A customer relationship management (CRM) system is a business tool that helps organizations manage, store, and analyze lead and customer data. It helps facilitate prospecting and sales processes to improve customer relationships. Here, we explain what a CRM system is used for and why it is essential for small businesses. We also outline essential CRM features and functionalities, different types of CRMs, and top examples of CRM providers.
Download our free, in-depth CRM e-book to learn more about how to choose and implement a CRM for your small business.

The Expert’s Guide to Customer Relationship Management
Small Business Use Cases + Pro Tips
What Is a CRM System Used For?
CRM systems enable streamlined sales, marketing, and service activities, as well as strengthen relationships by allowing agents to provide more personalized interactions with contacts. They work by pulling together lead and customer data collected by business websites, social media, emails, and third-party apps into a single customer database.
Some CRMs provide more robust functionality beyond contact management and workflow automation. For example, a business can also use a CRM platform to analyze data and uncover patterns to make your sales, marketing, and CRM campaigns more efficient. It can also be used to predict future sales trends.
Pro tip: A CRM’s use case depends on the individual application. CRM features vary from one provider to another and between pricing tiers. Some platforms only provide sales tools, while others include marketing features. There are also some all-in-one solutions that help you manage and improve all aspects of your CRM process.
Advantages of CRM Systems
A CRM solution simplifies your CRM process, helping you manage your leads and increase customer retention. It is equipped with tools and features that automate some aspects of your business operations, make customer interactions more efficient and effective, and improve your overall customer satisfaction score. Some of the top benefits of utilizing CRM platforms include:
- Centralized access to customer information: 74% of companies reported improved data access since implementing their current CRM.
- Higher productivity: 73% of small business professionals reported improved productivity through automation of repetitive tasks and sales processes.
- Improved customer satisfaction (CSAT) rate: Using a CRM resulted in higher customer retention rates for 61% of its users.
- Increased sales through targeted communication: More than half of businesses said their CRM contributed to their improved sales quota achievement and conversion rate.
- Data-backed insights for improved decision-making: 76% of businesses said their reporting accuracy increased with the use of CRMs.
