With the vast number of ecommerce terms—plus new terminology appearing regularly—it’s important to keep abreast of the vocabulary you’ll encounter as an online retailer. Here, we’ve compiled an ecommerce glossary of terms and definitions with more than 70 of the most common acronyms, words, and phrases in use today.
1. 301 Redirect
This is an HTTP status code sent by a web server to a browser to indicate a permanent redirect from one URL to another. For example, if you change your company name, you may have a 301 redirect from the old website domain name to the new one. That way, customers who may not yet know your new name will still be able to get to your new website.
2. A/B Testing (or Split Testing)
A/B testing, or split testing, is a way to judge which of two or more different elements within a campaign or on a page produces better results. In A/B testing, you randomize delivery of the tested elements so that half of your audience receives version A and the other half receives version B. A/B testing is used on everything from websites to emails to ads.
An example of A/B testing is creating two separate page titles and testing them against each other to see which performs better. You can test single or multiple elements, including price, link colors, images, font size, call-to-action statements (CTAs), length of copy, and more.
3. Above the Fold
Above the fold is a phrase that originated in newspaper publishing where the most important content was always placed above the newspaper’s fold. In online terms, above the fold refers to the amount of content a page visitor can see without scrolling down. Just as with newspapers, in online content, it’s vital to keep your most important elements above the fold where they are the most visible.
4. Acquisition Cost
In ecommerce terms, acquisition cost refers to the total amount of money spent on marketing and promotions divided by the number of sales acquired.
Acquisition cost = Total expenses / Number of sales
For example, if you spend $2,000 on marketing and promotions (including marketing salaries if applicable), and those efforts generate 100 sales, your acquisition cost is $20, shown as $2,000/100 = $200.
5. Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is a cost-effective advertising strategy that leverages word-of-mouth, particularly through social media platforms. In this setup, you collaborate with individuals or companies who promote your product or service. In return for their promotion, you offer them a commission for each sale or specific action they generate.
Affiliates can range from your own customers to partner businesses that bundle your product with theirs, or bloggers and social media influencers who endorse your offerings. This approach allows for targeted, incentivized promotion, often resulting in high conversion rates.
What Is an Affiliate Marketing Network?
