Customer relationship management (CRM) software is a tool businesses use to manage and improve their relationships and interactions with existing and potential customers. There are four fundamental types of CRMs: operational, analytical, collaborative, and strategic. Here, we outline the features and benefits of each type of CRM system, including their best use cases and examples, to help you choose which one best fits your business needs.
Download our free CRM e-book today to get a deeper understanding of CRM software features, integrations, strategies, and implementation.

The Expert’s Guide to Customer Relationship Management
Small Business Use Cases + Pro Tips
While there are four fundamental types of CRM software, each one aims to improve the quality of your customer relationships and the service you provide them. When choosing a CRM, it is crucial to consider the specialized features and functions to ensure that you can address your business requirements accordingly.
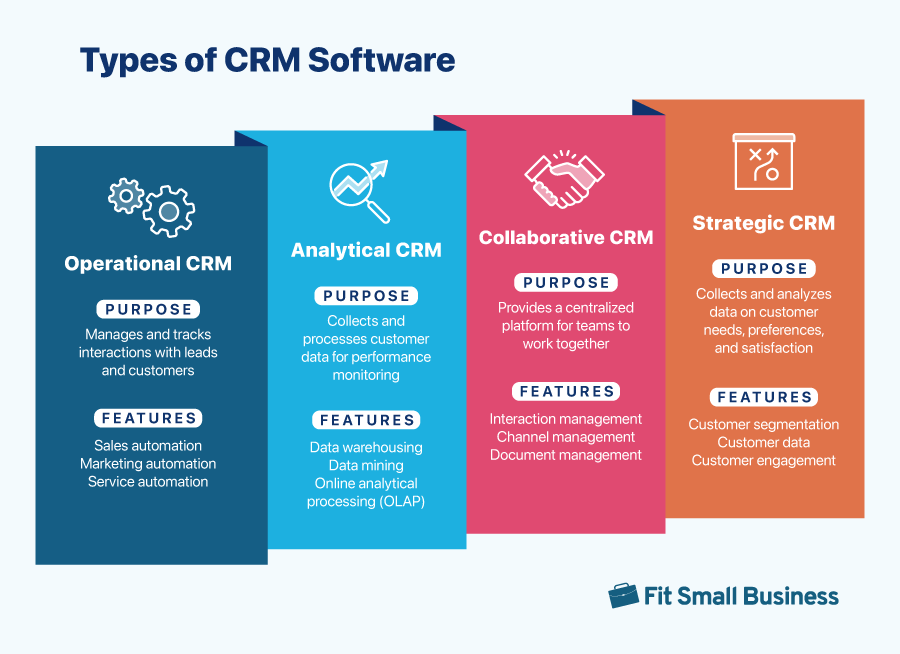
1. Operational CRM
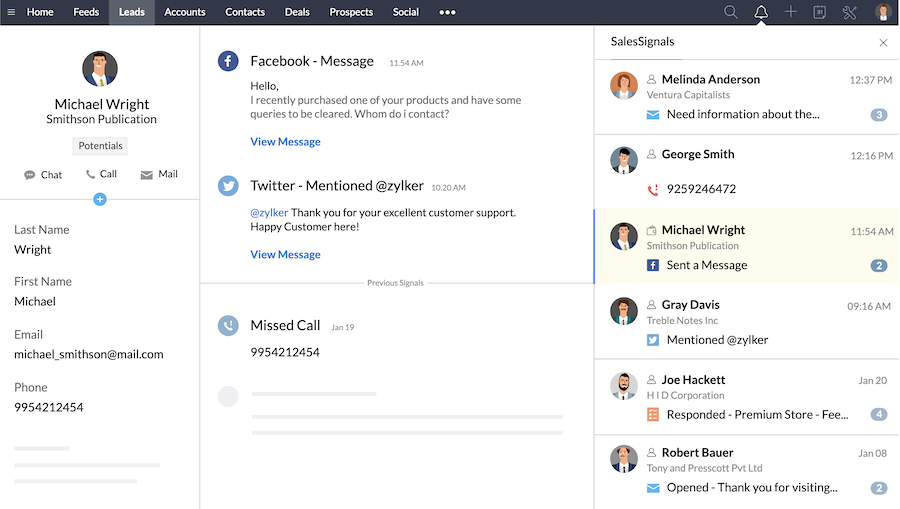
An operational CRM manages and tracks your company’s interactions with prospects and customers to help you acquire new customers and retain existing ones. It automates business processes like lead data entry and sending personalized marketing campaigns to save you time.
