A customer relationship management (CRM) database simplifies the process of collecting, tracking, and organizing client data. For an organization with hundreds of thousands or even millions of customers, this data could easily grow to monumental proportions—but that’s exactly where the CRM database comes into play. In this article, we’ll learn about what a customer relationship management database is while also exploring some of its outstanding benefits.
What Is a CRM Database?
The CRM database serves as a catch-all repository for any data related to your customers. But with more than 2.5 quintillion bytes of data created daily, CRMs need to focus on extracting data from certain datasets while ignoring others. Some of the most crucial data to collect includes:
- Personally identifiable information (PII): This covers entries like first and last name, birthdate, company name, mailing address, and other important contact information.
- Descriptive information: This describes a lead, customer, or company. These records include a customer’s current stage in the pipeline, their level of education, or their hobbies and interests.
- Numbers and statistics: Records that can only be expressed numerically are considered quantitative data. Figures like the potential value from an upcoming deal or projected revenue for a new customer are included here.
- Miscellaneous: Considered qualitative data by most modern CRM platforms, this category is for information that doesn’t fit into any of the other groups.
Generally speaking, the data collected by modern CRM systems can be broken into one of four groups: identifying data, descriptive data, qualitative data, and quantitative data.
How Does a CRM Categorize Data?
Once the data has been collected, it is further categorized into one of three categories within the CRM database. These categories include:
- Analytical: This data helps you identify patterns and make connections between different datasets. Executive leaders use this data to support strategic decision-making.
- Collaborative: Any data regularly shared between teammates or departments is considered collaborative data. It ultimately establishes a single source of truth regarding customer account information.
- Operational: This data tracks tasks and activities related to sales, marketing, or general service—like tracking support tickets, sorting through potential leads, or monitoring a new client’s progress through your pipeline.
Although some CRMs specialize in one particular category or another, many modern CRMs can handle all three categories. For example, operational CRMs can accommodate and even generate analytical data and establish a collaborative setup for information updating procedures.
Categorizing data is only the first step in building your CRM database system. What follows includes setting up the data fields, tailoring specific automation and workflows in your contact management system, and generating reports. Following this process ensures your database remains functional and at its maximum operation.
Benefits of a CRM Database
Modern CRM databases are most beneficial for day-to-day operations, sales, marketing, and customer support, especially as features and functionality are improved periodically. When used strategically, however, the data contained therein can be applied to virtually any department, activity, or campaign.
1. Building a Centralized Repository of Data
Also referred to as a single source of truth, databases within the CRM system make it easy to establish a centralized data repository for all customer information, making it straightforward to organize, search, and filter your customer data. When stored on the cloud, this data can be accessed by teammates from nearly anywhere. Any changed data will automatically update in real time, so you’ll be able to eliminate duplicate or redundant records.
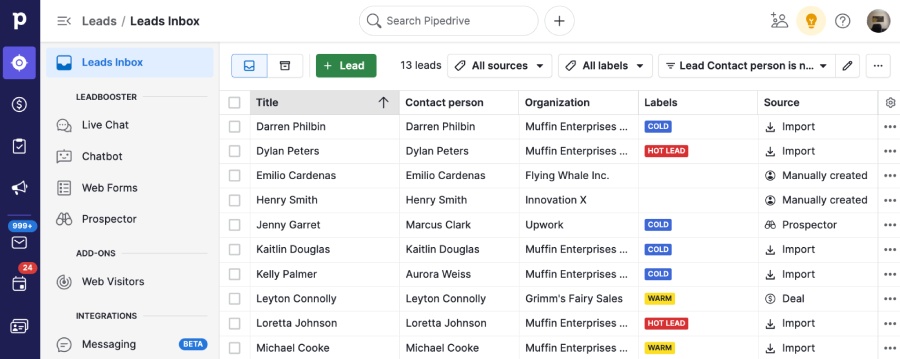
Pipedrive’s CRM gathers and sorts information about your leads. (Source: Pipedrive)
2. Strengthening Predictive Analytics & Forecasting
Predictive analytics are often used in sales and marketing to forecast revenue or anticipate future actions, needs, or desires. Storing customer records, like their purchase histories, for example, makes it easier to determine which products or services they are likely to purchase in the future. These results are really only accurate, however, when the data originates from a single source of truth—like a centralized CRM database.
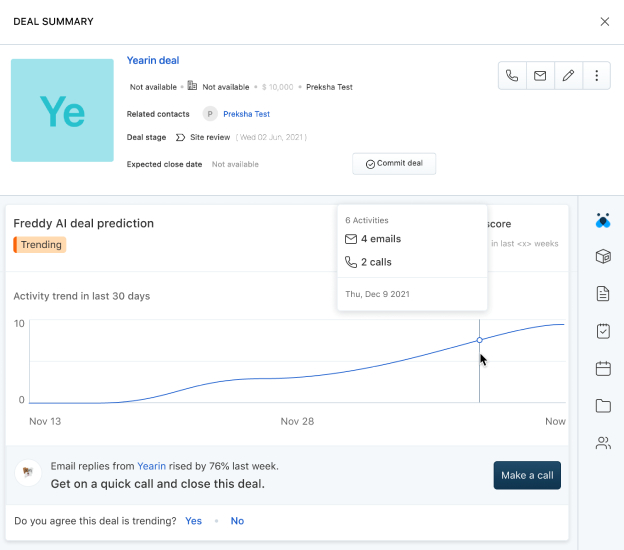
Freshsales’ Freddy AI suggests the next actions based on deal prediction. (Source: Freshsales)
3. Tracking Customer Actions & Activities
It’s important to keep track of your customers’ actions and activities because it lets you know which products or services they are purchasing and using and where they are in your sales pipeline. Are they a new customer who has yet to make a purchase, or are you trying to upsell additional services to an existing customer? Tracking their progress lets your team know exactly when they’re needed and what they need to do to move the customer to the next stage.
