Learning how to sell on Amazon can seem like an overwhelming and ambitious project. However, selling on the popular ecommerce platform requires only a few simple steps.
You’ll first have to plan which products to sell, and this involves understanding Amazon’s product restrictions and seller fees. Then, you’ll create a seller account and build your product listings. From there, you’ll need to manage your inventory and order fulfillment. Finally, because Amazon is such a competitive marketplace, you’ll need to manage your store’s performance.
Step 1: Choose a Competitive Product Offering
To create a selling strategy and decide which products to sell, you’ll need to get acquainted with the platform’s product restrictions and fees. From there, you can do product research to identify winning items.
Some products may be profitable and in demand, but their associated fees and regulations can incur additional labor and/or costs—which is important to keep in mind.
Step 2: Sign Up for an Amazon Seller Account
You need to register as an Amazon seller before selling products. Registration involves subscribing to one of two seller plans.
Amazon has two selling plans—Individual and Professional. Professional accounts give you access to far more features than Individual plans but have a $39.99/month fee. Individual accounts cost $0/month but charge 99 cents per item sold. Both programs include additional selling fees beyond this per-product listing charge.
Here are highlights of each Amazon seller plan:
Amazon Professional Seller | Amazon Individual Seller | |
|---|---|---|
Monthly Fee | $39.99 | $0 |
Product listing fee (charged when sold) | None | 99 cents |
Number of product listings/sales | Unlimited | 40 per month |
Amazon product-related fees | Same | Same |
Access to Fulfillment by Amazon | ✓ | ✓ |
Access to Amazon Seller App | ✓ | ✓ |
Sell existing Amazon products | ✓ | ✓ |
Add new products to the Amazon catalog | ✓ | ✓ |
Listings eligible for the Buy Box* | ✓ | N/A |
Offer coupons, shipping specials, and gift wrap | ✓ | N/A |
Can apply to sell in restricted categories | ✓ | N/A |
Bulk upload products or feeds to Amazon | ✓ | N/A |
Access to inventory reports | ✓ | N/A |
Connect with third-party services and product feeds | ✓ | N/A |
*Occupying the “Buy Box” means your product is the one that Amazon automatically sells when customers click the “Add to Cart” button on a product listing sold by multiple sellers.
An Individual Seller plan is ideal for low-volume merchants selling fewer than 40 items per month and developing stores still deciding what to sell. It’s also a good choice if you have no plans to advertise or use advanced selling tools.
Meanwhile, a Professional seller plan is recommended if you sell 40+ units per month, include advertising in your selling strategy, and want to qualify for top placement on product detail pages. It’s also notable for its use of advanced selling tools—such as APIs and reports—that benefit high-volume sellers.
If you’re going to sell products in restricted categories, you need to sign up under a Professional Seller plan.
Most sellers opt for Professional accounts because of the sales-driving features you get. But you can always start with an Individual account and upgrade in the future.
For example, if you’re just dipping your toes into Amazon using retail arbitrage (buying inventory from other sellers at a discount and reselling it for a profit), an Individual plan can get you started with minimal costs. But if you’re investing money in wholesale or private label products, the Professional plan is the best from day one.
After deciding on a seller plan, you need to register for a seller account. You have the option to use your Amazon customer account, or you can create a new seller account using your business email address.
Have the following ready to provide during the sign-up process:
- Bank account number and bank routing number
- Chargeable credit card
- Government-issued national ID
- Tax information
- Phone number
Go to Seller Central to register, then follow the prompts for setting up a seller account.
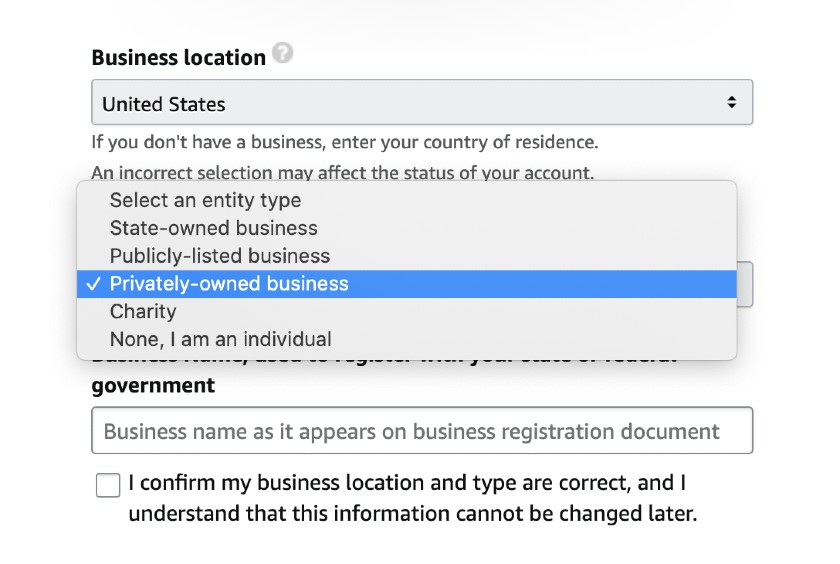
Your business type determines the requirements that will be asked of you when you sign up for a Seller account.