Business owners also employ this type of CRM to generate leads, convert them into paying clients, record contact details, and serve customers. It also allows you to facilitate accounting, inventory, project, and human resource functions from a single system.
Operational CRM systems are best for:
- Companies wanting to standardize and automate sales and CRM processes through automated workflows
- Sales professionals needing to manage pipeline stages and perform sales activities like appointments and quotes
- Teams that execute and track marketing campaigns and link them to leads and contacts
- Sales professionals and business managers who need to manage post-sale projects for the products they are selling
- Businesses that coordinate and execute inbound or outbound calling within their CRM
The core features of an operational CRM include sales automation, marketing automation, and service automation.
Sales automation involves streamlining manual and repetitive steps in the sales process, such as appointment scheduling, pipeline management, lead conversion, and taking notes. This frees up your sales team from administrative tasks and allows them to focus on selling products and interacting with customers. It also lessens tasks from falling through the cracks since it sends notification alerts to agents as each task moves through the sales pipeline stages.
Another aspect of sales automation is lead scoring, which involves ranking your prospects to let sales representatives hone in on which leads are worth pursuing or are ready to engage with your business. For instance, Freshsales, which is an example of this type of CRM, can be set up to monitor your leads and automatically enrich their profile based on available information on the web and interactions with your company.
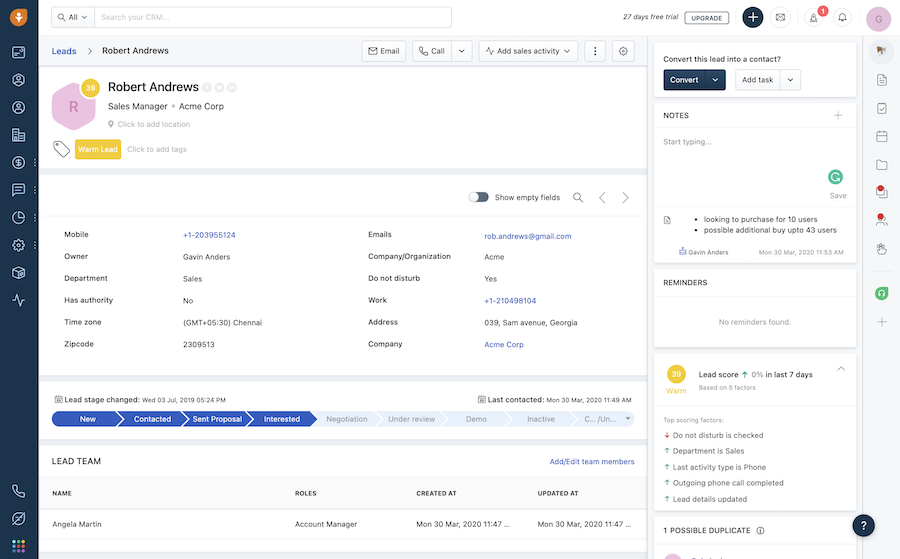
Freshsales lead record with score (Source: Freshsales)
An operational CRM’s marketing automation feature simplifies repetitive marketing tasks, such as initiating email marketing campaigns, workflows, and social media posts. This process nurtures leads by identifying your audience, choosing the right content, and automatically triggering actions based on a set schedule or the customer’s behavior.
