Lead qualification helps you prioritize sales activities toward leads that are most likely to generate revenue. It’s done by establishing qualification criteria for scoring leads, then distributing top prospects accordingly. This creates a more efficient sales operation and increases lead-to-customer conversions. We will define what lead qualification is in more depth, explain how to qualify leads, and provide a template to help you start the process.
Lead Qualification Template
Part of a sales management role is providing the tools and resources necessary for your sales team to do their jobs effectively. We’ve created a free template you can download that acts as a lead qualification checklist and worksheet. Use this to determine their purchase capabilities, fit for your product or service, and interest in your company.

Thank you for downloading!
Your lead qualification template is on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use customer relationship management (CRM) software to help you score and organize qualified leads. Zoho CRM can automate your lead scoring process to streamline your sales activities. Sign up today for a free account.
What Is Lead Qualification?
Lead qualification is the process of identifying and organizing potential customers best-suited for your products or services and who will most likely make a purchase. The purpose is to prioritize sales activities toward meaningful opportunities that have a better chance of becoming a won deal. Additionally, part of the lead qualification process includes categorizing prospects based on where they are in the customer journey.
Most sales process start with unqualified leads. These are prospects that may be a good fit for your goods or services but have not interacted with your business yet. It is marketing or the sales team’s job to get unqualified leads to take an action that indicates interest in learning more about your business. The action the lead takes will determine what sort of qualified lead they are. There are three types of qualified leads. The categories are:
- Marketing qualified lead (MQL): A lead who has expressed interest by interacting with a marketing campaign, such as downloading an e-book, subscribing to a newsletter, or clicking an email link.
- Sales qualified lead (SQL): A lead who has expressed interest by interacting with a sales representative, such as emailing to request pricing information or agreeing to a sales presentation.
- Product (service) qualified lead (PQL): A lead who has shown interest by using a free version of a product, free trial, or participating in a free consultation.
How to Qualify Leads in Five Steps
Once you have a robust understanding of what lead qualification involves, the process isn’t complicated if you know the attributes and behaviors that indicate a strong opportunity. For many of these steps, we recommend using customer relationship management (CRM) software to automate some of the processes and organize lead data accordingly. Here is how to qualify a lead in five easy steps:
1. Establish Lead Qualification Criteria
Lead qualification has two main components for evaluating and identifying leads. The first is whether the lead is a good fit for what you’re selling, while the other is looking at how interested they are in your offerings. When looking at a prospect’s “fit” and establishing criteria, start with the BANT methodology, which looks at four factors in a buying decision:
- Budget: Financial capacity of lead to make a purchase based on budgetary constraints and willingness to spend
- Authority: Position or power of a lead to make a purchase decision or the capability to finalize a deal
- Need: Usefulness of your product or service to the lead’s wants and solving their pain points
- Timeline: The level of urgency or expected timeline for a lead to make a purchase
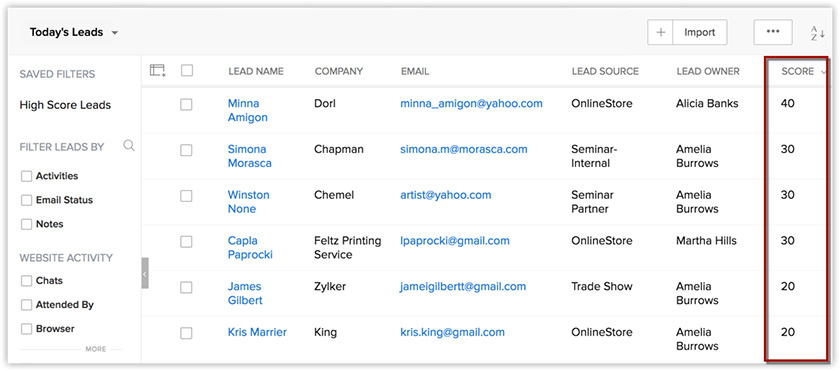
Zoho CRM lead scoring (Source: Zoho)
2. Generate Leads
Lead generation is a necessary stage in lead qualification because you need to attract potential buyers before you can identify the best ones. Once you have determined the attributes to look for in a lead, both inbound and outbound strategies can be used to effectively complete this step. Inbound involves methods used to get leads to come to you, such as creating content for web form submissions, seeking referrals, or running social media advertisements.
Outbound strategies, on the other hand, focus on actively seeking out potential buyers and directly connecting with them through sales activities. Cold calling, sending email introductions, and meeting decision-makers at networking events and trade shows are examples of outbound lead generation. Once leads are generated, you can move down the sales pipeline to lead qualification.
Pro tip: CRMs are useful tools for workflow automation—especially during lead generation. HubSpot, for instance, lets you design workflow processes where if a lead completes an action such as sending an email or submitting a web form, the CRM automatically adds their information as a lead in the database system. From there, they can be automatically added to an email list for nurturing and sales reps can reach them directly.
