PBX stands for private branch exchange, an internal telephone network enabling users to communicate with one another and those outside the company through private lines. A PBX phone system hosts various features, including call forwarding, call transfer, auto-attendant, and voicemail. Businesses benefit from this phone system as it allows organizations to scale communications and manage call volumes more efficiently at a lower operational cost.
How PBX Phone Systems Work
The way a PBX business phone system operates depends on the type of setup you have. For instance, an analog PBX uses the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and features old copper phone lines connected to the main PBX box. The on-site PBX box contains switches, enabling employees to call multiple devices across the building. It also connects to several trunk lines, allowing users to make external calls.
Meanwhile, a digital PBX telephone system uses the internet to facilitate communications between users. Rather than transmitting calls through PSTN, it uses the internet protocol (IP) network, converting analog voice signals into digital packets.
Inbound phone calls go to the voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) provider’s PBX and get transmitted over the internet, and then to the PBX server. The PBX server, which may be located on-site or hosted by a third-party company, classifies calls. It routes internal calls to the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) address of a user within the organization and sends external calls to the desired destination through a VoIP gateway or the service provider.
Unlike the traditional phone system, PBX uses digital signals and is able to provide as many extensions and trunk lines as the organization needs, enabling businesses to scale operations easily. In summary, if you’re wondering, “How does a PBX system work?,” the mechanism largely involves using copper or digital phone lines connected to a PBX box or server.
PBX Phone Systems Compared
Among the PBX phone systems we reviewed, RingCentral emerges as the best overall for its robust call management features, including the multi-level auto-attendant, call queues, call recording, and toll-free minute allowance. If you want to explore other options, check the table below for other reliable PBX providers for small businesses.
PBX Phone Systems | Monthly Starting Price (per User) | Key Features | FSB Review |
|---|---|---|---|
$30 |
| ||
$28 |
| ||
$30.95 |
| ||
$23 |
| ||
$14.99 |
| ||
$27 |
| ||
$19.99 |
| ||
To learn more about these providers, check out our in-depth buyer’s guide on the best hosted PBX providers. The article outlines each platform’s best use cases, pricing, and notable features.
Types of Business PBX Phone Systems
Ensure you have the right PBX phone system for small business operations by being familiar with its different types. Refer to the table below to quickly identify which one fits your communication needs best.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Crystal-clear call quality | Costly to set up and maintain |
| Operational even during electricity interruptions | Lacks advanced call management features |
| Easy to use, with little to no learning curve for team members | Less scalable than virtual phone systems |
An analog PBX primarily uses plain old telephone service (POTS) and a PBX box to establish communication between users. The PBX box is on-site, often kept in a server room in the office. Thus, the business handles all the maintenance tasks related to the phone system.
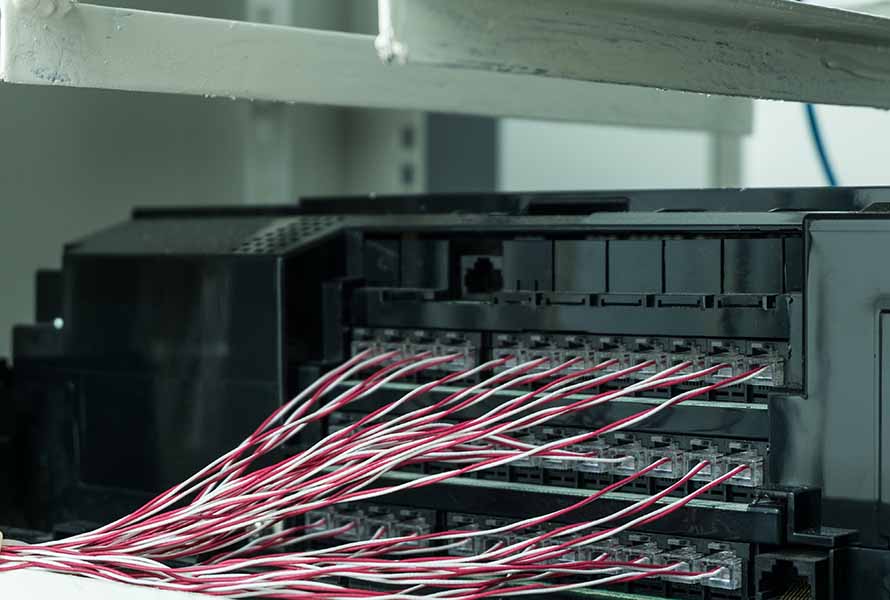

Phone cables are connected to the PBX box to facilitate communication between users.
