee of the firm, you may not need a real estate license | Less flexible schedule or have specific work hours, like a typical 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. position. |
| The firm may pay for your licensing, education, and training | You may have other administrative tasks like maintenance coordination and tenant management |
| Your mileage may be covered, or you could have access to a company vehicle | You might not have a choice in your clients, as they could be assigned from the company |
Step 5: Be Knowledgeable of the Legal Aspects of Leasing
Using the correct legal documents is essential for leasing agents, safeguarding landlords and tenants, and ensuring a compliant rental process. The lease agreement must outline rental terms, specify rent amounts, due dates, security deposit handling, maintenance duties, and eviction procedures. Properly executing these documents protects clients from potential lawsuits.
For instance, providing a well-defined security deposit receipt and agreement helps landlords adhere to state regulations, which often mandate deposit return letter timelines and written notice for deductions. Failure to use such documents can result in costly legal conflicts, affecting the leasing agent and the landlord’s reputation.

Understanding laws on leasing activities can avoid litigation.
Leasing agents must also understand landlord-tenant laws for successful rental transactions. This knowledge ensures accurate client advice, ethical conduct, and legal compliance. For example, awareness of rent control ordinances helps agents advise on rent limits, while understanding fair housing laws prevents discrimination. This expertise is vital when addressing tenant complaints, upholding legal responsibilities, and maintaining positive relationships with landlords and tenants.
Customizable compliant lease agreements (Source: Avail)
Avail, an online property management software, provides state-specific rental lease agreement templates that include all required disclosures and attachments to adhere to landlord-tenant laws. It enables the addition of unique conditions and gathers digital signatures from tenants, transforming responses into binding contracts. Avail also offers location-specific provisions, attachments, and disclosures, with the ability to track tenant progress individually.
Step 6: Build Your Clientele With Marketing Strategies
Generating real estate leads is vital to a leasing agent’s role. By attracting tenants, you can build a thriving client base and ensure a steady business flow. Effective lead generation strategies can set you apart as the go-to leasing agent in a competitive real estate rental market.
There are several ways to generate client and tenant leads, including networking and tapping your sphere of influence (SOI) for referrals. Additionally, nurturing relationships and delivering exceptional service can lead to repeat business from satisfied clients and referrals from their networks. Building a solid reputation for reliability and professionalism can be the cornerstone of your success as a leasing agent.
Here are additional ways to build your client base:
- Build an online presence: Create a professional website and utilize real estate platforms like Zillow for your agent profile and Realtor.com to showcase your listings and expertise.
- Social media: Leverage social media platforms to engage with potential clients, share property updates, and establish your brand.
- Networking: Attend local real estate events and join industry associations to build relationships with fellow professionals and gain referrals.
- Content marketing: Produce informative blog posts, YouTube videos, or webinars about real estate trends and local insights to showcase your expertise.
- Email marketing: Maintain a contacts database and send regular updates, newsletters, and property alerts to stay on the radar of potential clients.
- Client testimonials: Encourage satisfied clients to provide testimonials and reviews that can build trust with prospects.
- Open houses: Host open houses to meet potential clients and other agents and showcase your properties.
- Community engagement: Get involved in local community activities and charities to establish yourself as a trusted local expert.
- Direct mail marketing: Sending postcards, flyers, newsletters, etc., to generate interest in the properties you’re leasing.
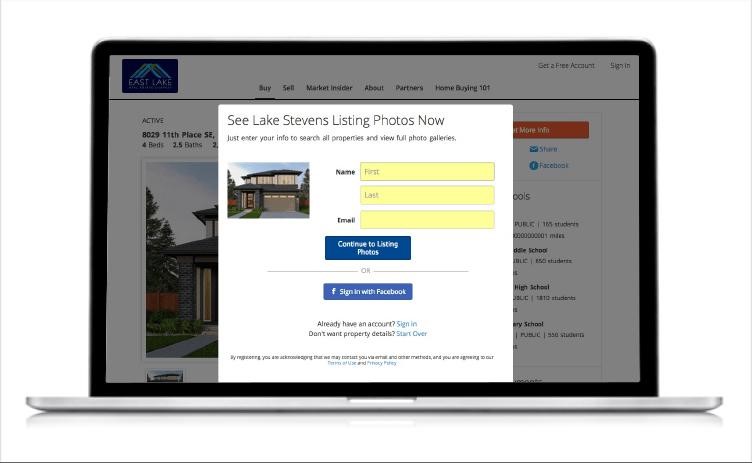
Capture lead information (Source: Market Leader)
Expand your network and engage more efficiently with prospective clients and tenants using Market Leader’s new feature, Network Boost. Network Boost has shown a 40% increase in agents successfully connecting with leads. Market Leader social media experts design highly targeted and optimized ads for your Instagram and Facebook. As visitors engage with your ads, they will be prompted to complete a form and funnel directly into your Market Leader client relationship manager (CRM). This will also trigger an automatic marketing campaign that nurtures your clients and lets you know they are ready to engage with you.