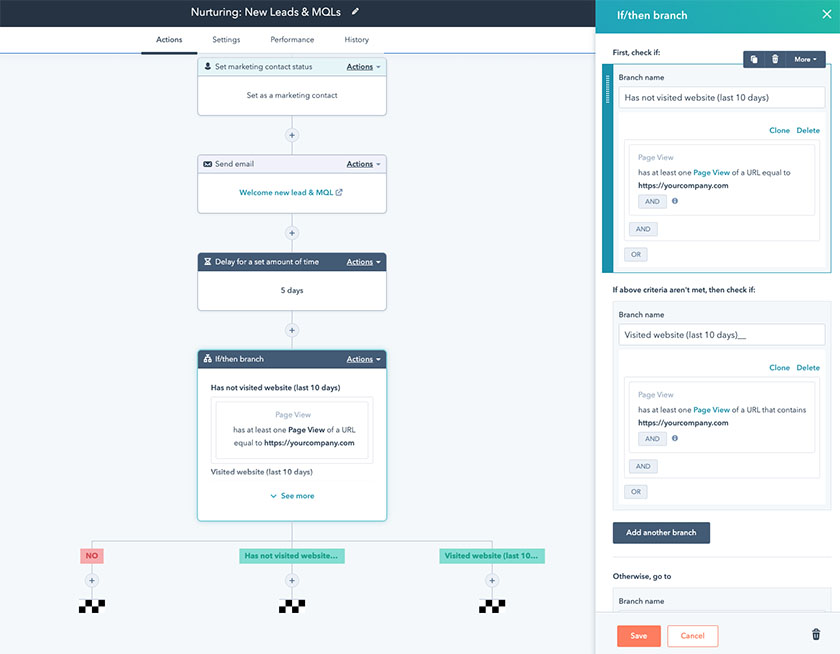
HubSpot process automation (Source: HubSpot)
3. Score & Categorize Leads
As leads begin pouring in, start using the criteria you set in step one to score and categorize them. Sales-qualified leads that have shown interest directly to a salesperson while doing your outbound sales activities or by contacting your sales team will earn higher points than marketing qualified leads.
If leads are being generated by interacting with marketing campaigns, they will earn fewer points, be classified differently, and require different actions in the next steps. While some CRMs can do this automatically, you can also manually assign points. The chart below provides a baseline point system you can use based on lead fit, interest, and purchase capability.
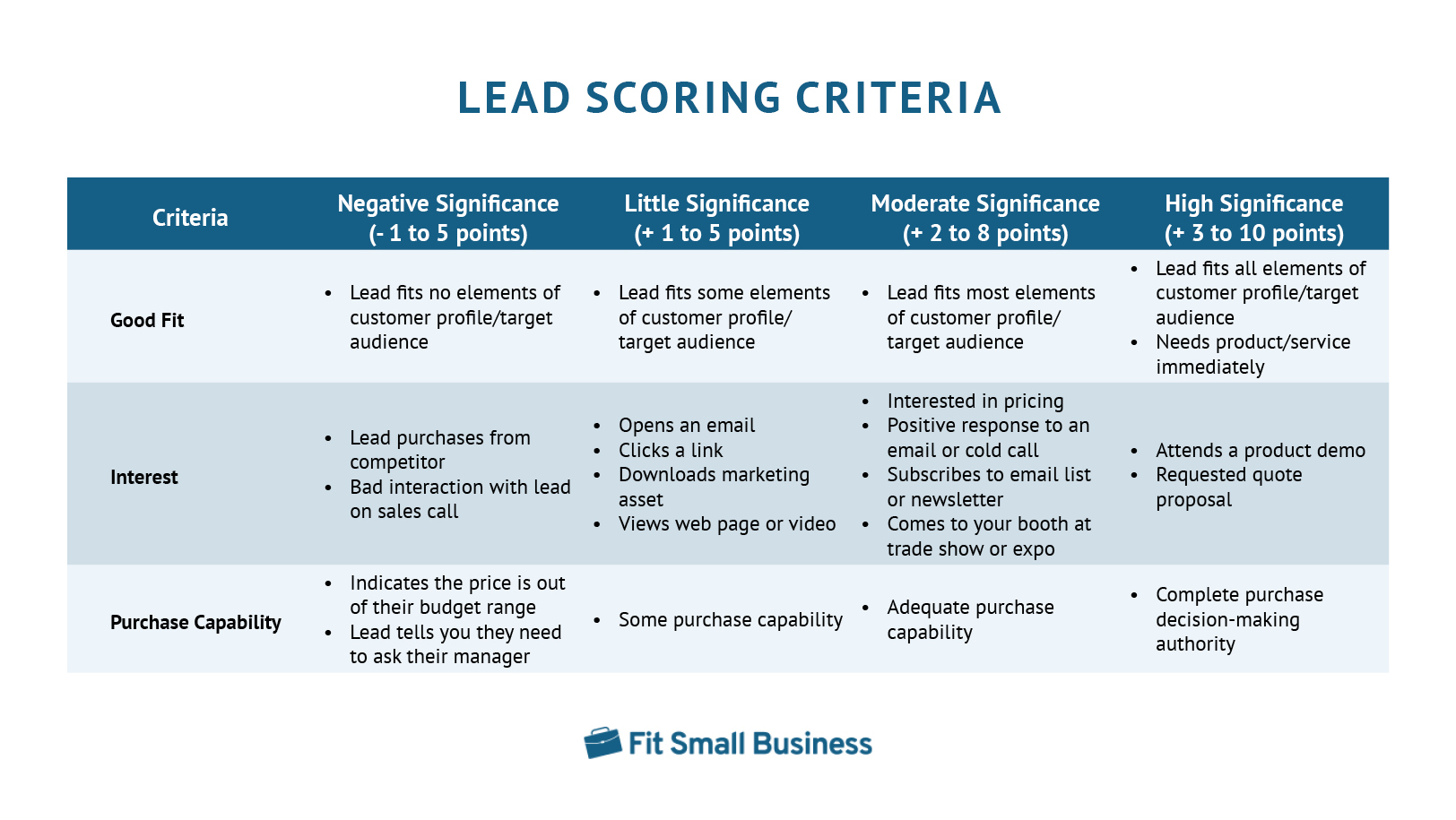
You can find more in-depth instruction about how to complete this step in our guide on how to effectively score quality sales leads.