This type of phone PBX system is highly reliable since it remains functional even during power outages, unlike those that rely on the internet. However, the disadvantage of going analog is that it lacks advanced features virtual phone systems offer, such as interactive voice response (IVR), voicemail-to-email, and unified communications (team messaging and conferencing).
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Feature-rich in terms of call handling and management | Costly and labor-intensive since it involves regular maintenance and upgrades |
| Easy to scale compared to analog systems | Dependent on high-speed internet to function |
| Long-distance calling fees are lower compared to landline systems | More expensive to set up compared to hosted PBX |
An on-premise PBX system, or IP PBX system, uses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunking technology to transmit data over your digital lines. The IP PBX box connects to the internet through an Ethernet cable. Similar to analog PBX, businesses host and maintain the equipment in on-premise systems, which include servers, modems, and routers.

An IP PBX box features Ethernet ports that allow the device to connect to the internet. (Source: Yeastar)
This type of PBX phone provides a wide range of call management features, such as an auto-attendant, call recording, and voicemail transcription. The drawback of using an on-premise PBX business phone system is that you shoulder the expenses and labor associated with hosting your own PBX on-site. This involves hiring IT personnel and constantly training them to ensure that the system supports high-quality calls and that all communications are secure.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Less expensive to set up compared to analog and on-premise PBX systems | Dependent on high-speed internet to function |
| Fast deployment, with users able to make calls as soon as they download the softphone | No control over infrastructure and data |
| Easy to scale, accommodating changes in communication demands | Involves trial and error in optimizing network router settings and ensuring high-quality VoIP calls |
Like an on-premise PBX, a hosted PBX system uses the internet to connect users. The only difference is that a third-party VoIP service provider hosts and maintains the servers. The service comes with a fixed monthly subscription cost. Hosted PBX providers RingCentral and Dialpad offer discounts for annual billing arrangements. Nextiva gives discounts as more users are added to the phone system.
If you want to manage costs better and set up the VoIP system easily without worrying about equipment installation and maintenance, go for hosted small business PBX systems. However, note that since a third-party entity hosts the PBX, you have no control over your data. Some businesses, like financial and healthcare organizations, favor on-premise PBX systems to ensure tight data security and comply with industry standards.
Benefits of a Business PBX Phone System
Now that we have learned what is a PBX phone system and explored its different types, let’s discuss its advantages. In a nutshell, a business phone system improves overall communications, making operations more efficient and delivering faster, more accurate customer service. Ultimately, it helps cut down costs and makes for loyal, satisfied customers.
These are the specific benefits a PBX system for small businesses offers:
PBX business phone systems feature a wide range of call routing tools, making call management easier. If you’re out of the office for an important meeting or a leisure vacation, use call forwarding to direct all calls to an alternate number that accommodates customer concerns. Maximize business hour settings and distribute off-hours calls to your round-the-clock customer support centers.
With skills-based routing, assign calls to agents who are most qualified to tackle specific inquiries. The phone system’s simultaneous ring alerts multiple devices and notifies several team members of an incoming call. All these features ensure that no customer inquiry goes unanswered.