Once you complete these steps, you’ll have access to your Seller Central Dashboard and can start listing products to sell on Amazon.
What is Seller Central?
Seller Central is the website where sellers (like you) go to monitor their Amazon sales activity. You can also manage inventory, update pricing, communicate with buyers, contact seller support, and add new products.
Step 3: Create Your Product Listings
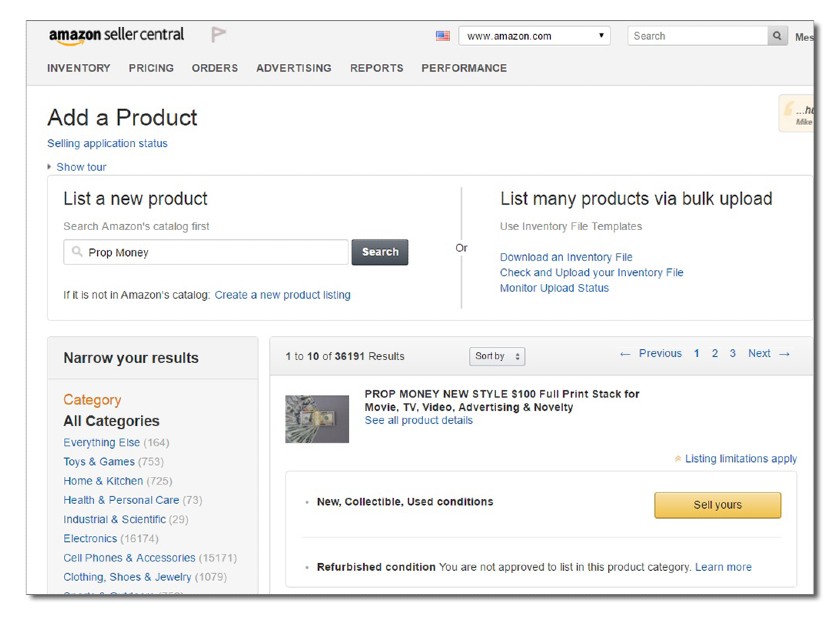
Amazon sellers can create product listings in two ways: by adding items to existing product listings or by creating new product listings.
Adding items to current listings is by far the easiest method, and it’s how most beginners get started on Amazon. So we’ll begin there:
Manually Add Your Product to an Existing Listing
You’ve probably noticed that many products for sale on Amazon have multiple sellers, as shown below:
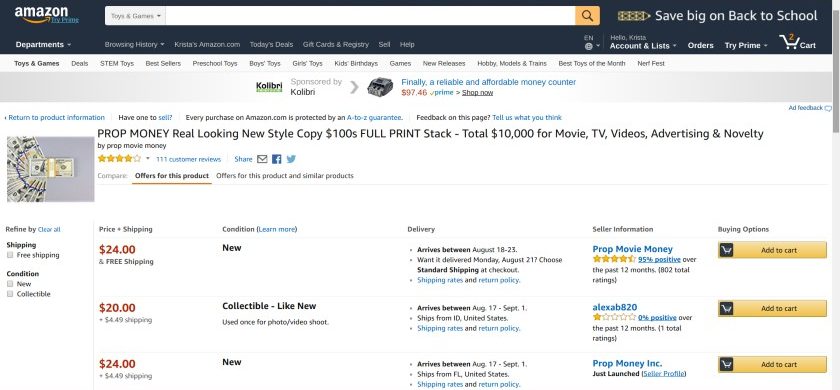
An example of a product listing with multiple sellers.