Affiliate marketing networks serve as intermediaries between sellers and affiliate marketers. They offer a platform where sellers can list products and/or select marketers to partner with, and marketers can choose products to promote in exchange for commissions.
These networks manage tracking, reporting, and payouts. Notable examples include ShareASale, CJ Affiliate, ClickBank, and Rakuten Marketing.
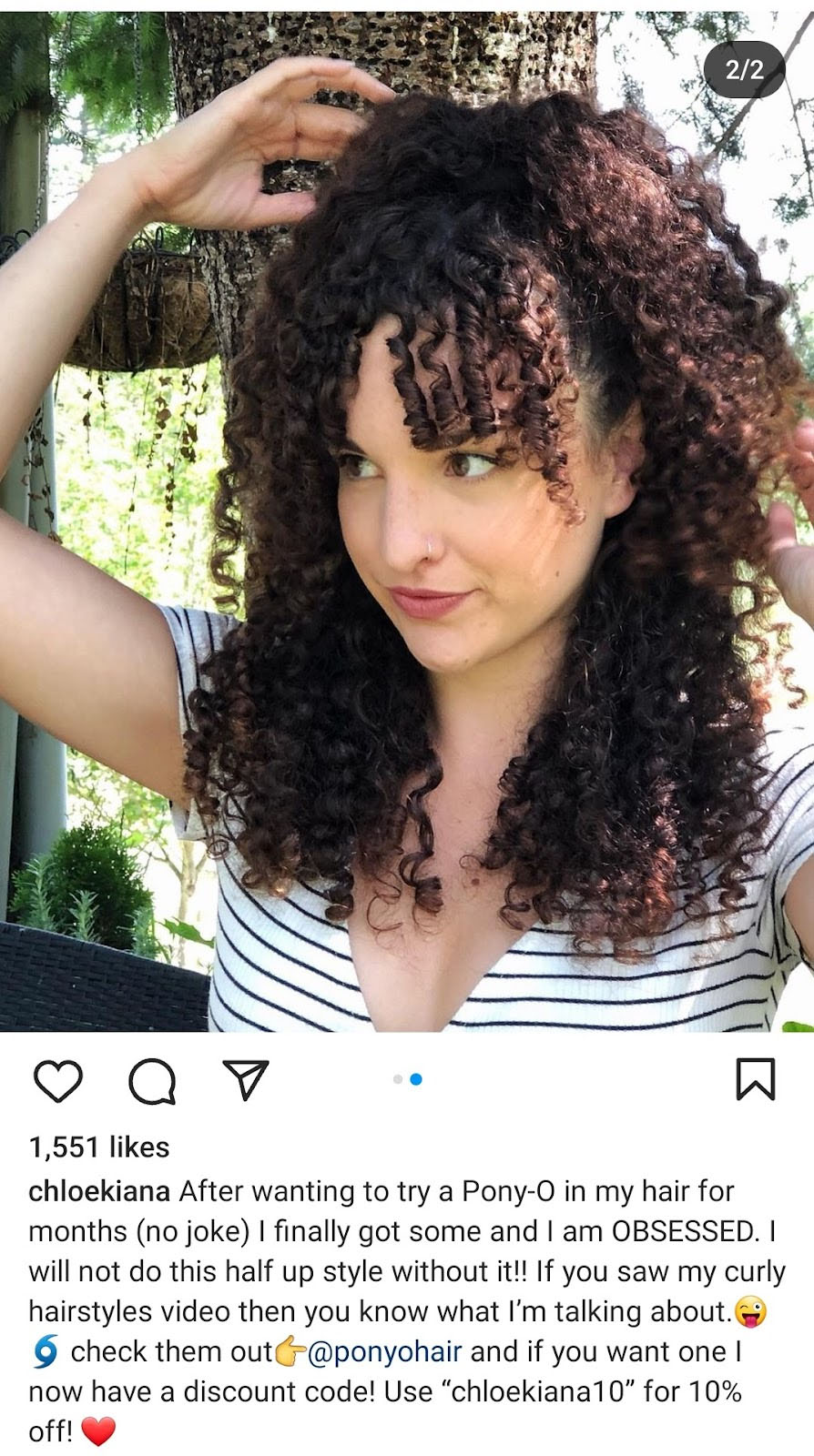
Affiliate marketing often takes place on Instagram, where influencers like this one post their opinion on a product along with a discount code that tracks the post’s success.
6. Alt Tag
An alt tag is an alternative text that is attached to an image on a website. When an image cannot be viewed for any reason, such as a slow connection or browser compatibility issues, the text in the alt tag is displayed instead. Keyword-rich alt tags are important for search engine optimization (SEO), and they’re a best practice for website accessibility.
7. API (Application Programming Interface)
An AP acts as a bridge between two different software programs, allowing them to communicate and work together. It’s a set of rules and tools that programmers use to build the connection.
For example, if you have a website on WordPress and you want to add an online store to it, you can use Shopify’s API to build a connection. This API will enable your WordPress site and your Shopify store to exchange information and features, streamlining the management of both platforms.
What Is an Open API?
An “Open API” is a type of API that is publicly available for developers to use. It allows easy access to a software’s features and functions. Open APIs can be used to create or modify custom integrations and new applications or services that can enhance or add new features to existing systems.
8. Amazon Standard Identification Number (ASIN)
If you sell on Amazon, your products will have an ASIN, which is Amazon’s own identifier. The unique 10-character alphanumeric identifier links to a unique SKU/EAN/ISBN code and is used as a reference to manage catalog attributes, prices, and inventory of the item.
9. ATV (Average Transaction Value)
ATV is the average dollar amount that each customer spends with your business in a single transaction.
To calculate ATV, divide the total sales revenue by the total number of completed transactions:
ATV = Sales Revenue / Total Number of Transactions.
For example, if you had $50,000 in monthly sales and had 500 sales, your ATV is $100.
Learn more about different retail metrics and how to apply them to your business.
10. Average Order Value (AOV)
AOV measures the typical amount every customer spends each time they place an order on your website. This aids in the identification of high-value customers and can also provide retailers with a good indication of how effective their pricing and marketing strategies are.
