Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
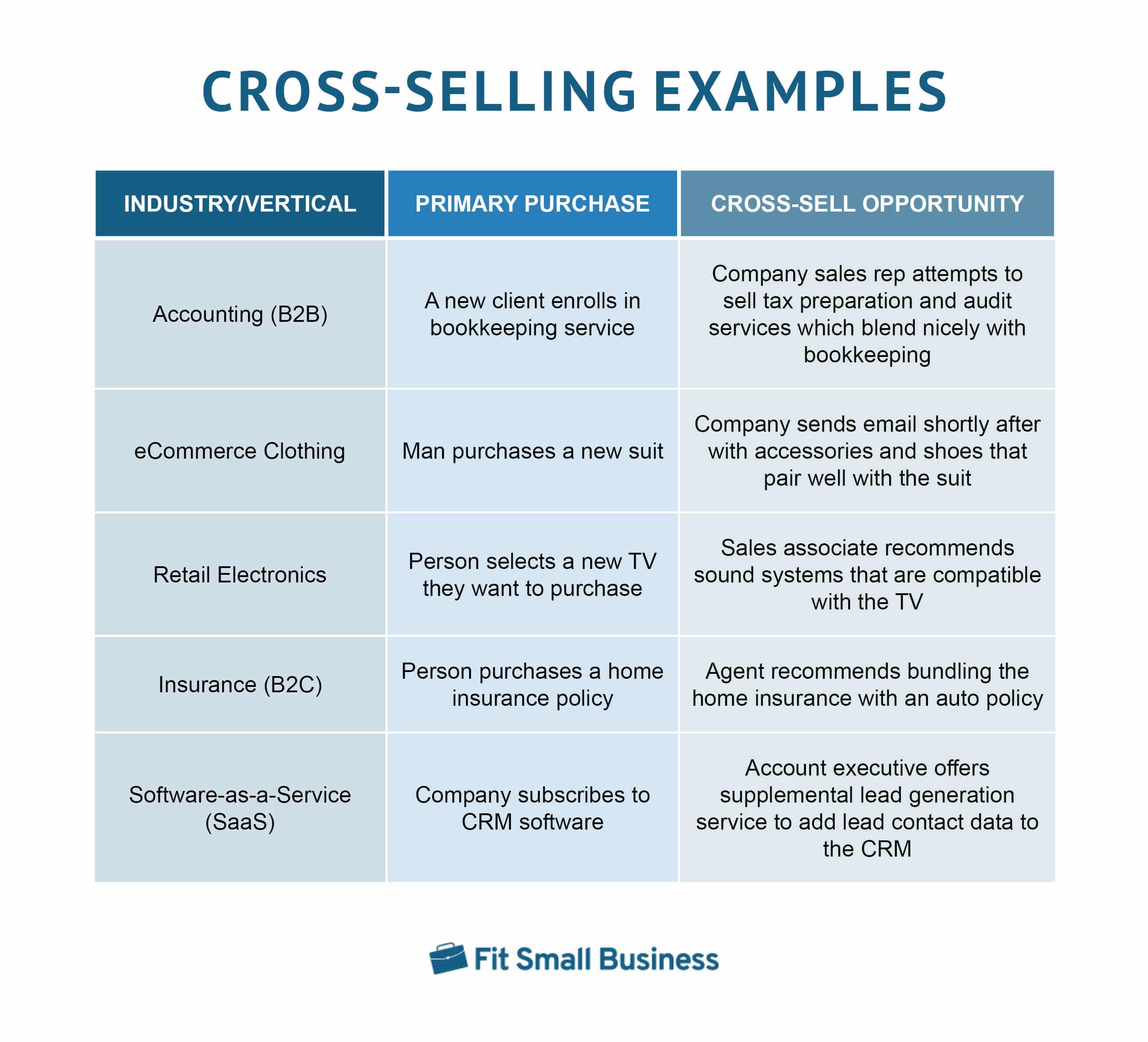
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:
Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because [value offered by complementary product/pairing].
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of [value attained by pairing].
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.
Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because [value offered by complementary product/pairing].
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of [value attained by pairing].
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because [value offered by complementary product/pairing].
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of [value attained by pairing].
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because [value offered by complementary product/pairing].
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of [value attained by pairing].
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because [value offered by complementary product/pairing].
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of [value attained by pairing].
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because [value offered by complementary product/pairing].
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of [value attained by pairing].
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because [value offered by complementary product/pairing].
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of [value attained by pairing].
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of Cross-selling is a sales tactic used to obtain more value from a deal or sales transaction. While commonly used for retail businesses, it can be applied to many industries in both the B2C and B2B markets. In this article, we explore cross-selling more in-depth and provide examples, tips, and script templates you can use to incorporate it in your sales activities.
When to Use Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting additional products or services complementing an existing purchase. The idea is that you can generate more revenue from one deal while also improving the value to your customers who are already in the buying mindset. Cross-selling is commonly used just before, during, or slightly after the primary transaction has been made.
How Cross-selling Differs From Upselling
While similar in the goal, cross-selling is different from upselling as it refers to suggesting a higher-end or more premium version of the product or service being purchased. In this sense, a sales rep isn’t focusing on selling additional items for more revenue, but a higher-quality solution to someone who already expressed interest.
Pro tip: Track your cross-selling progress using the notes features of customer relationship management (CRM) software. On top of managing leads and organizing data, CRMs such as Salesforce and HubSpot give you the ability to record notes in lead and contact profiles. With this function, sales reps can report if and how they attempted to cross-sell along with the end result.