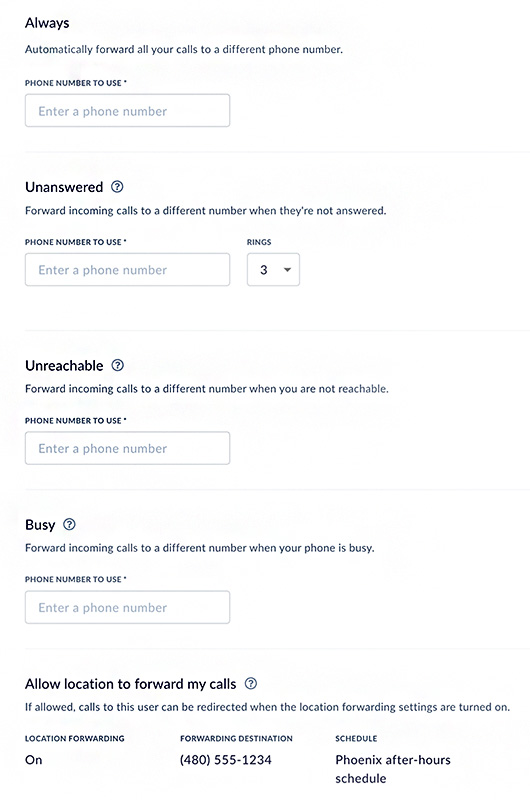
Nextiva lets users configure call forwarding rules. (Source: Nextiva)
Nextiva, a cloud-based PBX system, provides various call forwarding options for different scenarios: unanswered calls, unreachable phone numbers, and busy signals. These configurations help maintain communications with customers and give businesses flexibility in handling inbound calls.
A PBX system lets businesses connect multiple incoming phone lines, providing cost savings since you won’t have to pay more for one PSTN line per desk phone. Choosing a hosted PBX comes with more savings because it doesn’t require an on-site PBX server and other equipment.
Desktops and mobile phones are compatible with softphone apps from third-party VoIP providers, eliminating the need for analog telephones. Since your partner already handles server maintenance, you won’t have to hire and train an IT team. It’s easier to forecast and manage phone costs with a hosted PBX business phone.
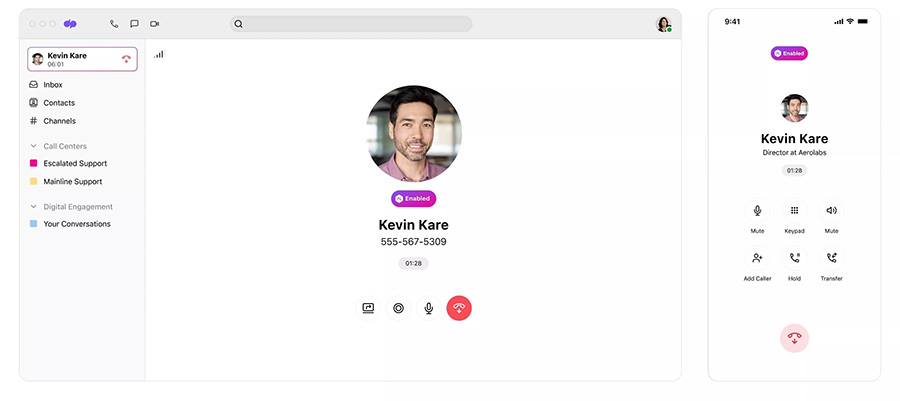
Dialpad lets you make and receive calls through its desktop and mobile apps. (Source: Dialpad)
Dialpad, another reliable phone system provider, has a desktop and a mobile app equipped with familiar phone system features, including a keypad, mute, hold, and transfer. Aside from calling tools, it has team messaging and video conferencing, which facilitates easy communication among customer service representatives.
A hosted PBX system allows businesses to respond to increased call volumes by adding more users easily. Virtual phone system Grasshopper features an “Add New User” option in its User Management Settings, letting you key in the name and email address of the team member you want to include in your list of customer service representatives. The VoIP provider sends an email notification and instructions for logging in.