To calculate AOV, divide the total sales revenue by the number of orders placed:
AOV = Sales Revenue / Number of Orders
For example, if you generated $2,000 in sales and had 100 orders, your AOV is $20.
11. B2B (Business-to-Business)
The term B2B refers to transactions with other businesses (business to business) as opposed to selling directly to consumers. Salesforce and Square are examples of exclusively B2B companies. Retail brands often incorporate B2B on top of D2C (direct to consumer) sales so their products can be sold through other retail outlets.
Learn more in our guide to B2B selling.
12. Backlink
A backlink is a hyperlink from another website that points to a page on your site. High-quality backlinks from reputable sources enhance your site’s search engine credibility and are an SEO best practice. A significant volume of such backlinks is strongly associated with higher Google page rankings.
13. BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later)
BNPL programs allow customers to pay for purchases over a series of smaller installments, essentially acting as point-of-sale loans. These programs often feature zero or low interest rates when payments are made on schedule, offering a flexible payment alternative.
Discover the best BNPL apps to add to your ecommerce.
14. BOGO (Buy One, Get One Free)
BOGO is a promotional strategy where customers purchasing one item receive a second item for free or at a discounted rate. This tactic is often used to incentivize bulk purchases and increase sales volume, offering customers more value for their money.
15. BOPIS (Buy Online, Pickup in Store)
BOPIS, or curbside pickup, allows customers to order online and collect their items at a physical store, offering both convenience and immediate availability. BOPIS has become increasingly popular after COVID-19.
16. Bounce Rate
Bounce rate measures the percentage of visitors who leave a website after viewing just one page, serving as an indicator of site engagement and effectiveness. When you install Google Analytics on your website, you can easily view and track your bounce rate in the Analytics dashboard.
17. Bundling
Bundling means putting two or more products together and selling them as a combined package. Insurance agencies bundle car and home insurance and offer a lower rate, for example. However, online retailers also bundle products to increase average order value (AOV).
18. Cart Abandonment Rate (or Shopping Cart Abandonment Rate)
Cart abandonment rate calculates the percentage of site visitors who add items to their online shopping cart but exit without completing a purchase. This metric helps gauge the effectiveness of your checkout process and potential areas for improvement.
To calculate it, divide the number of abandoned carts by the total number of carts initiated:
Cart Abandonment Rate = (Number of Abandoned Carts / Total Carts Initiated) x 100
For example, if 1,000 carts are initiated and 500 are abandoned, the cart abandonment rate would be 50% (500/1000 x 100). The industry average hovers around 60–70%.
19. Chargebacks
A chargeback is a return of funds to a customer who claims he or she received an inappropriate charge on a credit card. Card-issuing banks may enforce a chargeback when a dispute occurs between a cardholder and the business that collected funds from a credit card charge.
Learn more about how to prevent chargebacks.
20. Conversion Rate
A conversion rate refers to the number of people who take a certain action versus the total number of people who had the opportunity to take that action. Conversion rates typically refer to sales, but can also apply to other goals, such as getting people to subscribe to an online newsletter or sign up for a free trial.
To calculate it, divide the number of successful conversions by the total number of visitors:
Conversion Rate = (Number of Conversions / Total Visitors) x 100
For instance, if 1,000 people visit an online course page and 100 make a purchase, the conversion rate would be 10% (100/1000 x 100).
21. Churn Rate
Also called “attrition rate,” churn rate is the rate at which customers stop making purchases from a seller. This term is usually used when referring to subscriptions or customer loyalty.
To calculate churn rate, use the formula:
Churn Rate = (Lost Customers / Acquired Customers) x 100
For example, if you acquire 100 customers and lose 10, your churn rate would be 10%.
22. Cookie (also Website Cookie)
A cookie is a tiny amount of data that websites store on a user’s computer or mobile device that is unique to that visitor. Cookies keep track of certain user information that’s helpful if a user frequently accesses a website.
For example, you can use a cookie to store a user’s login information so they don’t need to type it in each time. Cookies can also track browsing history.
23. CMS (Content Management System)
A CMS manages the content on a website and allows site administrators and designated editors to add, change, and remove website content. WordPress is the most used CMS today. Other CMS solutions include Wix, Squarespace, and Weebly.
