A digital wallet, also known as ewallet or mobile wallet, is a type of mobile payment service that allows consumers to securely store information for multiple credit and debit cards and even hold a fund balance on a mobile app. The same app can then be used to complete transactions without the need to present a physical card.
Digital wallet apps can come from a bank (mobile banking app), a large merchant (such as Starbucks), or a third-party payment app service such as Apple Pay and PayPal.
Additional features like Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) vary depending on the provider you choose, but at its core, digital wallets are used to make cardless purchases in-person and online.
Types & Examples of Digital Wallets
Digital wallets are categorized by their use/accessibility:
Closed Digital Wallet
Closed wallets are apps that can be used to transact only with the wallet issuer/provider. This type of digital wallet is exclusive, created by (or for) large merchants. Starbucks, for example, is a closed wallet where the user can only spend the funds within their Starbucks app for purchasing goods sold by Starbucks.
Semi-closed Digital Wallet
A semi-closed wallet can be used to transact with the wallet issuer’s partner merchants. Unlike closed digital wallets, this type is created by a third-party platform and often provides services other than purchasing such as bills and payments. One good example is Uber Eats, where the user can only use the funds in their account to purchase from merchants listed in the app.
Open Digital Wallet
An open digital wallet allows consumers to pay any merchant in person and remotely. There are no restrictions or list of partner businesses—it only requires that the merchant has enabled its system to accept digital payments. One of the best examples of this is mobile banking apps that can be used to make payments. Third-party providers like Apple Pay and payment processors Service that provides merchants with the ability to process card and other non-cash payments like PayPal are also among the popular digital wallets being used today.
Examples of Digital Wallets
- Cash App
- Apple Pay
- Google Pay
- Samsung Pay
- PayPal
- Venmo
- AliPay
- Amazon Pay
- Zelle
- Walmart Pay
How Digital Wallets Work for Merchants