The second and third sellers in the list above added their items to this existing product listing. It might seem like a waste of time because of the existing competition—however, remember that the majority of sellers only keep a few items in stock. So, as others sell out, your listing will be the one available—and the one that shoppers buy.
To make your listing the top pick, you can also lower your price, offer free shipping, or use FBA (discussed below).
Manually adding your product to an existing listing is accessible from your Seller Central Dashboard. You can follow the steps below:
Manually Create a New Product Listing
Amazon Professional sellers can create entirely new product listings for items not already sold on the marketplace. Generating new listings takes more time than adding products to an existing listing. However, it allows you to create a high-quality listing that sells using keyword research, product images, and detailed item descriptions.
Remember that not all product categories are open to all sellers. Some product categories require a Professional seller account, while others may require approval to sell. There are also products that third-party sellers cannot sell.
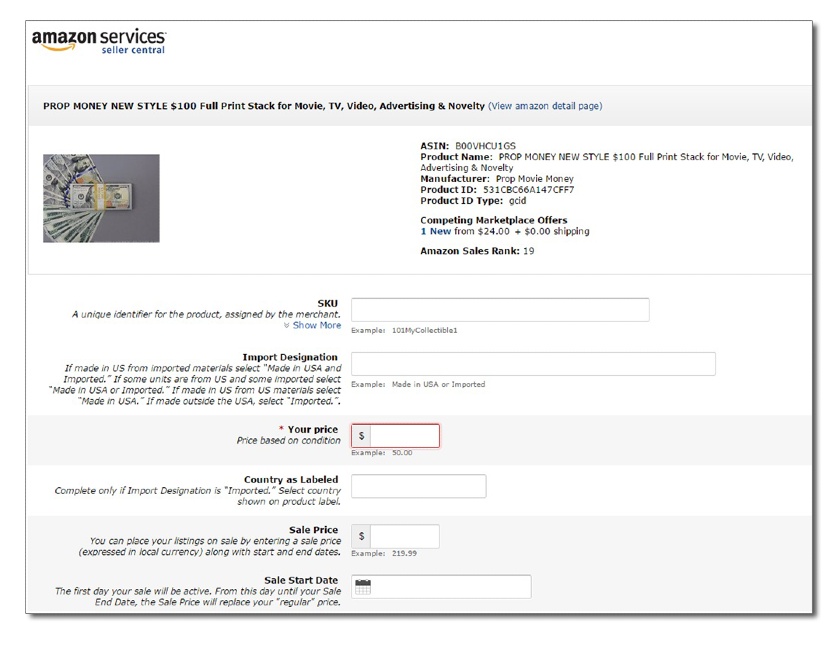
To create a new product listing, you need the following information:
- A product identifier: GTIN, UPC, ISBN, or EAN to specify the exact item you’re selling; find out more about which identifier is relevant to your product listing in Amazon’s listing requirements
- A stock-keeping unit (SKU) number: A product ID you create to track your inventory
- Offer details: Price, product condition, available quantity, and shipping options
- Product details: Name, brand, category, description, and images
- Keywords and search terms: Applicable keywords to help buyers find your product
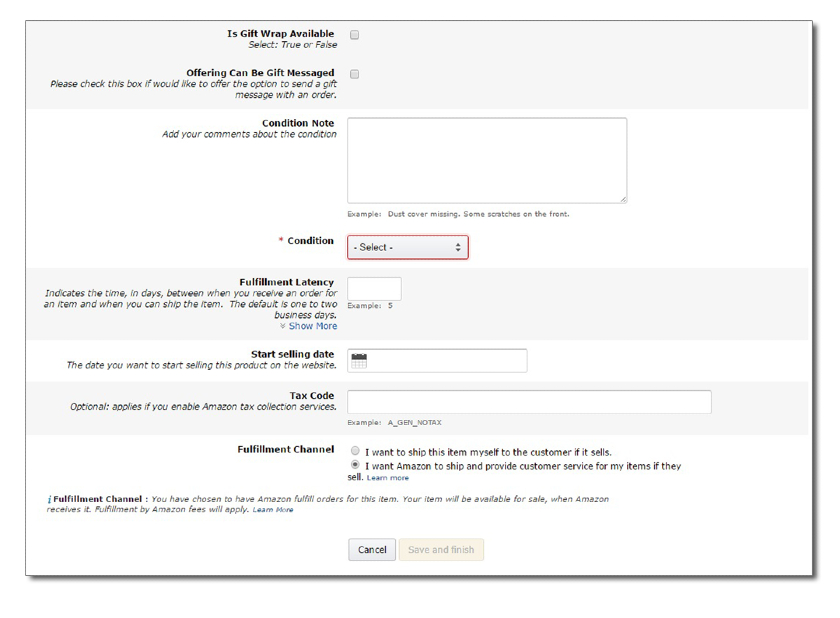
You also need to build out your product detail page. If you’ve ever shopped on Amazon.com, you’ve seen one. Product detail pages are where customers find vital information about an item.