24. CPC (Cost-per-Click)
CPC is a metric commonly used in pay-per-click (PPC) advertising campaigns on sites like Google or Facebook. It indicates the price you pay each time someone clicks on your online ad. CPC helps you gauge the financial efficiency and effectiveness of your PPC campaigns. By tracking your CPC, you can optimize your advertising budget and make adjustments to improve campaign performance.
The formula for calculating CPC is straightforward: divide the total cost of the ad campaign by the number of clicks the ad receives.
CPC = Total Ad Spend / Number of Clicks
For example, if the cost of advertising is $50 for 500 clicks, the CPC is $0.10.
25. CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
A CRM system is a tool that helps you keep track of interactions and transactions with your customer base. By tracking your encounters with customers, you can create effective engagement strategies that help you optimize sales and loyalty. Popular CRMs include HubSpot, Salesforce, Freshsales, and Zoho.
26. CRO (Conversion Rate Optimization)
CRO focuses on increasing the percentage of people who make a purchase after seeing your promotion or visiting your website. It involves using various strategies to improve your conversion rate, turning more browsers into buyers. The goal is to make the most of every promotional effort and drive more sales.
27. CSV (Comma Separated Values)
You may have had to download a report or data as a CSV. This means it’s a delimited file, where each value is separated by a comma. Data records are individual lines holding fields separated by commas so your spreadsheet program knows what to look for.
28. Customer Acquisition
Customer acquisition in ecommerce refers to the strategic efforts made to attract new customers to your store. Unlike merely driving traffic, the focus is on attracting the “right” traffic that is most likely to convert into sales. This involves utilizing various channels and running targeted campaigns throughout the year.
29. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
CLV is the total amount a customer is expected to spend at your business over the course of their relationship with you. This metric is invaluable for making data-driven decisions on how much to invest in acquiring new customers versus retaining existing ones.
30. CTA (Call-to-Action)
On a website, a CTA is a text link, image, or button that tells visitors what action you want them to take next. A CTA could direct people to take such actions as visiting a certain page, subscribing to a newsletter, or making a purchase.
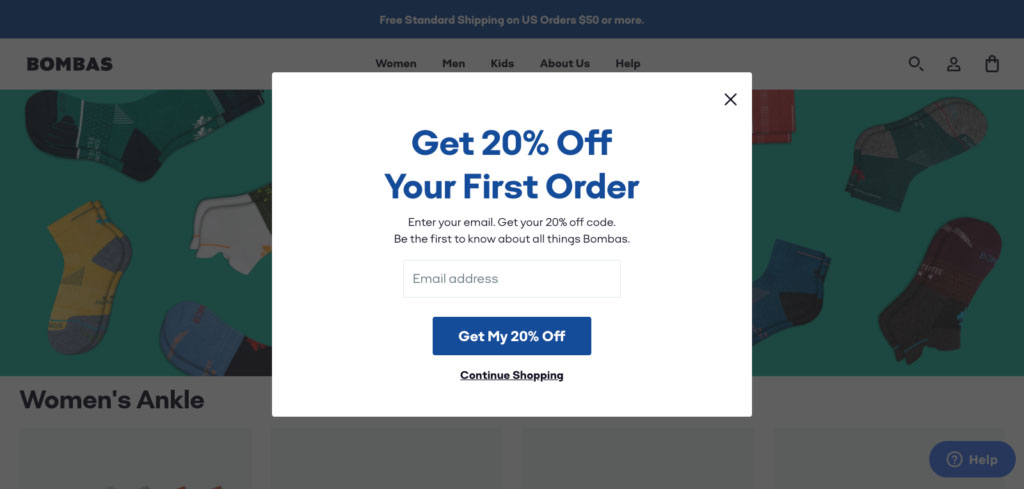
The blue button that says “Get My 20% Off” is an example of a CTA prompting the visitor to provide their email address in exchange for a coupon. (Source: Drip)
31. CTR (Click-through Rate)
CTR is the percentage of people who click a link compared to those who see it.
For example, if 1,000 out of 10,000 email recipients click a link, the CTR is 10%. It’s a key metric for evaluating campaign effectiveness.
32. Domain Name
A domain name is a string of characters that defines a specific address on the internet. For example, Shopify.com is the domain name for the Shopify ecommerce business website. Popular domain extensions include .com, .net, .org, .edu, and .gov, though there are dozens more.