All digital wallets work similarly in terms of payment processing. The app is designed to securely store a user’s payment information and use the same details to make purchases without the need to present their physical credit or debit card.
To do this, the digital wallet is equipped with a variety of payment technology for communicating with a merchant’s payment processor.
- Near-field Communication (NFC), EMV chip for tap to pay, and QR code to transmit data
- Encryption to secure data
Primarily, customers use digital wallets to pay for online purchases, but nowadays, digital wallets are also widely used for in-store transactions. Contactless payments are possible with NFC, tap-to-pay, and QR code payment technology.
Additionally, digital wallets employ encryption methods, not only to securely store customer payment information within the wallet but also to safely transmit the same data to a merchant’s payment processor. Digital wallets use algorithms to convert credit card data into random text, numbers, and symbols, making them unreadable even if intercepted by hackers.
As an example, we can look at how Apple Pay processes payments:
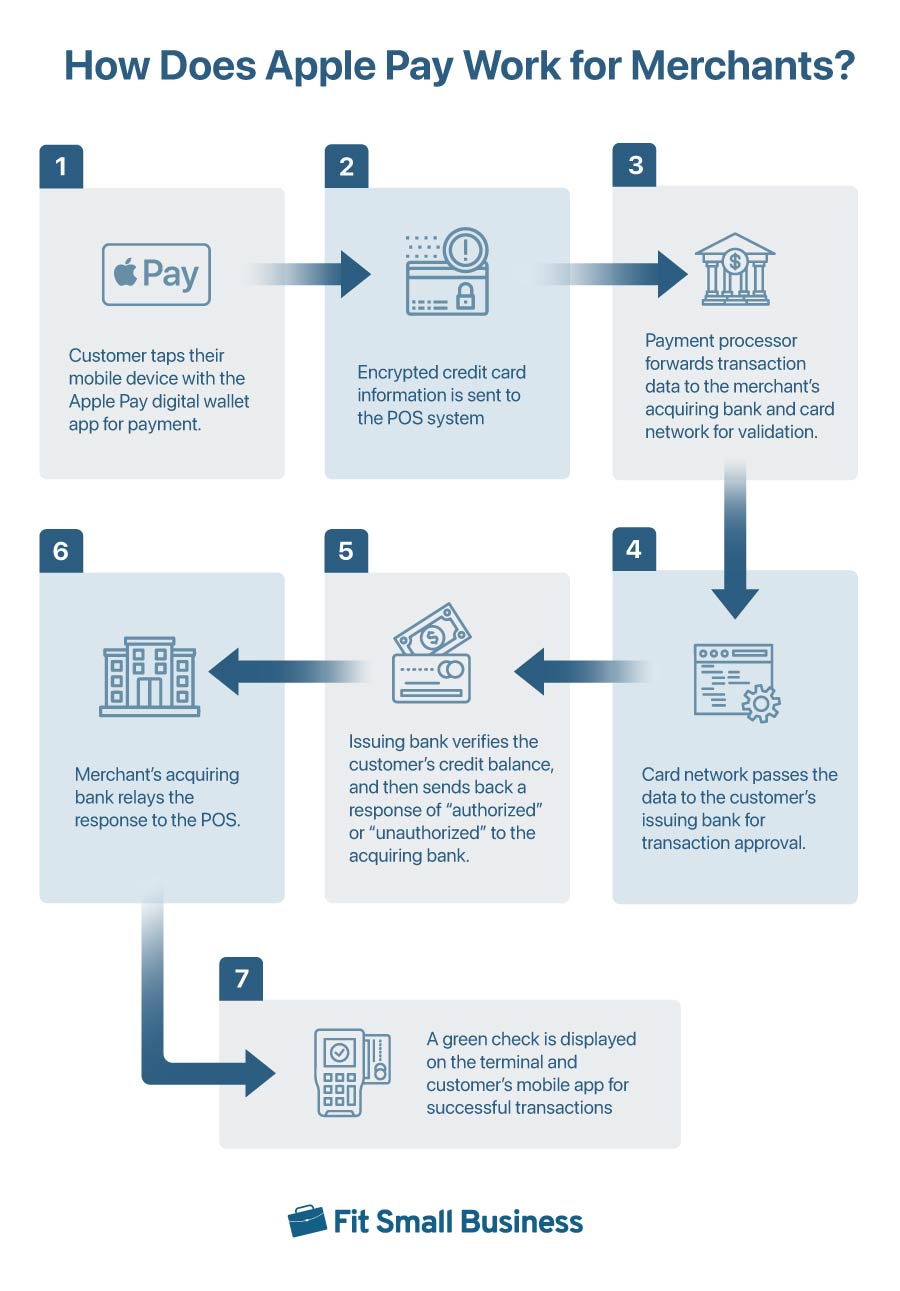
The illustration above shows how a customer’s payment information is moved from the digital wallet within the smart/mobile device to the POS system and eventually sends the request for verification and approval of the transaction to the card network, merchant bank, and customer’s issuing bank. This is the same procedure for other digital wallets.
Related reading:
How to Accept Digital Wallet Payments
To start accepting digital wallet payments, merchants will need to have a compatible payment processing system. Nowadays, most payment processors already come built-in with this service and it is just a matter of which digital wallet service provider (Apple Pay, Google Pay, etc.) it is compatible with and how much they charge for this type of transaction.

Digital wallet payment for in-person transactions
When enabled, your online checkout page should show digital payment method options. For in-person transactions, your payment processor’s hardware should also be NFC- and EMV chip-enabled so it can receive payment data from a customer’s phone and other smart devices.