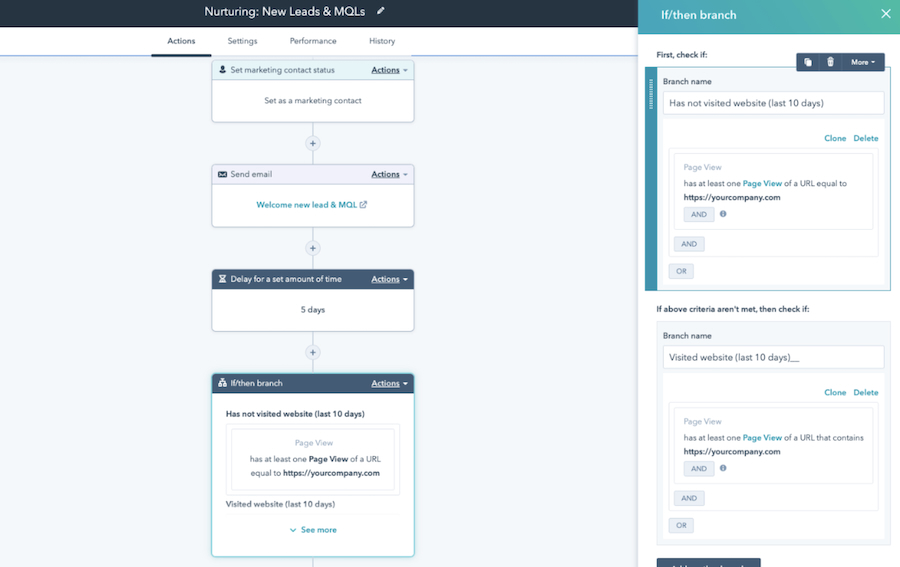
HubSpot CRM customized marketing automation workflow (Source: HubSpot)
Customer service automation significantly reduces human labor when servicing clients, improving customer satisfaction, and decreasing labor costs. Modern CRM systems incorporate help desk tools, such as a knowledge base, artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots, canned responses, a self-service customer portal, and an interactive voice response (IVR) system.
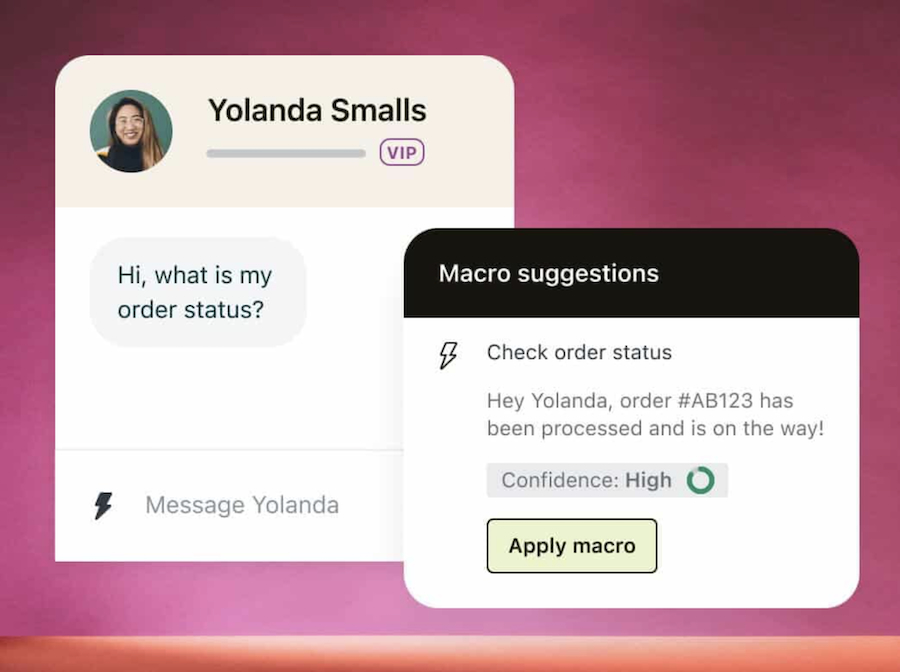
Zendesk AI chatbot showing key insights and suggested actions (Source: Zendesk)
2. Analytical CRM
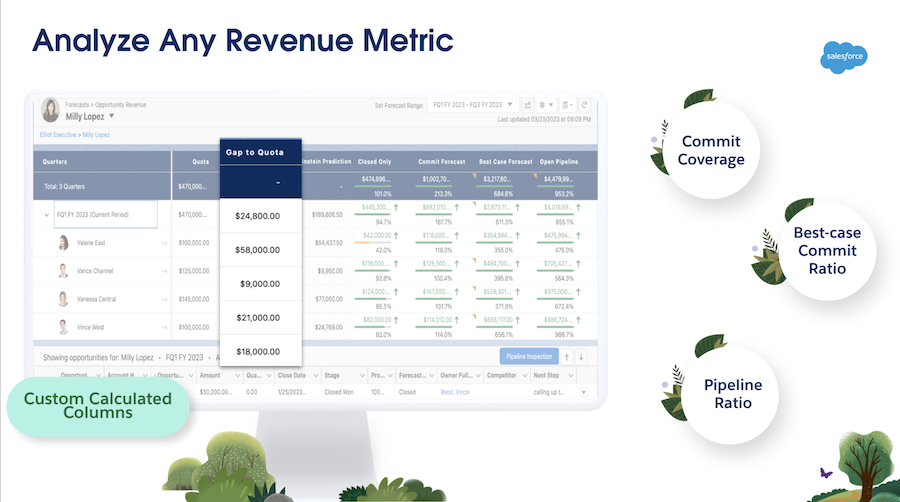
An analytical CRM collects and organizes sales, marketing, and customer service data, making it easy for business owners to discover insights based on their current business performance. It also displays detailed reports that you can use to make strategic business decisions.
Analytical CRM systems are best for:
- Managers who need information like performance metrics and dashboards for making data-driven decisions
- Data analysts who monitor customer service efforts and make recommendations based on customer data
- Sales team managers who want visibility on their sales reps’ performance, including the volume of their activities and the value of revenues they bring into the company
- Accountants who need centralized data storage for their referrals, leads, partners, and clients
- Business intelligence professionals who analyze sales metrics and trends, and use this data to formulate sales forecasts
The primary features of an analytical CRM include data warehousing, data mining, and online analytical processing (OLAP).