33. Drip Marketing
Drip marketing is a tactic where marketers set up a series of messages to send to a specific audience over time. The messages may be sent through email or SMS platforms. When messages are sent via email, drip marketing campaigns are also known as email sequences.
34. Dropshipping
In dropshipping, the retailer serves as an ecommerce store for customers to buy products. Rather than managing inventory ownership and order fulfillment themselves, the retailer relies on a third-party manufacturer or wholesaler to receive a portion of the payment and send the products to the customers.
Starting a dropshipping store offers entrepreneurs a low-risk, cost-effective avenue for online selling, eliminating the need for investment and operational infrastructure.
35. DTC (Direct-to-Consumer)
DTC is a business model where products are sold directly from manufacturers to consumers, usually via a brand’s own website or store. This eliminates the need for middlemen, offering more control over brand experience and profitability.
36. Evergreen Content
Evergreen content and evergreen products are those that stay relevant year-round, rather than being tied to seasons or trends. This long-lasting appeal makes them valuable for both SEO and consistent sales, offering businesses a reliable return on investment. For example, phone cases are an evergreen product, whereas swimsuits are seasonal.
37. Fulfillment
Fulfillment is the end-to-end process of getting products into your customers’ hands once they’ve placed an order. This usually takes place in a warehouse and includes everything from inventory management to packing and shipping.
Ecommerce businesses can either handle order fulfillment themselves in-house, outsource it to a third-party fulfillment company, or use a combination of the two strategies.
38. Google Ads
Google Ads is an advertising platform that lets you place paid advertising on Google. The Ads platform offers thorough tracking and reporting functionality so you can easily see how your ads are performing.
To learn more, check out our article on advertising through Google.
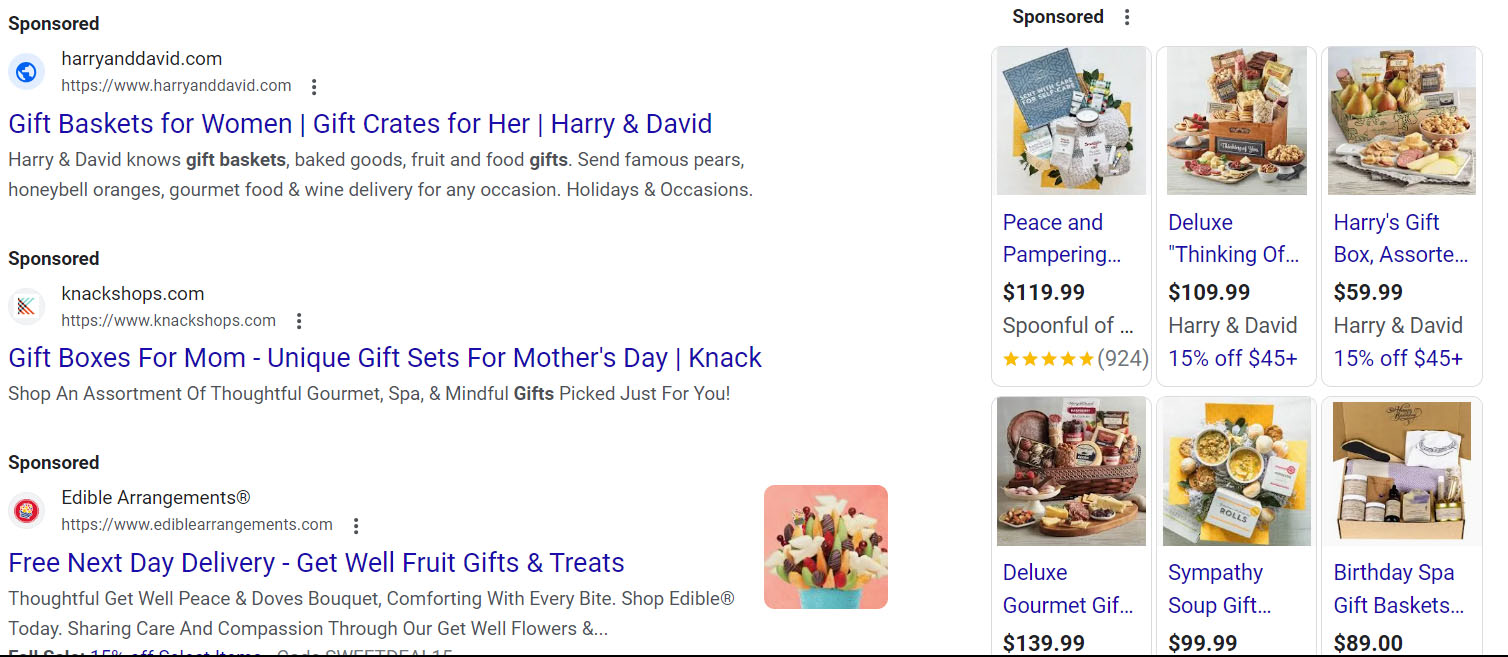
When Google users search for a related phrase, Google shows them a variety of ‘Sponsored’ results that are paid advertisements.
