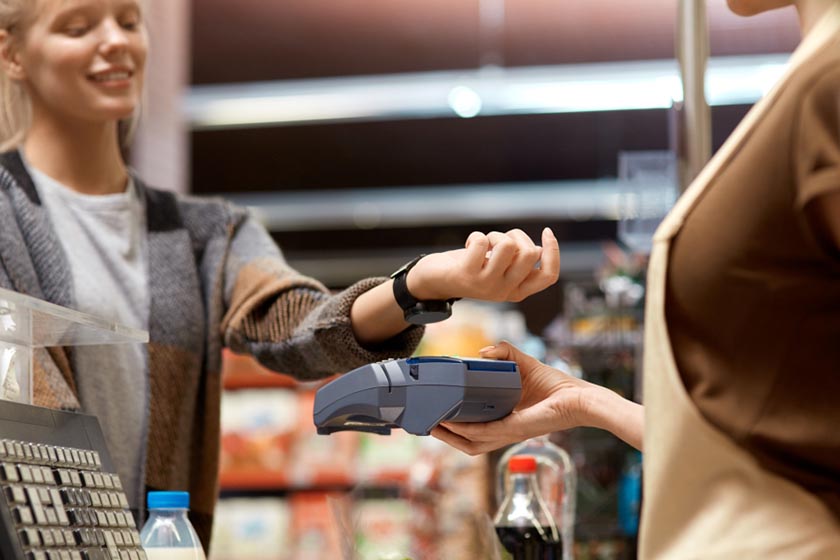
NFC payments are contactless payments that use near-field communication (NFC) technology to exchange data between readers and payment devices—like Apple Pay and Google Pay e-wallets in smartphones and wearables or tap-to-pay credit and debit cards.
NFC payments (often called “tap-to-pay” or simply “tap” transactions) are widely used because they are contactless, encrypted, and highly secure. Plus, they can help speed up the checkout process.
Key takeaways:
- NFC payments offer a convenient alternative to traditional payment methods.
- Payment transactions through NFC technology function through close-range data exchange between payment devices and readers.
- To accept NFC mobile payments, you need a specialized card reader. Due to contactless payment popularity and increased adoption rates due to the COVID-19 pandemic, most merchant accounts offer NFC readers.
- The increasing popularity and integration of NFC payments emphasize a shift towards seamless, secure, and efficient transaction experiences.
How NFC Payments Work
When payment and reader devices are close together (typically less than 2 inches apart) and activated, their NFC chips exchange encrypted data to complete a payment.
The process creates a lightning-fast checkout flow that’s both convenient and highly secure. Because of this, NFC-driven payment options, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, are fast becoming a preferred consumer payment method.
The wireless or “contactless” connection between the two devices uses radio waves similar to radio-frequency identification (RFID) labels used in stores, warehouses, and other wireless tracking applications. NFC chips use a specific RFID radio frequency (13.56MHz) that only works when the chips are very close together.
For added security, e-wallets only communicate with NFC readers when the user unlocks the app and completes the payment.
iPhones use a secure thumbprint or facial recognition to unlock the payment screen.(Source: Apple)
Another security feature is that NFC payment readers connect to only one NFC payment device at a time. This ensures there’s no risk of a customer paying for a different, nearby purchase accidentally.
In addition to the security benefits covered above, shoppers can store multiple credit and debit cards on their mobile devices. This reduces shoppers’ need to carry cards in wallets or purses.
NFC vs RFID
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a one-way communication method that can be used at long distances, whereas NFC is a two-way communication method that requires very close proximity. NFC is a subset of RFID that operates on a similar frequency using the same basic principles.
RFID tags are frequently used to track inventory and prevent theft in retail stores and warehouses. Meanwhile, NFC chips are built into most modern credit and debit cards, phones, smartwatches, and other devices. Since NFC chips can send and receive data, they’re capable of facilitating payments, transferring media, user authentication, and more.
NFC vs QR Code
While NFC enables two-way communication at close range and involves tapping an NFC-enabled device near a reader, quick response (QR) codes function as a one-way communication method that relies on visual scanning of a barcode using a smartphone camera.
Similar to other contactless payment options, QR code payments are easy to set up by merchants and easy to use by consumers. One advantage of QR code payments over NFC payments is that merchants do not need a point-of-sale (POS) system or card reader to accept payments via QR codes. Many payment processors can generate a QR code for accepting payments. Check our list of the best QR code and scan to pay apps.
Aside from payments, QR codes may also be used for other business purposes such as sending customers to a website or landing page or providing access to a menu or product list. Find our top picks for the best QR code generator for businesses.
How Customers Pay With NFC
There are two main ways customers can pay with NFC: by using tap-to-pay cards or mobile devices or wearables as smart cards.