- Improved collaboration among your departments: 81% of reps collaborate with other teams like marketing and customer service in order to close a deal—an aspect which CRMs can help facilitate through centralized customer data access.
Pro tip: Curious to learn more data-backed insights on the use of CRM systems? Check out our article on 20 interesting CRM statistics every small business should know.

Essential CRM Features & Functionalities
Various CRM providers have their own set of features and functionalities that set them apart from competitors. However, there are certain fundamental CRM features that should be included in the lineup of capabilities you should look for—no matter which provider you’re considering. These include the following:
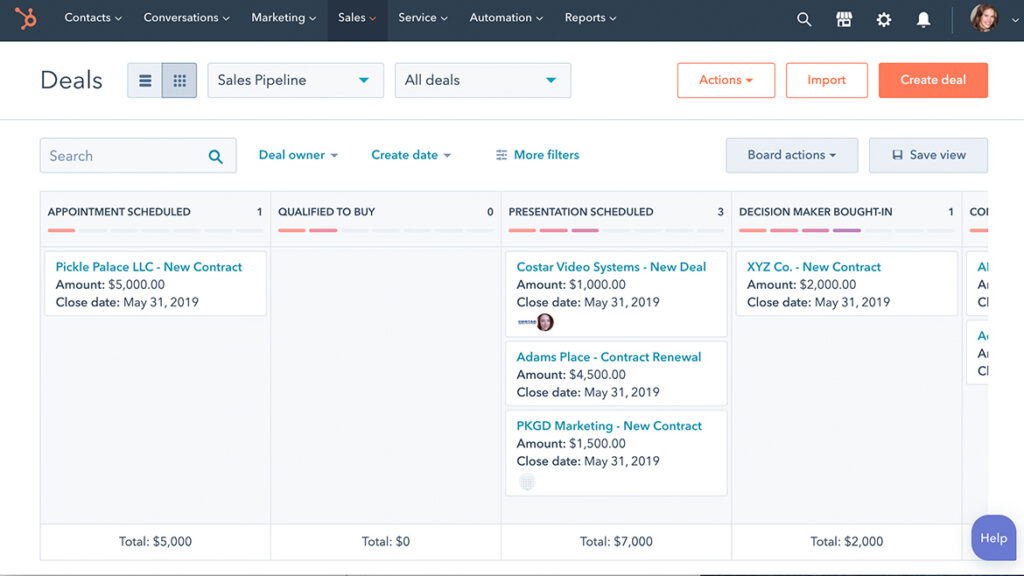
- Contact management: Creating, storing, tracking, and organizing customer data
- Account management: Tracking and delivery of tasks related to a client or project
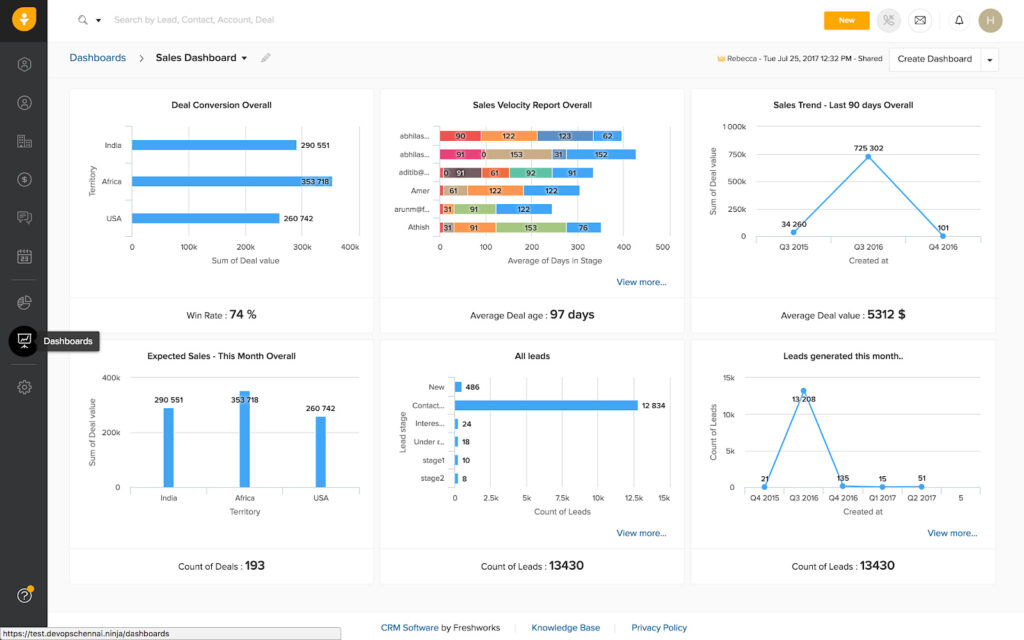
- Reporting and dashboards: Data and metrics to monitor business performance
- Workflow automation: Automating steps to complete a sales process
- Customer database: Storing customers’ personal information, including lead source and levels of engagement
- Lead management: Capturing, managing, and qualifying leads
- Territory management: Assigning leads or accounts to specific agents based on location, product, or account size
- Email marketing: Sending individual or mass emails to leads and contacts
- Sales forecasting: Predicting when sales opportunities may close and the revenue they bring
- Document management: Capturing, storing, tracking, and sharing electronic documents such as business proposals and contracts
- Customizations: Adding new or altering existing features to make the CRM a better fit for your business needs
- Integrations: Providing seamless connections to third-party apps to extend the CRM’s capabilities and address gaps in its features
- Cross-platform compatibility: Ability to support several operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Android and iOS mobile devices
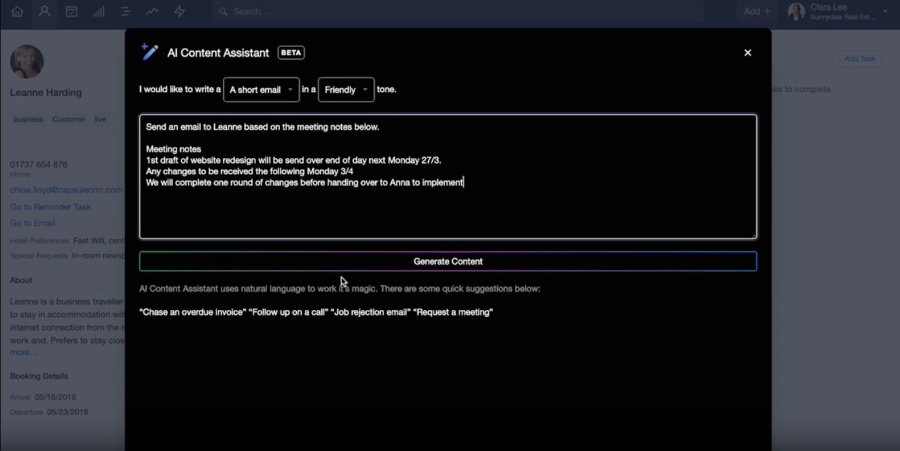
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Using technology that simulates human intelligence to improve efficiency and productivity, like predictive analytics and customer sentiment analysis
- Quote management: Creating, sending, and tracking quotes associated with sales opportunities
Types of CRM Platforms
There are three fundamental types of CRM solutions: operational, analytical, and collaborative. While they have different sets of functions and purposes, each has the same goal: to improve customer relationships and grow your business.