39. Hosted vs Self-hosted Websites
In a hosted website setup, your website’s files are stored on servers owned by a third-party provider, such as WordPress.com or Wix. This option often comes with limitations on customization and control.
In contrast, a self-hosted website means you choose and pay for your own hosting service, like DreamHost or Bluehost, and you have complete control over your website’s files. Self-hosting is generally better for those looking to fully customize their site and generate revenue.
40. Inbound Marketing vs Outbound Marketing
Inbound marketing focuses on attracting customers by providing valuable content and experiences tailored to them. This approach uses digital techniques like SEO, social media, and content marketing to pull customers toward your brand.
Outbound marketing, on the other hand, is more traditional and proactive, reaching out to potential customers through methods like advertising, direct selling, and mail campaigns. In this model, the company initiates the conversation about its products or services.
41. Keywords
Keywords are specific terms used in online marketing that capture the essence of your website, post, or product. They’re vital for SEO, helping your content rank higher in search engine results.
For example, if you’re targeting buyers of “lightweight waterproof tents,” that phrase would be a key keyword. Popular tools for keyword research include Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, and Ahrefs.
42. Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is when you add inappropriately high volumes of keywords to a web page, often to the point that the content does not sound natural to readers. Some sites do this in an attempt to improve their SEO results, but the technique is certain to backfire. Keyword stuffing is considered a black-hat marketing practice that can prevent your pages or even your entire site from ranking highly in search results.
43. KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
In ecommerce, a key performance indicator (KPI) serves as a specific retail metric for evaluating business success.
Companies often monitor an array of KPIs to gain a comprehensive view of their performance. Common ecommerce KPIs include total sales, average order value, net profit, cost of goods sold, cart abandonment rate, conversion rate, and website traffic. The KPIs that are regularly used may differ among businesses due to varying goals and operations.
44. Landing Page
An ecommerce landing page is a specialized webpage designed to serve a singular focus—usually promoting a specific product, service, or topic.
Businesses commonly use various marketing channels like social media, email campaigns, and paid ads to funnel potential customers to these landing pages. The ultimate objective is to prompt visitors to take a specific action, such as signing up for an email list, registering for an event, or making a purchase.
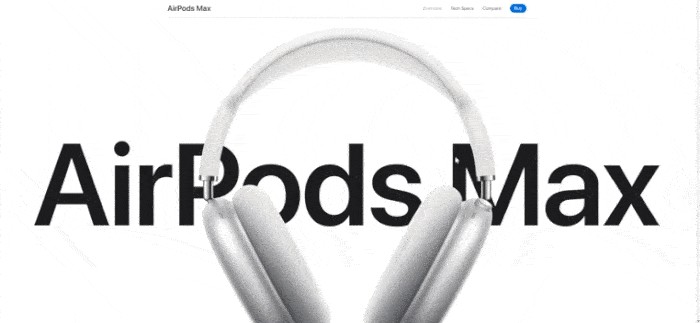
Example of an effective product landing page by Apple (Source: Apple)
45. Lead Magnet
In ecommerce terms, a lead magnet is a free gift or resource you offer in exchange for someone giving you their contact information. Popular types of lead magnets include checklists, e-books, resource guides, cheat sheets, and toolkits.
Read about lead generation in our article.