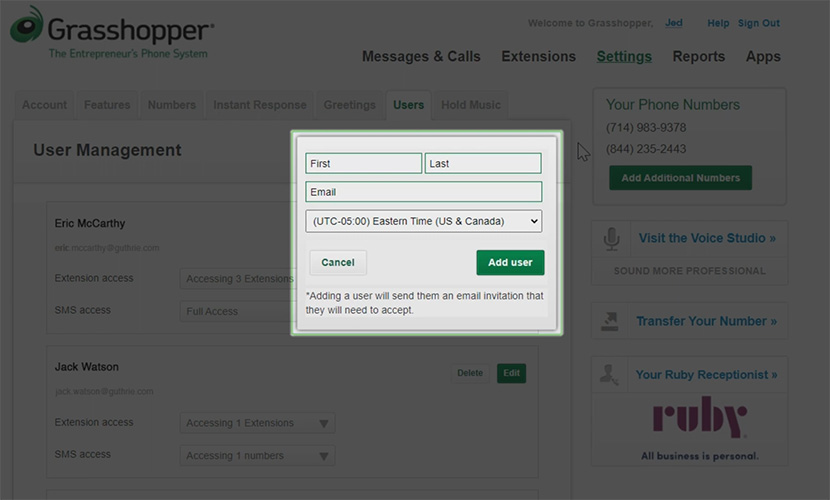
Add new users to your phone system using Grasshopper’s User Management Settings. (Source: Grasshopper)
Another advantage of using Grasshopper is that its subscription plans support unlimited users. As your business grows, you can add more team members to your phone system at no additional cost. All of the PBX system’s VoIP features are included in every subscription package. Explore more of this provider’s advantages and features in our Grasshopper review.
PBX systems work with different platforms, including customer relationship management (CRM) and help desk software, making it easier for service representatives to refer to important data. Team members won’t have to switch from one tool to another to check customer profiles, saving precious time and delivering faster service.
Similarly, PBX phones integrate with workforce optimization (WFO) and management platforms. Through these tools, managers are able to create strategic agent schedules based on the business’ current needs and evaluate team performance more objectively. Ultimately, these contribute to efficient operations and better customer service.
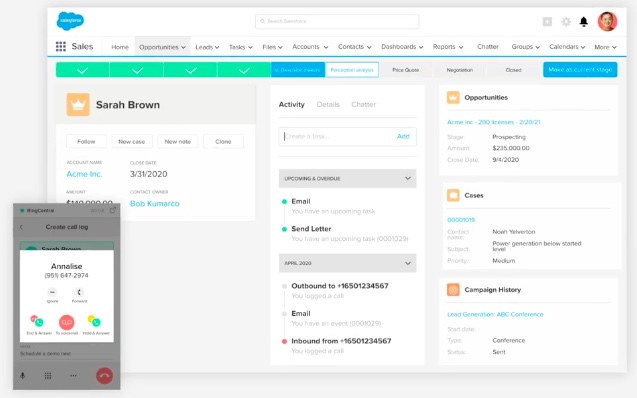
RingCentral integrates with CRM tool Salesforce. (Source: RingCentral)
Top business phone system RingCentral connects seamlessly with Salesforce, letting users call contacts right from the customer relationship management (CRM) platform. In one glance, a service representative is able to see past interactions with the customer, as well as opportunities to close a deal.
PBX systems display real-time data, helping businesses measure the effectiveness of customer service campaigns. In most hosted services, the analytics tool shows the total number of calls waiting, number of answered calls, average talk time, average hold time, and average handle time (AHT). These metrics should give you insight into re-configuring call routing rules, revisiting agents’ scripts, and optimizing auto-attendant menus.