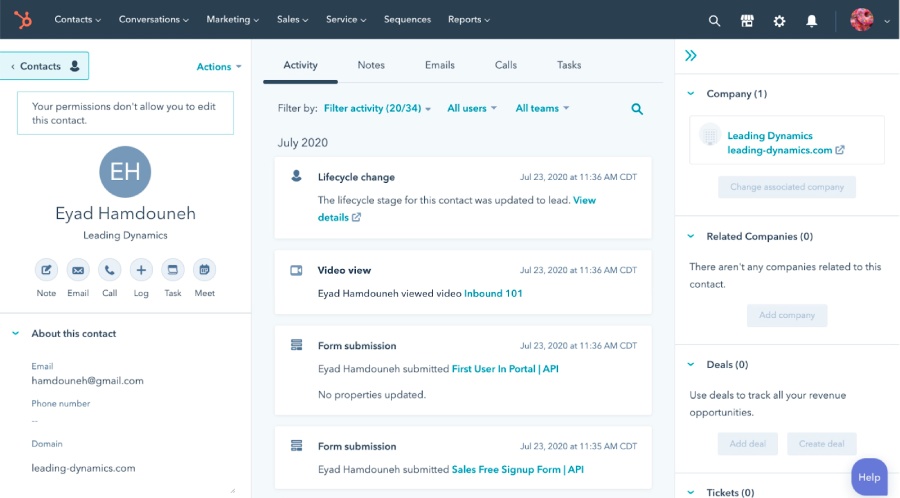
HubSpot CRM allows users to keep track of contact activities. (Source: HubSpot)
4. Maintaining Communications
CRM databases help maintain communications with in-house staff, remote or hybrid teammates, and customers. This is especially true for cloud-based CRMs, which teammates can access from nearly anywhere with an internet connection.
Modern CRM platforms also let you track customer communications and interactions, so you won’t have to worry about sending duplicate introductory emails or sales confirmations. You can even track customer-specific feedback, including official replies or notes from other teammates.
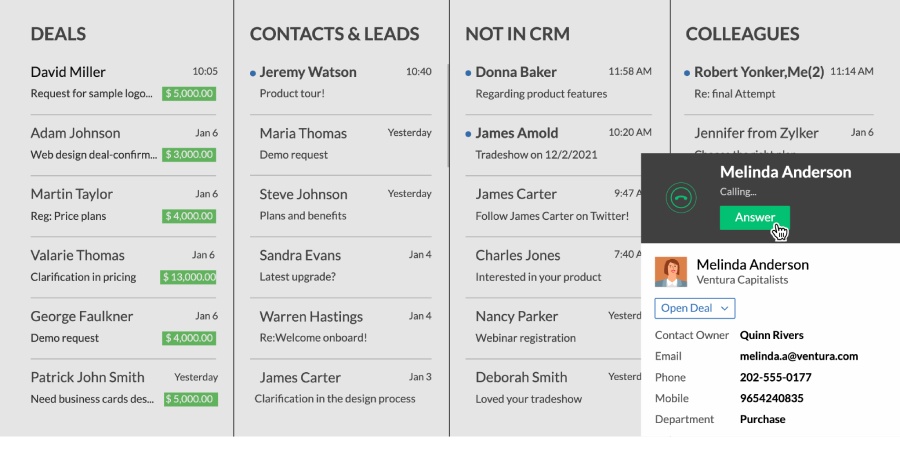
Communicate with leads and customers from the CRM. (Source: Zoho CRM)
CRM Database Examples
Your contact database is your ultimate source of customer information that can direct your campaigns, lead qualification, deals management, and other sales activities. Having a CRM system that automates contact updates, pipeline movement, and deal prediction can maximize the function of your database to a ten.
When choosing a CRM with robust customer data management features, we recommend the following CRM database examples.
Our Review Rating | 4.3 out of 5 | 4.31 out of 5 | 4.18 out of 5 | 4.13 out of 5 |
Best For | Data and content management at no cost | CRM customization and scalability | Lead management and telephony features | Sales automation and proposal generation |
Standout Features |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Learn More | ||||
Frequently Asked Questions
While this article covers the basics of CRM databases, some users might be left with a few remaining questions. You’ll find a list of the most common questions and answers below, which should give you a better understanding of the nuances of modern databases.
Technically, Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet application and not a CRM database. Although some functionality of Excel does mimic that of modern CRM platforms, and while Excel can be used as a rudimentary CRM platform, it is typically not recommended for use as such.
There are several steps one should take when maintaining a CRM database. Start by ensuring the input of accurate data. Make sure this data is updated regularly and try to remove obsolete or outdated information whenever possible, including dead leads. Use the remaining data to create timely reports as needed. These best practices provide a great starting point for your database maintenance routine.
Most CRMs utilize cloud-based servers for data storage. Not only does this ensure that everyone has access to the most up-to-date information, but it preserves new data in the case of a sudden power outage or network interruption. These cloud servers also have additional network security to help guard against malware, viruses, hackers, and identity thieves.
Bottom Line
The data collected and contained by today’s CRM platforms covers a lot of territory. Databases in CRM make way for tagging personally identifiable information and building lists of potential leads and customer support tickets. But beyond its function as a digital Rolodex, a CRM database enables sales teams to better understand their leads using predictive analytics features and helps them facilitate more efficient coordination.