- Title: 200 characters max, capitalize the first letter of every word
- Images: 500 x 500 or 1,000 x 1,000 pixels to increase listing quality
- Variations: Colors, scents, or sizes
- Product description bullet points: Short, descriptive sentences highlighting key features and benefits
- Featured offer (“Buy Box”): The featured offer on a detail page; customers can add to their cart or “Buy Now”
- Other offers: The same product sold by multiple sellers offers different prices, shipping options, etc.
- Product description: Keywords improve the chances that people will find your listing
Optimize your listings for maximum visibility. Use Amazon SEO practices to tailor your listings to appear higher in search results and generate more traffic.
Manage Your Product Listings: Use a Bulk Upload or Product Feed Tool
If you’re a Professional seller, you also have the option to add many product listings at once by uploading all of your product data using a spreadsheet.
If you also sell on your own website or plan to in the future, you can directly connect your products to Amazon. Here’s how both of these options work:
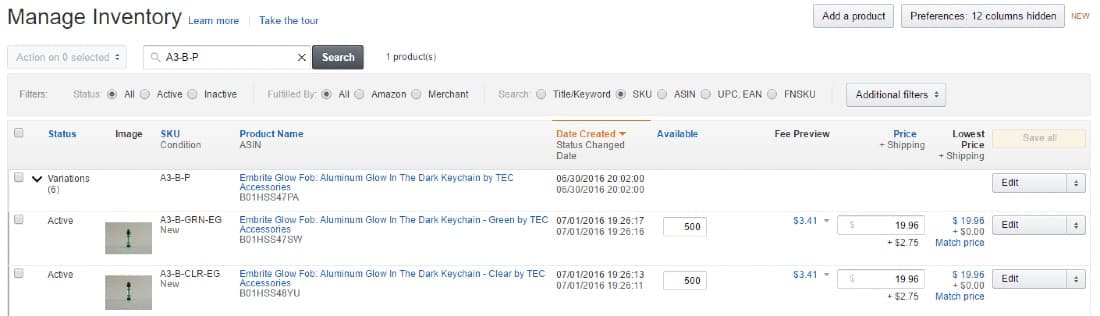
Step 4: Manage Your Inventory on Amazon
Accurately managing inventory is key to your success on Amazon since the platform will dock your seller rating for not promptly shipping items on that show as “in stock.”
Like the product listing methods described above, you have several choices regarding inventory management. Whichever method you choose, stay diligent about it to keep your Amazon seller rating high.
Amazon automatically reduces your inventory count as your Amazon items sell. If you sell only on Amazon, this should keep your counts correct. But if you sell the same stock on your website or in a retail store, you’ll probably need a different solution.
Step 5: Set Up Fulfillment & Shipping
As an Amazon seller, you have three options for delivering your products. First, you can do it yourself—maintaining your inventory and shipping products to customers—which is called merchant fulfillment. You can also let Amazon package, label, and ship products through FBA, or you can use a third-party fulfillment provider.
Read our guide to learn more about order fulfillment and its processes and strategies. You can also check out our comparison of in-house fulfillment vs a fulfillment center to help you decide which is right for your business.
Many beginners start out shipping Amazon orders themselves. Plus, many established ecommerce sellers ship all Amazon orders from their warehouse. Amazon calls this Fulfillment by Merchant, or FBM.
If you choose to go this route but are new to shipping, Amazon makes it pretty easy to handle on a small scale. You can print orders as well as US Postal and UPS shipping labels right from your Seller Central dashboard. You’ll need to have packing materials ready to go, including:
- Shipping boxes
- Packing tape
- Filler such as paper or bubble wrap
- A shipping scale
- Easy access to shippers for package drop-off or a secure place for pickup
Amazon’s Buy Shipping tool can help you get a great deal on shipping labels. You can choose from Amazon’s network of trusted shipping partners, ship and confirm your orders, and track your shipments.