Tap-to-Pay Cards
Customers can make in-person purchases using a physical card embedded with NFC technology. They complete the payment by placing or tapping the card against an NFC-enabled payment terminal, which receives their payment information data. EMV credit cards and debit cards are popular examples, but this technology is also used for access cards and school meals or library cards.

Many modern credit cards and debit cards come with NFC capabilities.
Mobile Device as Smart Card
Using an NFC-enabled device (like a smartphone or smartwatch), customers can install a payment application that emulates an NFC card and holds their payment info. They can then unlock the app and tap their device to the in-store reader, which completes the transaction. Popular examples include payment apps, such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay, and Cash App (by Square).
How To Accept NFC Payments
You need an NFC-enabled reader to accept NFC payments, but that’s only one part of the equation—your credit card processing plan has to accept digital e-wallet payments as well.
Most (but not all) merchant account providers do this. Typically, processing fees for NFC payments are the same as regular card-present payments. Exact pricing will vary depending on your specific merchant account and plan.
Read more about credit card fees and how they work.
Learn more about some of our preferred merchant accounts that offer NFC payments below:
Best For | NFC Reader Cost | Processing Fee | |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Individuals, new and small businesses | $49 | 2.6% + 10 cents |
 | Individuals and occasional payments | $29 for first reader, additional readers $79/ea | 2.29% + 9 cents |
 | Storefronts and brick-and-mortar businesses | $109 | 1.86% + 8 cents (average); varies based on interchange |
 | Businesses that want to use their existing merchant account (Clover is compatible with many different processors) | $49 | 2.6% + 10 cents; lower rates available with certain plans |
Benefits of NFC Payments
NFC Payments are experiencing increased adoption due to the many benefits it offers to both businesses and consumers. Here are some of them:
- Faster checkout process: According to Mastercard, contactless payments are up to 10 times faster than other in-person payment options.
- Improved customer experience: The availability of NFC payments enables customers to choose the payment method they’re most comfortable with and increases overall convenience. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, around 70% of consumers have changed the way they pay, preferring the conveniences of things like curbside pickup and contactless pay.
- Increased security: Using NFC technology is more secure than swiped card payments. In fact, NFC technology has contributed to a decline in in-person credit card fraud.
NFC Payment Outlook for Small Businesses
NFC mobile payments are a technology that dates back to the 1990s, but the retail industry has been slow to adopt it. That said, the availability and use of tap-to-pay is now widespread and steadily on the rise. The global contactless payment market was valued at $38.55 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.71% from 2022 to 2032, ultimately reaching $162.56 billion.
COVID-19 Accelerated Contactless Payment Adoption Rates
Much of the hesitation around NFC payments from both shoppers and business owners receded at the start of the pandemic. Reports show that 87% of consumers prefer using contactless options when shopping in-store. Contactless payment use increased by 150% year over year from 2019 to 2020.
A study conducted by the National Retail Federation (NRF) and Forrester found that, by 2020, during the height of the pandemic, 58% of retailers accepted contactless payments—up 40% from 2019. Of retailers surveyed in August 2020, 19% said that no-touch payments accounted for more than half of all in-store transactions.
More Consumers Are Choosing Contactless Payments
According to a 2022 report, nearly nine in every 10 Americans are now using some form of digital payment. In another survey, 57% of consumers said they were more likely to do business with those who offer a contactless payment option.
Security Is a Top Concern Around NFC Payments
Though NFC payments are on the rise, security concerns related to NFC payments may still restrain its growth. Among the reasons for consumer apprehensions are the absence of PIN verification, privacy of personal data, and unauthorized use of contactless devices.
The need for more robust security measures around NFC payments contributed to the increase of biometric authentication such as fingerprint or facial recognition. Biometric payment has emerged as a promising solution to address security concerns around NFC transactions.
NFC Payments Are Here to Stay
Among the different contactless payment methods, a significant number of consumers prefer to use digital wallets on their smartphones. The number of consumers in the US who use mobile wallets rose from 64% in 2020 to 71% in 2022.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
NFC payments are generally safer than traditional card payments due to several security features. Users must initiate transactions by unlocking and logging into the payment platform, often with secondary verification. NFC transactions occur over very short distances, minimizing the risk of interception, and NFC cards or devices connect only with a single reader during each transaction, enhancing security.
An NFC tag is a microchip transponder that can be used to send and receive data from nearby devices at close range. NFC tags (or ‘chips’) are commonly built into smartphones and credit cards but have wider-reaching applications as well.
It takes 5-15 seconds for a smart card or NFC-enabled device to finish a contactless payment in-store. After the transaction, it can take anywhere from one to four business days for the payment to be processed and posted to the customer’s bank account (although it may appear as ‘pending’ in the interim). The processing time varies depending on the merchant as well as the customer’s bank.
Bottom Line
An NFC payments-enabled reader is what you need to accept NFC payments in your store or business. Startups and small to midsized retailers can add this capability easily by purchasing low-cost NFC payment readers from top-rated small business payment processors.