An analytical CRM, like Salesforce, acts like a data storehouse, which saves data from various sources in a centralized location. It also organizes the stored data so it can be easily accessed, analyzed, and used in generating reports. This could include details about your customers, business interactions, and even agent performance.
Data mining is analyzing warehoused data to uncover meaningful patterns, trends, and relationships in your data. It automatically interprets the pieces of information so you can use them to improve your sales, marketing, and customer service strategies.
OLAP is a technology that enables users to analyze information and extract business data from multiple database systems simultaneously. It also gives your CRM system forecasting capabilities, allowing you to make data-driven decisions concerning business trends, demands, and budgets.
3. Collaborative CRM
A collaborative CRM makes cross-team communication and collaboration systems more efficient—improving customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and company profitability. It covers sales, marketing, customer service, and technical support teams, as well as customers, creditors, vendors, suppliers, and distributors. This type of CRM also uses automation to accomplish its goals.
Collaborative CRM systems are best for:
- Businesses with multiple locations or departments that heavily depend on cross-team communication
- Teams that need to track customers across multiple channels, especially on the digital side
- Companies that want to gain a better understanding of their customers and increase customer retention and loyalty
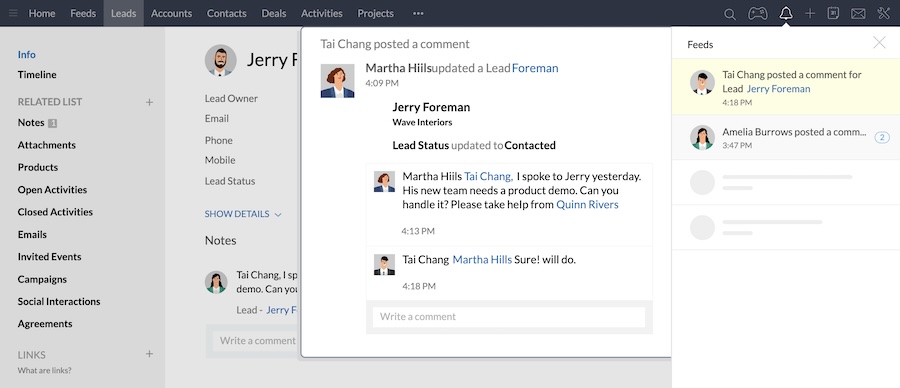
The three main features of a collaborative CRM are interaction management, channel management, and document management.