Packing a few orders each week isn’t overwhelming for most. However, it is crucial to ship promptly. That’s why sellers of all sizes tend to use the next option.
With Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), you ship your products to Amazon, and it stocks, packs, and ships your products for you. When products are ordered, Amazon collects payment from the customer and pays you available funds every two weeks. Read our in-depth review of FBA and how it works.
Of course, this comes with added FBA fees on top of your Amazon seller fees, but it also comes with many major sales-driving perks, including:
- Prime-eligible product listings: Most FBA items are listed as Prime products on Amazon
- Free shipping to Prime buyers: FBA makes your products eligible for Prime free 2-day shipping
- Higher rankings for product listings: Amazon gives FBA sellers preference in rankings
- More Buy Box listings: When prices are the same, FBA sellers win the tie for the coveted Buy Box
- Trust factor: Buyers trust packages will arrive as expected when items are fulfilled by Amazon
- Post-sale servicing: FBA handles every customer interaction for your orders, from inquiries to returns to refunds. Its customer service representatives are available by phone, email, or live chat 24/7.
The six steps of Fulfillment by Amazon include (1) Inventory is sent to an Amazon warehouse, (2) FBA receives and stores the goods, (3) Customer orders come in, (4) FBA packs and ships the orders, (5) FBA performs customer service for the orders, and (6) FBA handles customer returns.
Another option that takes fulfillment tasks off your plate is using an outsourced fulfillment company. Like FBA, these businesses store, pack, and ship your orders for you. However, this method is considered a type of FBM since you use a company of your choosing. And, since it’s not FBA, you don’t get the sales-driving perks listed above.
Most fulfillment partners are geared toward mid-to-high-volume multichannel ecommerce companies that sell in many places—including websites and Amazon.
That being said, some 3PL partners, such as ShipBob, have no minimum volume requirements to get started. ShipBob offers fast, two-day shipping and flexible resources to facilitate growth. Contact the provider for a free quote.
Step 6: Manage Store Performance
Once your store is up and running, it’s crucial to monitor, analyze, and promote your store’s performance for ongoing success.
Amazon is a customer-centric marketplace and holds its sellers to a high standard. It expects you to provide a seamless and satisfactory customer experience every time. Amazon requires these minimum key metrics that you should take note of:
- Order defect rate (a measure of a seller’s customer service standards): < 1%
- Pre-fulfillment cancel rate (initiated by the seller before shipment): < 2.5%
- Late shipment rate (orders that ship after the expected date): < 4%
Anything that falls outside these metrics might earn your store a negative performance review and affect how high or low your product listings rank on Amazon.
You can monitor your performance targets in Seller Central. Amazon also has a list of best practices for its sellers.
Customer product reviews play an essential part in the Amazon shopping experience. They benefit sellers and customers alike.
Familiarize yourself with the right and wrong methods to get more Amazon product reviews to avoid policy violations. You can learn more from Seller University.
Seller University is an online resource from Amazon. It lists videos that feature step-by-step guides, tutorials, and training to help you start (and grow) your Amazon business.
Amazon offers advertising solutions for sellers to reach and engage shoppers. You can use these advertising methods through Seller Central:
- Sponsored Products: These ads for individual product listings on Amazon help drive product visibility and, ultimately, sales. You can find them on search results pages and product detail pages.
- Sponsored Brands: These search-result ads feature your brand logo, a custom headline, and up to three of your products. They help to showcase your brand and product portfolio.
- Amazon Stores: These custom, multi-page shopping landing pages enable sellers to share their brand story and product offerings.
Promotions are an incentive for customers to purchase now. You can offer three types of promotions in your Amazon store: money off, free shipping, and buy one get one free. You can also offer percentage or money-off discounts with digital coupons.
Bottom Line
Amazon is a highly accessible platform that welcomes all kinds of merchants—from individuals selling a few items per month to power-sellers moving thousands of products each day. But while the barrier to entry is low, the competition is fierce and success is demanding.
You need to approach every Amazon product opportunity from a profit perspective. This considers the cost of the goods you sell and the time it takes to source products, create listings, manage inventory, and ship orders. Once you understand the basics of how to sell on Amazon, you can make decisions to help balance efficiencies, increase net profits, and find ways to grow.