46. Loyalty (or Brand Loyalty)
Brand loyalty is the consistent preference customers have for a particular brand over its competitors. It’s gauged by repeat purchases and customer lifetime value. Achieving brand loyalty boosts long-term profitability and is shaped by factors like product quality and level of customer service.
47. Marketplaces
Ecommerce marketplaces are platforms where multiple sellers offer their products or services for sale. These platforms handle transactions and may offer additional features like customer reviews, payment processing, and fulfillment options. Well-known examples include Amazon, Etsy, and eBay.
48. Mobile Commerce (M-commerce)
Mobile commerce or m-commerce refers to the buying or selling of goods on mobile devices. It’s becoming increasingly popular, so it’s crucial that your online store and website be mobile-friendly to accommodate mobile commerce.
49. Multichannel Ecommerce
Multichannel ecommerce is the practice of selling using multiple paths such as your own website, social media marketplaces, eBay, and/or Amazon.
Similarly, retailers who sell both online and through physical locations (such as brick-and-mortar stores or farmers markets) are known as multichannel sellers. This approach allows them to reach a broader customer base and diversify sales streams.
See: Omnichannel vs Multichannel Retailing: Key Differences in 2023
50. Niche
In ecommerce terminology, a niche is a relatively small group of people that have certain traits or interests in common. Niche websites target a narrow audience rather than a larger audience. For example, dog owners are a large market while corgi enthusiasts would be a niche market. Corgi puppy owners would be an even narrower niche.
CorgiThings caters to a niche market: people who own or love corgis.
51. On-page SEO vs Off-page SEO
On-page SEO involves all the strategies that are done on a webpage to improve the likelihood that the page will rank high on Google. On-page SEO tactics include using targeted keywords in page text, alt-tags, page titles, headers, and URLs.
Off-page SEO focuses on activities outside your website to boost its traffic and domain authority (a metric that gauges the credibility and trustworthiness of a site)—ultimately helping it rank higher in search results. Typical strategies include earning high-quality backlinks, guest blogging, participating in podcasts, and sharing engaging visuals on social media that direct users back to your site.
52. Open rate
In ecommerce terms, an open rate typically refers to the number of people who open an email relative to the number of total emails sent. The formula to calculate email open rate is:
Email Open Rate = Total Emails Opened / (Emails Sent – Emails that Bounced)
For example, if you send 1,000 non-bounced emails to customers and 300 open them, that’s a 30% open rate. According to Mailchimp, the average email open rate is 21.33%.
53. Organic Traffic vs Paid Traffic
Organic traffic refers to visitors who land on your website through unpaid search results, typically via search engines like Google. These visitors find your site after typing a query into the search bar, and your website appears in the search results due to effective SEO strategies.
Paid traffic, on the other hand, consists of visitors who come to your website through paid advertising campaigns. These can include pay-per-click ads or sponsored social media posts. Unlike organic traffic, paid traffic is a direct result of advertising spend.
54. Payment Processor (or Payment Gateway)
A payment processor is a company that processes credit card payments and other electronic payments. It’s a vital part of any online store or website that sells anything. Popular processors include PayPal, Square, and Stripe.
55. PCI (Payment Card Industry) Compliance
PCI compliance is a standard that credit card companies require to ensure credit card processing and personal information is secure. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) was formed in 2006 to help protect sensitive customer data, including name and credit card information.
56. PPC (Pay Per Click)
A popular advertising model in ecommerce is PPC advertising, which means the advertiser pays the publisher (such as Google or Facebook) a certain preestablished fee every time someone clicks on an advertised link or image. The purpose of a PPC campaign is to drive traffic to a website or designated landing page and ultimately generate sales.

An example of a PPC ad on LinkedIn (Source: LinkedIn)
57. QR Code
This square barcode is machine-readable and holds information about an item to which it’s linked. You can use them online and physically to let customers find a product on your website or direct them to a particular webpage. They’re also used in fulfillment warehouses to organize inventory.
Learn more about QR code payments.

QR codes are most often used for selling or marketing to mobile users, who scan them with their smartphones. (Source: Pixabay)
58. Ranking (Page Ranking)
A website’s ranking or page ranking refers to how high it appears in SERPs, or search engine results pages. The higher the page rank, the more visible the page, and the more traffic the page receives.