- Operational CRM: Automating business and sales processes to save time and effort
- Analytical CRM: Focuses on gathering data and analyzing it to help you deliver excellent service to your customers
- Collaborative CRM: Brings together your sales, marketing, and service teams to help you better understand your customers’ needs
Types of CRM Technology
When choosing a CRM solution, determine the type of technology you need based on several factors. These include the size of your team, your company’s budget, the level of customization you need, and the extent of data access by third-party vendors. Take a look at these CRM software examples below to see which one best fits your business needs.
- Cloud-based CRM: Stores data in a remote network so that users can access it online anytime, anywhere
- On-premise CRM: Installed on the company’s servers so that users can access the database even without an internet connection
- Open source CRM: Allows users to access its basic source code for free and customize it based on its intended use
Industry-specific CRMs
Some businesses benefit from using industry-specific CRMs, which typically have processes and ready-made tools that need minor customizations. Compared to general-purpose CRM solutions, they provide more niche and specialized tools to help them move customers through sales cycles more quickly. These tools include those used for payment collection, lease contract management, and integrations with popular real estate marketplaces.
Businesses that need industry-specific CRMs include companies in the following industries:
- Insurance industry
- Healthcare industry
- Real estate industry
- Hospitality industry
- Mortgage industry
- Call center industry
- Construction industry
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses
The complexity of a CRM system also depends on what other business tools it is designed to work with. CRMs, like Salesforce and Pipedrive, can be purchased as standalone systems. Alternatively, they may be integrated with other types of software as a value-added service, such as Mailchimp (which is primarily an email marketing tool) or Nextiva, a voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) platform.
Here are some of our top recommended cloud-based CRM tools for small businesses. Click on the tabs below to see each provider’s recommended use case, top key features, and starting price.
Looking for something else? If these providers have too many features you may not necessarily need, check out our guide on CRM alternatives if you only need a tool for organizing and tracking prospects and leads.
CRM Software Costs
CRM pricing models range from free to more than $100 per user, per month, depending on the type of CRM and the features included in each package. Free and low-cost CRMs are best for solo users and small teams as they often support a limited number of seats and have lower data storage capacity. These platforms range from $7 to $15 per user, per month. They also typically only include basic CRM functionalities, such as contact, lead, and pipeline management.
CRM packages for mid-range companies can range from roughly $30 to $150 per user, per month. These usually offer additional features for lead generation, collaboration, and reporting. Others offer more extensive CRM integrations, such as a built-in phone system. More advanced plans for large enterprises can cost as much as $300 per user, per month. These typically include deeper customization options and highly sophisticated analytics and reporting tools.
Pro tip: Some CRM providers advertise low per-user fees, but there are often additional fees for training, onboarding, and implementation. Some options also have separate charges for customer support. Ask your provider about these items before committing to a CRM plan to ensure the package you choose meets both your needs and budget.
Integrating Your CRM With Other Business Tools
Integrating your CRM with other applications your sales team uses helps facilitate more integrated customer data management and avoids information redundancies. For example, if a team member updates a contact record, it will automatically update the same information in both the CRM and the other integrated app. Some of the most popular CRM integrations are customer service, social media management, email marketing, and accounting software.
Here are the ways that you can integrate your CRM software with other apps:
- Leverage native CRM integrations that are built into your CRM
- Use products from a single provider that has an ecosystem of integrated apps
- Connect with other apps using application programming interface (API)
- Use a connector software like Zapier
- Write your own custom code to facilitate communication between your CRM and other tools
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A CRM system is the technology used for managing the relationships and interactions of a business or organization with its prospects and customers. The main goal of a CRM is to improve business relationships to grow the business.
Aside from the CRM providers mentioned in the previous sections, there are many other similar providers, such as Streak CRM, which is great for Gmail users. Another CRM software example is EngageBay, which is recommended for email marketing. Apptivo is a solid option for managing an entire small business, while Insightly CRM is ideal for project management.
Building good customer relationships entails various activities, such as continuous communication, re-engagement, and understanding your customers’ needs. CRM systems can help you manage these aspects using tools like contact management, omnichannel communications, email marketing, and analytics. They help you streamline your sales processes and customer communications, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks.
Bottom Line
CRM systems may seem overwhelming and, sometimes, like overkill for your business. However, using one often makes the difference between providing timely and informative follow-ups or allowing deals to slip through the cracks. This makes CRM solutions well worth the investment for businesses of all sizes, provided your team commits to keeping data up to date and is thoroughly trained on its expected use.