Step 7: Manage Rental Listings
Leasing agents are pivotal in efficiently managing listings. They create comprehensive property listings, highlighting the features and benefits. To attract potential tenants, these listings are then actively marketed through various channels, including online platforms, social media, and real estate IDX websites. As inquiries flow in, leasing agents diligently respond, scheduling property showings and negotiations to facilitate successful lease agreements.
During these appointments, they showcase the property’s features and answer questions, striving to secure favorable lease terms that satisfy both property owners and tenants. They are crucial in bridging communication gaps, addressing concerns, and ensuring a smooth transition from property viewing to the finalization of lease agreements.
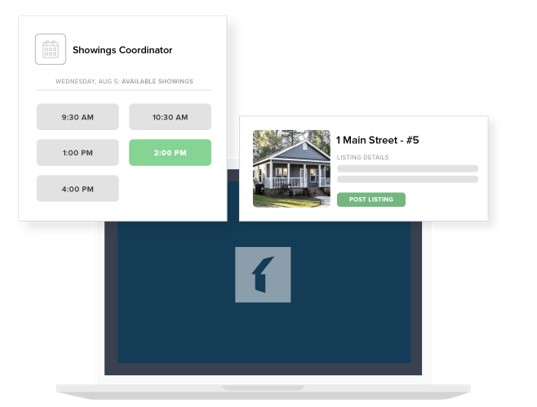
Schedule showings with ease (Source: Buildium)
With Buildium, prospective tenants can book showings quickly and conveniently online. The system seamlessly syncs with your calendar to ensure showings align with your availability. Additionally, the platform automates follow-up communications with email or text responses, maintaining tenant engagement throughout the leasing process. All your listings, showings, and prospects are easily monitored in one place, providing comprehensive insights through detailed reporting for efficient property management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Becoming a leasing agent offers several advantages. It provides flexible work hours and locations, potentially allowing for more work-life balance. The real estate industry often offers lucrative earning potential through commissions, and leasing agents can earn faster through rentals than when a house closes. Additionally, the role can be personally rewarding, as leasing agents help individuals find suitable homes while continuously expanding their market knowledge.
While being a leasing agent has advantages, it also has some drawbacks. The job often demands irregular hours, including weekends and evenings, to accommodate clients’ schedules. Earnings can be variable and commission-based, leading to income fluctuations. Handling difficult tenants or property issues can be challenging and stressful. Also, leasing agents must close more deals since rental commissions are lower than sales income.
The income of leasing agents can vary widely based on factors such as location, experience, and the number of transactions they complete. According to Salary.com, on average, leasing agents in the U.S. earn around $40,000 to $50,000 annually. However, those with more experience and in high-demand markets can earn significantly more, with top earners exceeding $80,000 annually. Additionally, commissions on rental transactions contribute to their overall income, allowing for further earning potential.
Several U.S. states, including California, New York, and Massachusetts, have notably strict landlord-tenant laws. These states offer tenants strong protections against eviction, rent increases, and other tenant rights violations. Some rent control or stabilization laws limit how much landlords can increase rents. Additionally, they impose strict regulations on security deposits and maintenance requirements to ensure safe and habitable rental properties, making them some of the most tenant-friendly states.
Bottom Line
This comprehensive guide on how to become a leasing agent outlines the crucial steps to becoming successful in real estate in your chosen career path. From understanding the role and educational requirements to navigating licensing, finding the right professional environment, and mastering marketing, it covers every aspect of how to be a leasing agent in this rewarding career. While there is no specific leasing agent license, by following these steps, aspiring professionals can embark on a path to success in the ever-evolving real estate industry.