Search engines rank pages according to what they feel offers the best answer to a user’s search. Google, for example, uses a proprietary algorithm to select which pages will appear (and in what order) once a user initiates a search on Google.
59. Recurring Payment
As the name suggests, recurring payments are paid regularly over a set time frame. Ecommerce sites offer recurring payment options when buyers purchase a subscription that renews monthly, quarterly, or yearly. A website might also set up a recurring payment plan that breaks down the cost of a higher-priced item into smaller periodic payments. Discover the ways to accept recurring payments.
60. SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS refers to cloud-based software that is hosted and maintained by a third-party provider. Instead of purchasing and installing the software on individual devices, users access it over the internet, usually through a subscription model.
The software provider is responsible for updates, security, and server uptime. SaaS platforms are increasingly popular in ecommerce for managing various business operations—from inventory and customer relations to marketing and analytics.
61. Sales Funnel
A sales funnel is a series of stages that a prospective customer goes through before making a purchase and becoming a loyal customer. A typical sales funnel includes several stages, as illustrated in the image below.
“Top of the funnel” refers to the stage where people in the funnel get acquainted with a product or service for the first time. “Bottom of the funnel” refers to the stage where prospects are close to making a buying decision.
62. SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
A business’s SEM efforts include everything it does with the goal of increasing visibility in search engines, including both SEO (search engine optimization) and paid ad strategies.
63. SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
SEO is the practice of improving your website’s visibility in search engine rankings to attract more traffic. It involves optimizing keywords, creating quality content, and securing reputable backlinks. A well-executed SEO strategy boosts your site’s authority and draws in a targeted audience.
See: SEO for Ecommerce Websites: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
64. SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
A SERP is a list of results that a search engine produces once someone has typed and submitted a search query. The higher you rank on SERPs, the more traffic you’ll generate for your website.
65. Shopper Profile
A shopper profile is a detailed snapshot of your target customer, outlining key demographics, preferences, and purchasing behaviors. Creating a shopper profile allows businesses to tailor marketing campaigns, optimize product offerings, and ultimately, drive sales and customer loyalty.
66. SKU (Stock Keeping Unit)
A SKU is a unique identifier used to track products in a retailer’s inventory. It aids in precise inventory management and often includes details like product size, color, and style, enabling efficient storage and order fulfillment.
See: What Is an SKU Number? A Complete Guide
67. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
An SSL is a security protocol. SSLs protect personal and sensitive information by ensuring it is properly encrypted. An SSL certificate demonstrates to search engines and everyone else that your site is safe and secure to use. Google flags websites that do not have an SSL certificate and may send your customer to a warning page before letting them in.
68. Tracking Code
A tracking code is a snippet of code that lets you see what users do after clicking on your ad. Some are installed on your website to track activity, while others are part of the URL. They are used to help you determine what marketing campaigns are the most effective.
69. User Interface (UI)
In ecommerce, the User Interface (UI) refers to the layout and design elements that customers interact with on your website or mobile app. This includes menus, buttons, product listings, and checkout pages. A well-designed UI enhances the user experience, making it easier for customers to navigate, find products, and complete purchases. Your store’s UI also contributes to its overall user experience or UX.
70. Upselling
In ecommerce terminology, upselling refers to the practice of asking a buyer to upgrade to a higher-priced product or consider buying add-ons to their initial purchase. Upselling is a common sales technique used to increase the average customer order value as well as boost business profits.
71. UX (User Experience)
The user experience refers to how easily a user can interact with your site, product, or service. It includes UI, but also encompasses their opinion on the ease of use, utilities, and efficiency in getting their task done.
72. Website Analytics
Website analytics measure key aspects of a website’s performance, including total traffic, page views, bounce rates, demographics, customer acquisition patterns, conversion rates, and site usage patterns. There are many different types of analytics software to choose from, although the most popular analytics tool is Google Analytics.
Bottom Line
This ecommerce glossary offers a strong foundation for understanding the most common ecommerce acronyms, terms, and online jargon that you’ll encounter as an online professional.
If you’re ready to start building your own ecommerce initiatives, creating an online store on Shopify is a terrific way to begin. You can launch a Shopify store for as little as $39 per month. Visit Shopify to learn more.