To provide a better understanding of your prospects and customers, a collaborative CRM lets you log all of their touchpoints with your company in a centralized access point. This way, even if not all of your teams interact with the customers directly, everybody can see their customer journey and improve customer service based on the recorded facts.
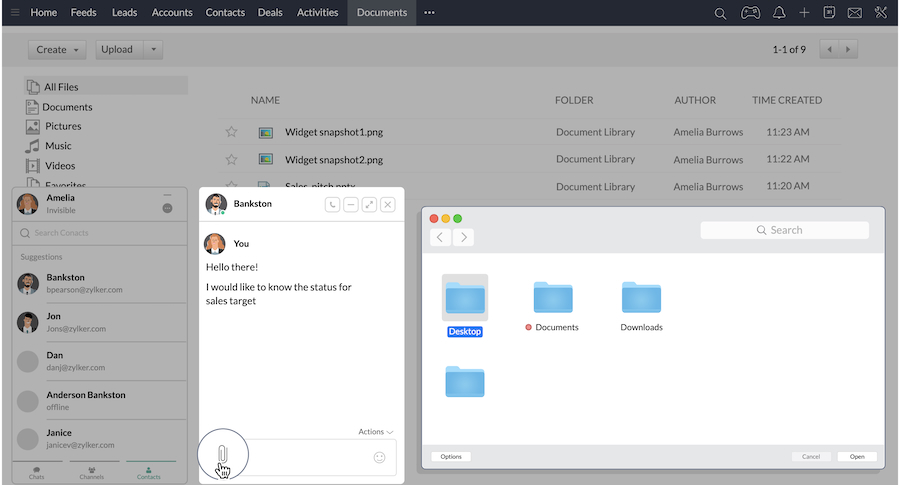
A collaborative CRM, like Zoho CRM, makes it easy for your company to track and communicate with your customers via their preferred channels—be it on the phone, email, or social media. It records how your customers get in touch with you and lets you respond to them using the same channel.
Document management is a process or system used to capture, track, store, and share electronic documents, such as proposals, contracts, and digital images of your business files. A collaborative CRM allows your teams to access these documents from a centralized location. It eliminates the need to go through a department’s desk or opening separate software to retrieve the CRM data you need.
4. Strategic CRM
A strategic CRM focuses on understanding the behavior, needs, and preferences of customers in order to provide tailored solutions and messaging. It helps improve customer acquisition, retention, and nurturing by streamlining and automating customer-related activities and interactions. These include product inquiries, product browsing, and purchases.
Strategic CRM systems are best for:
- Businesses that offer a recurring or subscription service
- Organizations seeking a solution that can gauge customer behavior and preferences across multiple touchpoints and channels
- Companies wanting to improve customer experience through tailored strategies and targeted communications
The main features of a strategic CRM are customer segmentation, customer data management, and customer engagement.
A strategic CRM like EngageBay divides customers into distinct groups based on criteria like demographics or purchasing patterns. Segmentation helps businesses understand what their customers really want or need so that they can tailor their strategies for sales, marketing, communication, and product or service development.
This customer-centric CRM collects and analyzes customer data from multiple touchpoints to gain insights into how they behave, what they like, and how satisfied they are with a product. The strategic CRM pulls this information from website visits, purchase histories, and social media interactions to form a complete view of the customer. Based on the data obtained, businesses can spot trends, anticipate what the customer needs, and personalize engagement.