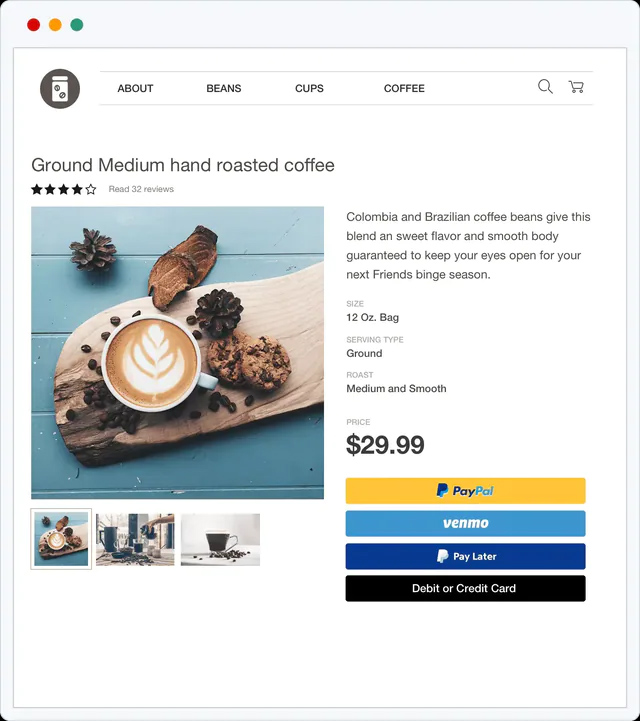
Digital wallet payment option for online transactions
As with digital wallets, payment processors also have security features to encrypt and transmit customer’s payment information.
If you are a gig worker, solopreneur, or part-time freelancer, having your own digital wallet business account is the fastest way to accept digital wallet payments without signing up with a larger payment processor.
PayPal is the pioneer of peer-to-peer (P2P) digital wallet apps for accepting payments (including cryptocurrency). However, others like Cash App, Venmo, and Zelle are also popular and offer business accounts should you need one.
Related reading:
Benefits of Accepting Digital Wallet Payments
Generally, adding a digital wallet to your list of payment methods can do more good than harm.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to set up (immediate) | Reporting limitations |
| Provides customer convenience | Varying fund transfer speed |
| Adds biometric security from the mobile app | |
| Includes additional services from partner merchants | |
Not only does a digital wallet allow you to offer a convenient payment option that’s growing in popularity, but digital wallet payments are also inexpensive and easy to set up.
Additionally, digital wallets include other functions for their users that can benefit you as a merchant.
For example, most digital wallets include these features:
- Send and receive funds
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL)
- Bill payments
- Short-term loans
Other digital wallets may even include the following features:
- Personal insurance sales
- Stock trading
- Cryptocurrency trading
Needless to say, accepting payments from a digital wallet that offers BNPL can potentially increase your sales. If you run a business where cryptocurrency is popular, a digital wallet with a cryptocurrency function can further broaden your payment options.
On the other hand, working with a digital wallet means some of your business tools will be somewhat limited by the app features. For example, most digital wallet apps only keep basic transaction information, which can be difficult for reporting and payment tracking.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
These are some of the questions we often encounter about digital wallets. Click through the sections to learn more.
Adding a digital wallet payment option usually does not cost any extra. Transaction fees often follow the typical rates for in-person and online payment rates. For example, PayPal does not charge a monthly fee for simple payment processing but digital wallet transaction rates vary from 2.29% + 9 cents (for QR code payments) to 2.59% + 49 cents (for Apple Pay), and 3.49% + 49 cents (for Venmo).
Freelancers, solopreneurs, and gig workers that only need simple transaction handling can likely run their business with a digital wallet business account (think PayPal, Venmo, and Zelle).
However, you will need a full POS and payment processor if you need additional tools such as inventory management, delivery, and payroll integrations.
Yes, PayPal is a pioneer digital wallet service provider. Lately, it has expanded its functions to peer-to-peer payments and even point-of-sale (POS) services.
Bottom Line
As cashless transactions are the new norm, digital wallets are becoming a more essential part of running a business. The question is no longer whether you should have a digital wallet, but which one(s).
Knowing what a digital wallet is and how it works can help to smartly allocate your working budget to the combination of digital payment methods that’s perfect for your type of business.