Effective Cross-selling Examples
Without consciously realizing it, cross-selling happens every day during sales conversations or a marketing campaign. For instance, you likely receive emails or see online advertisements after you purchase a product on Amazon for other things that would go well with that product. Cross-selling also doesn’t have to be product-plus-product or service-plus-service either.
For instance, cross-selling works best when a product is paired with a complimentary service such as purchasing a service warranty when buying a new or used car. Within all industries or verticals, this tactic is utilized effectively. In fact, it’s estimated that 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated by cross-sells and that effective cross-selling increases profits by 30%. The below chart shows examples of what is cross-selling in action:

Tips to Make Cross-selling More Effective
Cross-selling is extremely effective in growing a business due to the revenue and profitability it offers as well as its capabilities to develop more meaningful customer relationships. When done poorly, however, you do run the risk of being tagged as more sales-focused than customer-focused—countering its initial purpose. Here are some tips to make sure cross-selling is being done properly and with sales integrity.
Create Complementary Solutions
Even before generating a sales plan outlining how cross-selling tactics will be incorporated into your daily sales activities, you need to have something to cross-sell. Some industries already have organic opportunities for cross-selling, such as a coffee shop cashier recommending food items when you purchase coffee.
For many others, however, you might have to create the solution from scratch by designing another product or service that pairs well with your primary offering. For software, you might create a side service to help enhance the user experience or develop a native software tool that supplements the primary application. For clothing lines, you could add an accessories department that nicely pairs with the clothing items.
There are limitless opportunities in creating complementary solutions in your business. This is your chance to find ways to stand out from the competition and further your unique selling proposition.
Focus on Building Value
As you’re finding conversational gaps to make a cross-sell, make sure you first understand their needs and why they made the initial (primary) purchase to begin with. Asking questions about the problems they are looking to solve and their preferences in a product or service provider prove you’re more focused on helping them rather than just trying to collect extra revenue.
This level of transparency helps build trust between a buyer and seller. It also makes it easier to add value to a customer’s purchase with relevant complementary solutions when understanding their needs. For example, assume someone came into your electronics store because they want a newer TV to stream their favorite shows.
Because you know their main priority is streaming, you could find them a relatively inexpensive flat-screen TV and cross-sell a compatible smart device such as a Roku or Apple TV to fulfill their streaming needs. Not only did this solution prove you’re focusing on their needs, but the overall value is increased to the customer based on the priorities they expressed.
Ensure the Timing Is Relevant
A key element of cross-selling is the timing of when you make the attempt. Make sure you’re doing it while they’re in the purchasing mindset just before the translation, while the transaction is taking place, or a short time after the translation. Post-purchase emails with recommendations are typically sent a day or so after the first transaction to keep it fresh in the buyer’s mind.
If you wait too long, such as a month or year after, the purchaser could already be satisfied and comfortable with what they have and not wish to make any changes—a common sales objection. Make sure your drip email campaigns are configured to send cross-sell messages within a day or two of the purchase while training your sales reps to make their attempts near the point of sale.
Simplify Conducting Business
No one wants to do more work than necessary to make product or service add-ons. Therefore, operationally you’ll need to ensure the complementary solutions can be purchased with minimal effort and that there’s no extensive process for the add-on involved.
For instance, in insurance, if an agent attempts to have the insured bundle their home and auto insurance together, they can make it easy by transmitting the personal data acquired from the home insurance underwriting to the auto application—only requiring additional information about the vehicle. Furthermore, the insured would also be able to pay the premium as one bill instead of separate bills.
If the cross-selling technique was being deployed after a purchase was made, the process of going in to make the add-on should be just as easy. For example, if an automated email is sent after someone purchases a pair of shoes, the email should have a link connected to the complementary products that let the user add the item to the cart and check out in one click. Simplification is a huge factor for getting a customer to follow through with an add-on purchase.
Cross-selling Scripts
To help you incorporate cross-selling in your sales and marketing activities, we’ve created some script and email templates to help you get started. Your sales management team should make sure all sales reps are comfortable with the script before implementing it.
Retail (In-person) After a Product Selection but Before Checkout
This [product] is a great selection you’ll definitely be satisfied with. Also, because you mentioned that [priority/preference/problem they want solved] was why you wanted to shop for this today, I would also recommend pairing it with [complementary product]. Many of our customers find that it’s awesome because [value offered by complementary product/pairing].
Business Service (on Conference Call) After Proposal Is Agreed to But Before Deal Finalization
So great to hear that you’ve agreed to work with us for your [product/service] needs. One thing many of our clients also like doing is pairing this with our [complementary product/service]. Doing so gives you the value of [value attained by pairing].
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell..
Marketing Email After Purchase
Dear [customer name],
Thank you for your recent purchase of [product purchased]. As part of enhancing your overall experience with our brand, we’d love to recommend the following items that pair nicely with your purchase:
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Item name
Item information
[Image]
[Link to add to cart and checkout]
Thank you for downloading!
Your cross-selling scripts are on the way!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a CRM like Freshsales to organize information about cross-selling opportunities, track deals, and collaborate with your sales team more effectively. Sign up for a free account today.
Pro tip: Store your cross-selling scripts and other sales resources in your customer relationship manager (CRM) using the document management tools. Pipedrive, for instance, lets you upload documents, spreadsheets, and presentations to a centralized location for everyone on your sales team to access. Once there, users can download or access their sales resources while being able to make changes where needed.

Pipedrive template storage (Source: Pipedrive)
Bottom Line
Cross-selling lets businesses acquire more revenue from one transaction while also adding value to a customer’s purchase by suggesting complementary products or services. This tactic is used in all industries during sales conversations and when crafting marketing emails. The examples and templates we’ve provided will help you further the solutions you offer your customers while also reaping the limitless financial benefits of an effective cross-sell.