A strategic CRM helps businesses build meaningful relationships with their customers through proactive engagement, personalized offers, and excellent customer service. It also allows businesses to communicate with customers via multiple channels, including email, live chat, social media messaging, text messaging, and voice calls.
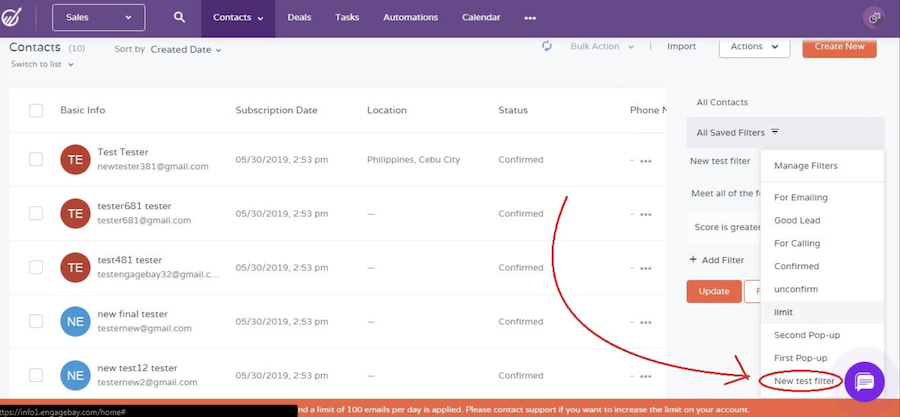
EngageBay contact segmentation using filters (Source: EngageBay)
Examples of Different Types of CRM Software
Below are examples of each of the four types of CRM software systems, which are also included in our list of the best CRMs for small businesses. Click through the tabs below to learn the basic details of these CRM software types.
CRM Pricing
CRM pricing for different types of CRM software varies. Operational and collaborative CRMs tend to be more affordable compared to analytical CRMs, as reflected in the examples above. Other factors that contribute to the pricing include the features, number of users, and billing frequency. Overall, pricing can range from $12 to $300 per user, per month, depending on the abovementioned factors and feature inclusions.
Free & Low-cost CRMs
Free and low-cost CRMs, which typically include operational and collaborative CRMs, can range from free to $8 to $15 per user, per month. CRMs in this pricing category usually support a few user seats and only include basic CRM functionalities, such as contact, lead, and pipeline management.
Midrange CRMs
Midrange CRMs, which can include the four different types of CRM system, can cost from $30 to $150 per user, per month. These usually offer additional features for lead generation, lead scoring, collaboration, and reporting. Others offer more extensive CRM integrations with project management, accounting and invoicing, social media management, and email marketing software.
Enterprise CRMs
More advanced plans for large enterprises can cost as much as $300 per user, per month or even as high as $1,000 per month for a set number of user seats. The most expensive CRM systems include deeper customization options and highly sophisticated analytics and reporting tools—typically beneficial for larger-sized enterprise companies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The newest among the different types of customer relationship management systems is strategic CRM. It helps businesses plan for their company products, sales processes, and customer experience by following the customers’ perspective and line of thinking. In addition, it possesses the capability to identify customer behavioral trends so that the company can adapt to them.
The five most important components that a CRM should have are contact management, sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service, and reporting. These essential features will help you manage your sales pipeline so that nothing falls through the cracks. They will also help you maintain and grow your customer relationships by organizing communication channels and outreach campaigns.
In CRM, there are four stages of the customer life cycle. The first one is Acquisition, which involves identifying prospects and attracting new customers. The second is Conversion, which involves turning prospects into paying customers through targeted campaigns. Next is Retention, which refers to efforts to keep existing customers satisfied with your products or services. The last stage is Loyalty, which involves turning customers into loyal supporters.
Bottom Line
Many modern CRM providers offer some overlap in the features associated with the four types of CRM systems—some of them could even offer all four in one robust software. When choosing which type of CRM tool you should use, it’s essential to explore your objectives for using one so you can easily decide which one best addresses your business needs and goals.