Nextiva Analytics displays different metrics, including the total number of calls and total talk time. (Source: Nextiva)
Features of a PBX Phone System
To get a full understanding of what a PBX phone system is, it’s wise to be familiar with its features. When choosing among providers, check which capabilities come with the subscription packages and which ones are add-ons. Compare different phone systems’ pricing and inclusions to find the one that suits your budget and communication needs.
Below is a list of the common features of a PBX phone system:
Call Management
Aside from the call routing capabilities mentioned earlier, virtual PBX phones come with an interactive voice response (IVR) system, which gathers customer information through key presses and distributes calls to the right departments and agents. Some advanced IVR tools facilitate self-service, removing the need for live agent interaction. Other call management features include ring groups, call screening, call park, call queues, and call monitoring.
Team Messaging
Aside from voice capabilities, PBX systems allow users to collaborate via team chat. It can be a private or group message. Some providers, like RingCentral, support file sharing, task management, and emojis, making virtual discussions productive and interactive. If you need to revisit a conversation, these systems allow searching using keywords.
Video Conferencing
Escalate virtual discussions to a full-blown meeting with PBX systems’ video conferencing feature. It has built-in collaboration tools, such as team chat, hand-raising, screen sharing, whiteboards, and breakout rooms. The participant capacity depends on the VoIP provider you choose. Dialpad has a maximum of 150 attendees.
Number Management & Porting
Many hosted PBX systems offer business phone numbers, local or toll-free, in their subscription plans. Some charge an extra for vanity and international phone numbers. Nextiva supports number porting, allowing businesses to retain their existing phone numbers.
International Calling
Connect with your global audience by taking advantage of PBX phone systems’ global calling capabilities. RingCentral has local PSTN support in over 45 countries, including Mexico, France, Germany, Ireland, Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Hong Kong, Singapore, and Japan. Its international calling plan includes up to 1,000 minutes of monthly regional calling per user.
How to Choose a PBX Business Phone System
Deciding which PBX business phone system involves various considerations, including your budget, need for flexibility, and scalability plans. Take into account the following factors:
Financial Capacity
When you choose the analog system, be prepared for the expenses involved in the installation of new lines and hardware phones. For the on-premise or hosted PBX, the monthly subscription is the primary cost. Compare quotes from different providers and the inclusions for each subscription plan. Consider the discounts provided for annual billing and bulk purchases.
Current Infrastructure
Remember, different phone systems have various hardware requirements. If your office is already retrofitted with wall jacks, cables, and outlets, analog may be a good consideration. However, note that your business must be ready to troubleshoot problems as they arise.
In the same way, you must have a well-equipped, properly trained IT team if you choose to go for on-premise PBX. Meanwhile, if you’re a solopreneur or a small business that doesn’t have a dedicated IT staff and only relies on the internet for communications, hosted PBX systems are the best option.
Future Communication Demands
If you anticipate expanding or downsizing customer service operations soon, it’s ideal to go for hosted PBX systems, as they support scalability. It allows you to add or reduce the number of phone lines easily. They come with a wider range of valuable features as well, including advanced call management and unified communications tools, which help accommodate increased call volumes and the need for closer collaboration among teams.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is PBX a VoIP?
No, PBX is different from VoIP. A phone PBX system is a type of private telephone network businesses use. It transmits calls through the PSTN (old copper phone lines) or VoIP, which is the technology that allows voice calls to be delivered over the internet.
Do IP phones need a PBX?
Yes, a physical IP phone works with an IP PBX while plugged directly into the internet. When you use a softphone, you won’t need an on-premise PBX since it will be cloud-based. Learn more about business phone hardware and software essentials in our guide on how to set up a VoIP system.
How much does a cloud PBX cost?
The exact cost depends on the provider. Pricing normally ranges from $14 to $45 per user, paid monthly.
Bottom Line
A PBX system offers various benefits for businesses, streamlining call management, reducing communication costs, and enabling scaled operations. Its wide range of features boosts agent and team productivity and enhances customer experience. Now that you know what is a PBX system, consider adopting this tool in your customer service efforts.