Pro tip: Tagging features in your CRM software pairs nicely with the lead scoring functionality to understand your leads better. Freshsales, for example, lets you assign labels or “tags” to your contacts based on their actions and characteristics. Sales teams can use these during lead qualification to label the type of lead a person is, such as MQL or SQL, to easily assign opportunities to the right team.
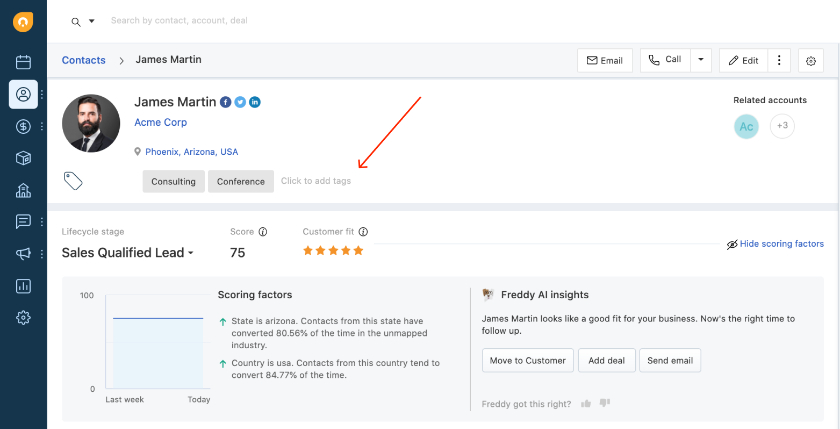
Freshsales lead profile with tags (Source: Freshworks)
4. Distribute & Rank Leads Accordingly
Based on how you categorize the newly generated leads on their qualification type, they will require different actions moving forward. Sales qualified leads should be distributed to your sales team. From there, a sales rep will likely conduct a sales presentation or product demo to help them understand your product or service better. This also gives your sales reps an opportunity to ask qualifying questions to gain an understanding of their buying priorities.
Furthermore, you should rank the new SQLs based on lead scoresor BANT analysis to prioritize them. For instance, if you generated six new sales qualified business leads last week during cold call campaigns but you know two of those leads aren’t urgently looking to change providers or suppliers, take that into consideration and focus on the ones that do fit that “timeline” aspect of BANT first.
For the other common type of qualified leads, like MQLs, engage them in the nurturing process, where you continuously send emails to them on company updates, promotional deals, and reminders of what your business offers. Additionally, you can use a ranking tiered system for nurturing campaigns based on how high their lead score is.
For instance, consider sending MQLs in the highest tier more in-depth content such as a whitepaper or e-book, since they’ve expressed more interest. Those in the middle tier may receive email newsletters while those in the lower tier could get emails for free trials to increase their interest and lead score.
Pro tip: Email automation software like Mailchimp makes it easy to design and deploy your lead nurturing campaigns. In addition to the features it offers, Mailchimp also integrates with most CRM software platforms so you can use the lead data stored in your CRM system to compile your email list.
Mailchimp email design templates (Source: Nutshell)
5. Continue Qualifying Leads Throughout the Pipeline
The last step for lead qualification is to continue down the steps of your sales pipeline. As your sales reps conduct presentations and demos, they may obtain information from probing questions that qualify or disqualify your lead. For example, let’s say you sell software that only works with specific operating systems. During the product demo, the lead indicates their business uses an incompatible one to your software—disqualifying them as an opportunity.
For MQLs, your goal is to further qualify them with nurturing and eventual outreach from your sales team to get them sales qualified. Similarly, they’ll continue receiving lead scoring points as they interact with your campaign—showing additional interest and further qualifying those leads.
Bottom Line
Lead qualification involves determining whether a sales opportunity is worth pursuing along with focusing efforts on those best qualified. Using this process lets you prioritize sales activities so you are only actively pursuing prospects with the strongest chances of becoming customers. Our step-by-step guide and lead qualification template worksheet helps you separate the qualified from the unqualified and distribute leads according to their customer behaviors.